This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Ta Quang Hung - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.
The brachial plexus is a rather complex organ and there are many different ways to anesthetize. In which, the way to numb the brachial plexus in the armpit is the simplest and has the highest success probability.
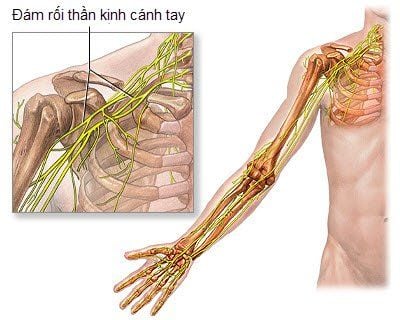
1. Location of brachial plexus on the body
The brachial plexus begins at the cervical nerve roots C5, C6, C7, and C8. They sometimes include branches from C4 or D1, D2. These nerve roots usually merge into three trunks. Before reaching the axillary fossa, the capsular and musculoskeletal nerves separate from the plexus.The brachial plexus is a rather complex part, so the job of numbing these nerves is often very difficult and requires good skills.
2. Principle of brachial plexus anesthesia
When anesthetizing the brachial plexus, the operator needs to use a large volume of anesthetic because the volume of this space is quite large. In addition, the performer should also note the following points when administering brachial plexus anesthesia:The upper and inner parts of the brachial plexus are foramen close to the spinal cord, so when anesthetized, In the midline of the trapezius muscles can poke the spinal cord. This will cause a complication of total spinal anesthesia. Beneath the brachial plexus there is a pleural apex, so when performing anesthesia above the clavicle, it is easy to poke the pleura and cause injury.

3. Indications for axillary brachial plexus anesthesia
3.1 Surgical indications For use in upper extremity surgeries and patients with contraindications to general anesthesia. Or use in surgeries from the elbow to the bottom of the hand. 3.2 Indications for medical treatment Treatment of pain in the stump, pain caused by neuritis (shingles). Pain in the hand due to exercise. Cases of patients with anemia in the upper extremities cause pain. 3.3 Indication to choose technique according to surgical site Axillary anesthesia: applicable to surgery from elbow to hand and with additional anesthesia of dermatophyte and brachial nerves. Supraclavicular/subclavian anesthesia: applied to surgeries in the lower third of the arm and down the hand. Anesthesia between the trapezius muscles: applied to surgeries in the shoulder area and down the hand.4. Contraindications for axillary brachial plexus anesthesia
The physician should consider the axillary brachial plexus anesthesia in the following cases:The patient has pre-existing peripheral and central nerve damage of the upper extremities. Presence of infection with blood clotting or are taking anticoagulants. In case the patient, technician does not agree with the technique or the patient does not cooperate with the doctor. Relative contraindications for patients with atrioventricular conduction disturbances, arrhythmias. Patients with hepatic impairment should avoid ester local anesthetics. Patients with a history of porphyria, malignant hyperthermia, should avoid using local anesthetics of the amide group.
5. Anesthesia technique for brachial plexus axillary line
Axillary anesthesia is one of the methods of numbing the brachial plexus. They are commonly used in elbow-to-hand surgeries. Following are the specific steps to perform the technique of axillary brachial plexus anesthesia:Step 1: Prepare equipment Sterile syringe tray: syringe 20ml, 10ml, 5ml needles of different sizes for injection muscle or intravenously. Sterile gloves 1 pair. Anesthesia needle type 22-23G short 3cm. Iodine alcohol cotton ball, alcohol 70 degrees. Antiseptic pan 2 pcs. Step 2: Prepare anesthetic drug of 1mg adrenaline in 1ml of the Central Pharmaceutical factory. Lidocaine 2% is not available Adrenalin of the Central Pharmaceutical Enterprise. Lidocaine 2% available type Adrenalin 1/100.000 US. Mix with distilled water to make a 1.5% solution for adults; 1% for the elderly and weak, adrenaline 1/125,000. Dosage: 6mg/kg (for healthy adults); 5mg/kg (for the elderly and weak over 60 years old) Step 3: Carry out the technique The patient lies in a supine position, with his head turned to the opposite side of the arm that is being anesthetized. Tilt the head to create an obtuse angle to the body, forearms pronated and turned outward, back of hand resting on the operating table. Place the tourniquet below the area to be anesthetized. The anesthesiologist palpates the brachial artery to locate the artery with fingers 2 and 3 of the left hand. An anesthetic needle will be inserted straight from the skin into the artery. You need a puncture through the nerve and blood vessels. When there is a feeling of "thump", the needle has entered the nerve sheath. When the needle is pulsating with the pulse or the patient has paresthesia, it is also another sign that the anesthesiologist can be sure the needle is in the brachial plexus. You can now inject the anesthetic. For added certainty, you can also use a nerve stimulator to know the most precise position. Before and during the anesthetic injection, the anesthesiologist should be sure to aspirate the syringe to ensure that there is no blood spurt before administering the anesthetic. This will help you avoid pumping the wrong blood into the artery. The volume of drug needed is 40-50ml to be enough for anesthesia. The axillary brachial plexus anesthetic method has a high success rate and few associated complications. That's why they are most commonly used by doctors.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Master. Doctor Ta Quang Hung has over 10 years of experience in teaching and practicing in the field of Anesthesia and Resuscitation. Currently, working as an Anesthesiology and Resuscitation Doctor, General Surgery Department - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital
Customers can directly go to Vinmec Health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline to Supported.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.