This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Vu Thi Duyen - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Non-insulin dependent diabetes (also known as type 2 diabetes) is the most common type of diabetes today. The disease, if we do not promptly diagnose and treat it, will leave many dangerous complications.
1. What is type 2 diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic carbohydrate metabolism disorder that occurs when the amount of glucose in the body is higher than normal.If you have non-insulin dependent diabetes, also known as type 2 diabetes, your body still produces enough insulin but the insulin does not work or the body has even excess insulin but uses it. improper insulin. Type 2 diabetes is not the same as type 1 diabetes.
Mechanism of type 1 diabetes is because the pancreas cannot secrete insulin, leading to a lack of insulin for the body to use. In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas works as it should and produces enough insulin even in excess, but for some reason the cells cannot use the glucose in the blood as a source of energy. This will lead to high blood sugar and can damage organs in the body. Type 2 diabetes usually begins in adults aged 40 years or older who are overweight or obese. However, due to the development of society and diet, more and more children and young people suffer from type 2 diabetes because obesity tends to increase in children.
2. Subjects at risk of type 2 diabetes

Age: Common at age ≥ 40 years There are genetic factors in the family: Having parents or brothers. Race. Overweight, obesity. Less physical activity. Unhealthy eating: a diet high in calories, saturated fat, high in sugar, low in fiber. High blood pressure or hyperlipidemia. Gestational diabetes.
Trắc nghiệm dành riêng cho người mắc đái tháo đường: Chế độ ăn của bạn đã hợp lý chưa?
Người bị bệnh đái tháo đường cần phải quan tâm nhiều hơn đến cách tính toán khẩu phần ăn sao cho phù hợp với nhu cầu và tình trạng sức khỏe. Nếu chưa rõ, bạn có thể tìm hiểu kỹ hơn thông qua bài trắc nghiệm ngắn sau đây.3. What tests to diagnose diabetes?
Blood sugar at any time ≥ 200 mg/dl (11.1 mmol/l). Fasting blood sugar ≥ 126 mg/dl (7 mmol/l) for at least 8 hours. HbA1C ≥ 6.5 % This index assesses whether the actual blood sugar level has been well controlled during the past 3 consecutive months. Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) ≥ 200mg/dl shows blood sugar 2h after drinking 75g glucose.4. Complications of diabetes
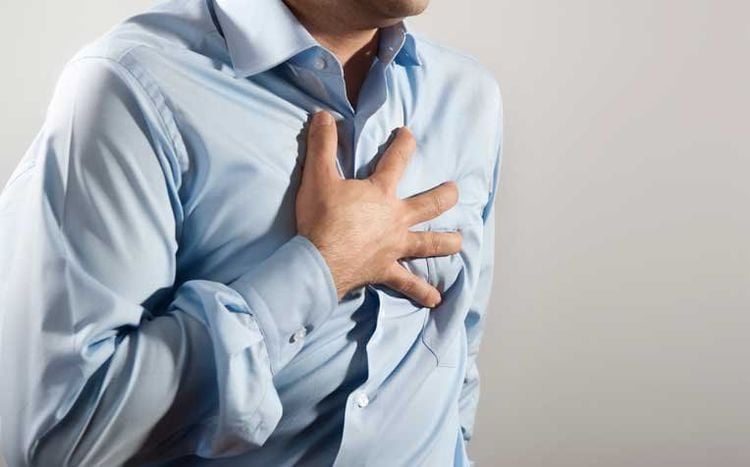

Heart disease: Diabetes greatly increases the risk of various heart problems such as coronary artery disease with chest pain (angina), heart attack, and heart attack. heart attack, stroke, narrowing of the arteries (atherosclerosis) and high blood pressure. Neuropathy: An accumulation of too much sugar can damage the walls of small blood vessels (capillaries) that nourish nerves, especially in the legs. Clinical: Numbness, burning or pain is usually at the tips of the toes or fingers and spreads to the upper body. Poorly controlled blood sugar can cause you to completely lose feeling in your extremities. Injury to the nerves gastrointestinal complications: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation. For men, it can lead to erectile dysfunction. Kidney disease: When high blood glucose damages the kidney blood vessels, leading to kidney failure or irreversible end-stage kidney disease, the patient needs hemodialysis or a kidney transplant. Eye damage: Diabetes can cause damage to the blood vessels of the retina, which can lead to blindness. Diabetes also increases the risk of other serious vision problems such as cataracts and glaucoma. Damage to the feet (diabetic foot): Damage to the nerves in the feet or poor blood flow to the legs increases the risk of various foot complications. If left undetected and untreated, a foot infection can often be difficult to heal and may eventually require amputation of the toe or foot. Skin and mouth disease: Diabetes can make you more susceptible to skin problems, including bacterial and fungal infections. Complications in pregnancy: High blood sugar can be dangerous for both mother and baby. You have a higher risk of miscarriage, stillbirth and birth defects when your diabetes is not well controlled. For the mother, diabetes increases the risk of diabetic ketoacidosis, diabetic retinopathy, gestational hypertension, and preeclampsia.

5. How to prevent diabetes?
To reduce complications of type 2 diabetes, you need to make up a healthy diet plan for each patient:Maintain an ideal weight (if overweight, lose weight). weigh). Exercise 30 minutes a day of moderate intensity. Healthy eating. Avoid tobacco and alcohol. Stress control. Regular health check every 6 months. When there are any unusual symptoms, people should immediately go to reputable medical facilities for timely examination and treatment.
Currently, Vinmec Times City International General Hospital is considered as one of the prestigious medical examination and treatment facilities, including endocrine diseases. The Department of Endocrinology - Diabetes is a place to treat and treat endocrine diseases including pituitary - thyroid - adrenal gland diseases and diabetes. The specialist works closely with the IVF Center - Obstetrics Department in the management of patients with thyroid disease during pregnancy, gestational diabetes.
Department of Endocrinology - Diabetes also applies new techniques in disease treatment: Research and application of stem cell technology in the treatment of diabetes; Treatment of benign thyroid nodules by radiofrequency ablation (Avoiding thyroid gland surgery for BMN). Along with that is a team of reputable doctors with many years of experience in the treatment of endocrine diseases.
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital offers a Package of Diabetes and Blood Fat Disorders Screening Package, which helps patients detect the disease promptly even when there are no symptoms, thereby taking treatment measures. suitable for your own health.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.