This is an automatically translated article.
Lotusone cream 15g is prescribed by doctors to treat dermatological diseases such as eczema, contact dermatitis, psoriasis. Depending on the patient's skin characteristics, the drug can be used or not. The following article will help you better understand the uses of Lotusone.
1. What are the uses of Lotusone?
Lotusone's main ingredient is Betamethasone dipropionate, which is prepared in the form of a topical cream, tube 15 grams. This drug is manufactured by TW Medipharco-Tenamyd Pharmaceutical Joint Stock Company.
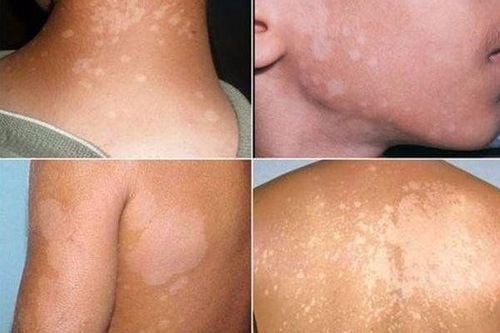
Betamethasone Dipropionate is a fluorinated synthetic corticosteroid. A topical agent that produces a rapid and sustained response in the treatment of eczema and dermatitis of all types, including atopic eczema, atopic dermatitis, lichen planus, lichen simplex, pruritus nodules, lupus erythematosus, lipoidica necrosis, prebacterial myxedema, and rosacea. It is also effective in less reactive conditions such as scalp psoriasis and chronic plaque psoriasis of the palms and soles, but not as much in widespread plaque psoriasis. . In addition, Lotusone may be used for a number of purposes not mentioned in the article. You should talk to your doctor about the full effects of the medication.
The extent of transdermal absorption of topical Lotusone is determined by many factors including the integrity of the epidermal barrier and the use of the dressing. Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed through normal, intact skin. Inflammatory processes and other diseases of the skin can increase absorption through the skin. The occlusive dressing significantly increases the percutaneous absorption of topical Lotusone.
Once absorbed through the skin, topical Lotusone has an action similar to that of a systemic corticosteroid, distributing very rapidly into all tissues in the body. The drug crosses the placenta and may be excreted in small amounts into breast milk. Corticosteroids bind to plasma proteins to varying degrees, mainly to globulin and less to albumin. The drug is mainly metabolized in the liver and excreted by the kidneys in the urine. Some topical corticosteroids and their metabolites are also excreted in the bile.
2. Contraindications of the drug Lotusone
Hypersensitivity to any component of Lotusone Patients with acne , perioral dermatitis, itching around the anus and genitals Tuberculosis and viral lesions of the skin, especially herpes simplex, vaccinia, varicella . Fungal or bacterial skin infections for which no appropriate anti-infective therapy is available. Infants under 1 year of age with dermatitis No treatment in ophthalmology
3. How to use and dose Lotusone
3.1. How to use Patients need to carefully read the instructions for use when applying Lotusone to get the best drug regimen. Only use Lotusone cream 15g topically when prescribed by a doctor. The drug is for external use only, do not apply to open wounds:
Before applying the medicine, clean the damaged skin surface. Squeeze a pea-sized amount of the medicine onto your finger, then gently apply it to the affected skin in a thin layer so that the medicine can be absorbed evenly. You should reduce the dose slowly when stopping the drug. Opened medicine should only be used within 30 days.
3.2. Dosage Take the drug according to the dose prescribed by the doctor or use the recommended dose to apply on the skin twice a day in the morning and evening. Experts recommend, a course of treatment lasts no more than 8 days
3.3. Overdose When applying too much Lotusone cream at a site or using it continuously for a long time will lead to increased absorption of the drug into the body, affecting the normal functioning of the pituitary and adrenal glands, leading to the syndrome. Cushing, adrenal insufficiency.
Patients need to adhere to the dose prescribed by the doctor. If you accidentally overdose and show unusual symptoms, you should immediately notify your doctor for timely treatment.
4. Undesirable effects of the drug Lotusone
Lotusone topical preparations are generally well tolerated and side effects are rare. Systemic absorption of betamethasone dipropionate may be increased if extensive surface areas or skin folds are treated for a long time or with excessive steroid use. Appropriate precautions should be taken in these circumstances, especially for infants and children.
The following local adverse reactions have been reported with the use of Lotusone: itching, burning, dryness, irritation, hyperpigmentation, folliculitis, hypopigmentation, acne vulgaris , allergic contact dermatitis, perioral dermatitis, itchy skin, secondary infections and milia.
Continuous application without interruption may lead to local skin atrophy, superficial vasodilation, especially of the face.
5. Drug interactions of the drug Lotusone
Lotusone may interact when used with some drugs or foods. Specifically:
Co-administration with high doses of Paracetamol for many days increases the risk of liver toxicity. Lotusone drug combined with antidiabetic drugs and insulin: leads to increased blood glucose levels. Co-administration with digitalis glycosides increases the risk of cardiac arrhythmias and hypokalemia due to increased digitalis toxicity. Lotusone medicine combined with coumarin anticoagulants increases or decreases the effect of anticoagulants. Co-administration with rifampicin, phenytoin, phenobarbital, ephedrine increases the metabolism of Lotusone, thus reducing the effect of the drug. To avoid drug interactions that affect treatment, patients need to inform their doctors of all drugs or supplements they are taking to monitor and can manage if there is an interaction. effect occurs.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.