This is an automatically translated article.
Usually doctors can diagnose an antibiotic allergy based on a patient's symptoms. However, in difficult to determine cases, experts will recommend conducting some antibiotic allergy tests to get accurate conclusions.
1. Overview of antibiotic allergy
Drug allergy is generally an abnormal response of the immune system to a drug. Any drug has the potential to cause an allergic reaction, including over-the-counter, prescription or herbal... However, drug allergies are more likely to occur with certain medications. , including allergies to antibiotics, eg penicillin.
The most common signs and symptoms of antibiotic allergy or drug allergy in general are:
Urticaria; Rash; Fever. An antibiotic allergy can cause serious reactions, such as anaphylaxis, which is life-threatening and affects many body systems. It should be noted that drug allergy is not a side effect of the drug, so it will not be known in advance to list on the drug label. Drug allergy is also different from poisoning due to drug overdose.
If diagnosed with a drug allergy, the best prevention is to avoid taking the suspected drug. In addition, you can also protect yourself by:
Notifying healthcare workers, including dentists, of your antibiotic allergy and this should be clearly noted in your records. medical; Wear a medical alert bracelet that identifies medications you are allergic to to ensure appropriate treatment in an emergency.
2. Antibiotic allergy test
While it is essential to make an accurate diagnosis of antibiotic allergy, studies have found that the condition is often overdiagnosed and that patients are unlikely to be allergic to that drug. If an antibiotic allergy is misdiagnosed, it will force the patient to use alternative medicines that are less suitable or more expensive than they should be.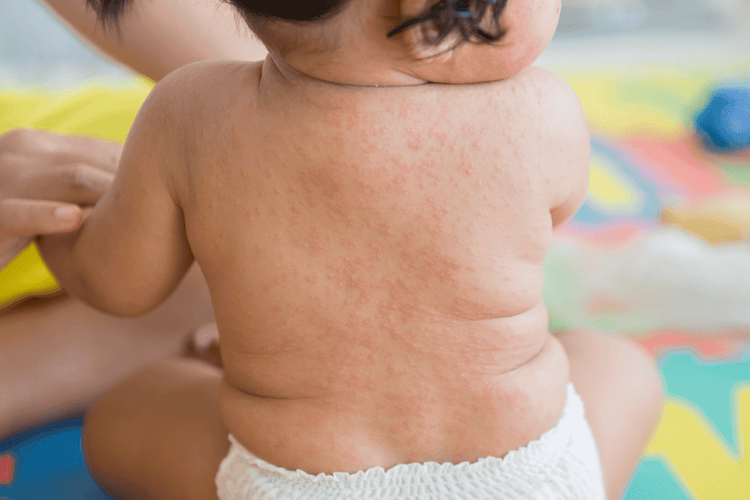
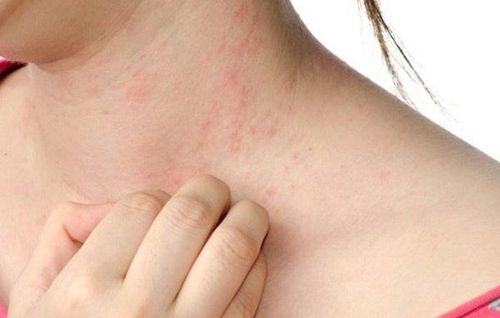
Phát ban, sốt là những triệu chứng trẻ có thể gặp khi bị dị ứng kháng sinh
2.1. Information extraction
First, the doctor will conduct a physical exam and ask the patient questions around issues such as:
Details of the onset of symptoms; Over-the-counter or prescription medications taken; Used herbs, vitamins or supplements (if any); Time to start and stop taking the drug; What improves or worsens symptoms; History of drug or food allergies in the past; Family history of drug allergy. Besides these important clues to help the doctor in the diagnosis process mentioned above, the patient may also be asked to do additional tests or refer to an allergist for some of the following antibiotic tests: :
2.2. Skin test
With a skin test, a doctor or specialist nurse will put a small amount of the suspected drug on the patient's skin and monitor for a reaction. The form of testing can be using a small lancet to scratch the skin into the endothelium, inject or stick a sample of the drug on the skin for about 2-4 days. Skin tests work only for certain drugs, including:
Penicillin and other antibiotics; Muscle relaxants; Some cancer drugs. The patch test is also used to check for delayed allergic reactions to antibiotics and other drugs.
A positive reaction to the test will cause a red bump, itchiness, a rash and indicates you may be allergic to that antibiotic. However, a negative result is not a definitive conclusion. For some medications, a negative test result usually means you're not allergic to them. However, there are still cases where a negative result will not completely rule out the possibility of an antibiotic allergy.
2.3. Blood tests
The doctor may ask the patient to have a blood test done in a laboratory to rule out other conditions that cause similar signs or symptoms.
Although there are several blood tests that help detect an allergic reaction to antibiotics, these antibiotic tests are not routinely used because their accuracy has not been widely studied and recognized. An antibiotic blood test is usually ordered when there is concern about a serious reaction to a skin test.
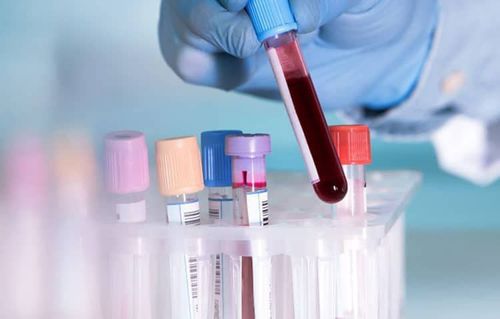
Xét nghiệm máu là phương pháp để chẩn đoán dị ứng kháng sinh
3. Treatment based on antibiotic allergy test results
After analyzing the patient's symptoms and test results, the doctor usually makes one of the following conclusions:
There is an antibiotic allergy; No allergy to antibiotics; Possible drug allergy - with varying degrees of certainty. These conclusions can help doctors and patients make future treatment decisions. Treatment regimens for drug allergies can be divided into two goals:
One is to control existing allergy symptoms One or a combination of measures can be used such as: withdrawal of the antibiotic causing the allergy. allergies, taking antihistamines to stop the immune system from triggering an allergic reaction, using oral or injectable corticosteroids to treat inflammation caused by a severe reaction, or treating anaphylaxis with an immediate injection of epinephrine as well as hospital care to maintain blood pressure and support breathing.
The second is to help the body adapt to the allergy medicine if they are necessary and irreplaceable Under the careful supervision of a qualified medical team, the patient will start using it from a very low dose. small and then gradually increased to a larger dose to desensitize to the allergenic antibiotic. If the desired dose can be achieved without a reaction, the patient can continue treatment.
In general, there are several different types of antibiotic allergy tests that help diagnose the body's allergy to drugs. The doctor will consider and choose the most appropriate form of examination for each specific case. In addition, the patient can also take pictures of the rash or swelling on the skin to show the doctor. This will make the diagnosis easier if signs and symptoms have subsided by the time of visit.
At Vinmec International General Hospital, skin prick test was performed for all patients before the first infusion of penicillin and streptomycin antibiotics (unless contraindicated), the patient took Lidocaine and had history of allergy, shock with anesthetics of the amide group or in bronchitis, atopic dermatitis to determine the causative allergen.
If you have unusual symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Webmd.com; Mayoclinoc.org