This is an automatically translated article.
Antiphospholipid antibodies APLs are present in 60% of people with lupus, supporting diagnosis. Positive results are also used to determine risk for monitoring and prophylaxis in women with lupus. The limitation of the test is that APL is also present in people without lupus.
1. Antiphospholipid antibodies (APLs) and lupus erythematosus
Antiphospholipid antibodies APLs are antibodies against the fatty phosphorus components of cell membranes - called phospholipids. Some proteins in the blood bind to phospholipids, and complexes form when proteins and phospholipids bind together. About 50 to 60 percent of people with lupus have these antibodies for a 20-year period. However, people without lupus can also be positive for antiphospholipid antibodies.
The two most common antiphospholipid APLs are: Lupus anticoagulant (LA) and anticardiolipin (aCL). These two antibodies are often found together, but can also be detected singly in an individual. Other antiphospholipid antibodies APLs include:
Glycoprotein 1 anti-beta 2 (anti-ß2 GPI); Antiprothrombin; A “false positive” result for syphilis. The presence of antiphospholipid antibodies APLs in an individual is associated with coagulation. Half of patients with lupus anticoagulant (LA) will develop a blood clot. Blood clots can form anywhere in the body and can lead to: stroke, gangrene (gangrene), heart attack, and other serious complications. In people with lupus, the risk of blood clots does not always correlate with the extent of the disease. So the presence of these antibodies can cause problems even when lupus is under control.
Complications of antiphospholipid antibodies in lupus erythematosus include:
Pregnancy loss, miscarriage or premature birth; A blood clot in a vein or artery (thrombosis); low platelet count; Stroke due to automatic thrombocytopenia or vascular occlusion; Ischemia (formation of a blood clot on a heart valve); Pulmonary embolism ; Pulmonary hypertension.
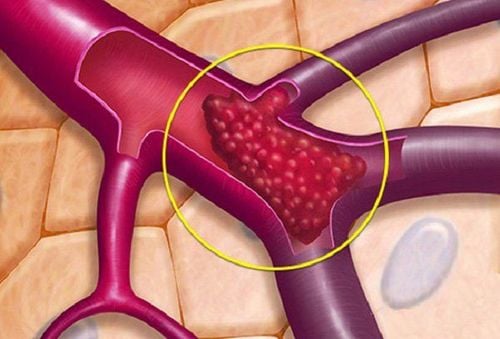
Kháng thể kháng phospholipid có thể gây tình trạng xuất hiện cục máu đông trong tĩnh mạch của người bệnh
2. Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome (APS)
Individuals experiencing complications from antiphospholipid antibodies APLs are diagnosed with Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome (APS). This condition can occur in both people with lupus (50%) and those without. Presence of one or more thrombosis (blood clots) and/or pregnancy complications, such as miscarriage or preterm delivery, in association with high levels of anticardiolipin, antiphospholipid and/or antiphospholipid antibodies GP2... is usually indicative of APS. When APS Syndrome is present with lupus erythematosus or another connective tissue disease, it is considered secondary. This classification is controversial, however, because some people with primary APS (about 8%) later develop lupus, suggesting a link between the two conditions.
In fact, antiphospholipid syndrome is also called anticardiolipin syndrome, although lupus anticoagulant antibodies have a similar effect.
3. Antiphospholipid antibodies
3.1. “False-positive” test for syphilis In the 1940s, during premarital examinations, doctors realized that some women with lupus erythematosus had tested positive for syphilis. Further studies indicate that 1 in 5 people with lupus have a false-positive syphilis test. Testing for syphilis during that period relies on the reagin antibody, which is found in patients with syphilis. People who test falsely for syphilis have a form of anticardiolipin antibody. This was the first recognized test for antiphospholipid antibodies APLs, but it is no longer needed for antiphospholipid antibodies and vice versa. False-positive tests are not associated with an increased risk of blood clots.

Xét nghiệm giang mai dương tính giả có liên quan đến bệnh lupus ban đỏ
3.2. Lupus Anticoagulant Antibody (LA) Also in the late 1940s, an anticoagulant antibody present in some lupus patients dependent on phospholipids was discovered. However, more than half of people who possess this antibody do not have lupus. Although lupus anticoagulant antibodies make blood clot more easily in humans, it prolongs blood clotting time in vitro. . Therefore, if the blood takes longer to clot in the lab, experts will suspect the presence of this antibody.
3.3. Anti-cardiolipin antibodies Until the 1980s, a researcher started looking for antibodies to phospholipid antigens. Cardiolipin is a key element of a false-positive syphilis test. The presence of anticardiolipin antibodies has been associated with recurrent thrombosis (blood clots) and pregnancy loss. Other studies have shown a link between anticardiolipin antibodies and stroke, deep vein thrombosis, recurrent pregnancy loss, red-purple skin patches, seizures, and other conditions.
There are different classes of anticardiolipin antibodies, namely IgG, IgM and IgA. Among them, IgG is the type most associated with complications. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is used to check for anticardiolipin antibodies. High levels of the IgM pattern also indicate autoimmune hemolytic anemia - a condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks its own red blood cells.
3.4. Anti-beta2 Glycoprotein 1 This is a protein in the body that the anti-cardiolipin antibody binds to. An individual may be positive for anti-cardiolipin antibodies and negative for anti-GP2 or vice versa. Detection of an anti-2 GPI is not yet part of routine antiphospholipid antibody testing, which is performed in patients at increased risk of thrombosis.
Xét nghiệm kháng thể kháng phospholipid được bác sĩ chỉ định sau khi người bệnh đã thăm khám
In summary, the specificity of antiphospholipid APLs antibodies is evaluated for the diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. The false-positive syphilis test was one of the first three recognized indications for antiphospholipid antibodies. The other two are lupus anticoagulant antibodies and anticardiolipin antibodies. Lupus anticoagulant antibodies are a specific tool for the diagnosis of antiphospholipid antibody-induced thrombotic complications in systemic lupus erythematosus.
To register for an examination at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register online HERE.
Reference source: webmd.com; ncbi.nlm.nih.gov; hopkinslupus.org