This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Pham Thieu Trung - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.Anesthesia of the brachial plexus is a new technique and has not been widely applied, however, thanks to the application of ultrasound, the technique allows the doctor to clearly see the structure of the nerve and blood vessels in the plexus. brachial nerve and adjacent organs, ensuring accurate anesthetic performance, avoiding unnecessary complications.
1. Learn about brachial plexus
The brachial plexus in the human body is derived from the cervical nerve roots C5, C6, C7 and C8, in many cases with additional branches from C4, D1, D2. These nerve roots are grouped into three trunks, and when they emerge from the level of the trapezius, they meet the subclavian artery and divide into anterior and posterior branches.
Before reaching the axillary cavity, the capsular and cutaneous nerves have been separated from the plexus, making it very difficult to anesthetize the nerves, usually the doctor will have to inject local anesthetic. for the patient. All brachial nerves and blood vessels, from their origin to the axillary fossa, are located in a relatively closed cell compartment, in front of them the median cervical tendon, behind them the intervertebral fascia, Inside of them are two longitudinal columns, outside of them are the superficial cervical fascia, except for the capsular nerve and the musculoskeletal nerve which split early, the rest of the major nerve trunks are located in this fascia.
2. Principle of brachial plexus anesthesia
The important thing when anesthetizing the brachial plexus is to anesthetize the entire nerve branches, to do this requires a large amount of local anesthetic. Therefore, when injecting anesthetic to the patient, the closer the position is to the upper part of the clavicle and the closer to the fever column, the easier it is to numb the entire nerve branches.
The most common failure in brachial plexus anesthesia is due to insufficient anesthetic dose or injection outside the nerve and vascular capsule.
A rule to remember that is directly related to brachial plexus anesthesia is this: Above and in the brachial plexus are foramen vents with the spinal cord, which require special attention. In particular, when anesthetizes through the line between the trapezius muscles can puncture the spinal cord causing complications of total spinal anesthesia. In addition, below the brachial plexus there is a pleural apex, so if not careful, it can poke the pleura.
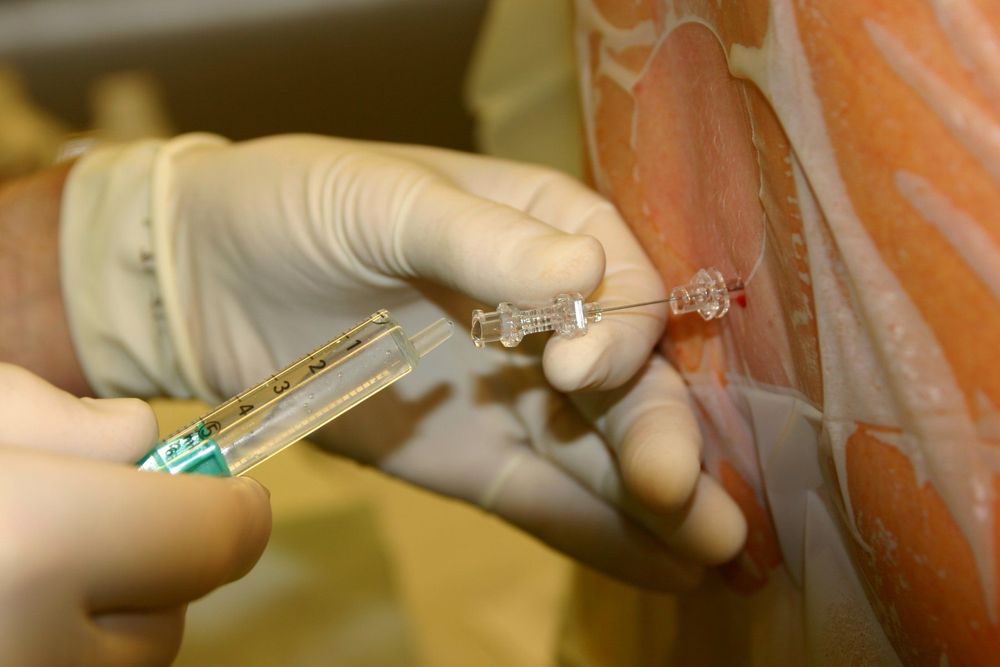
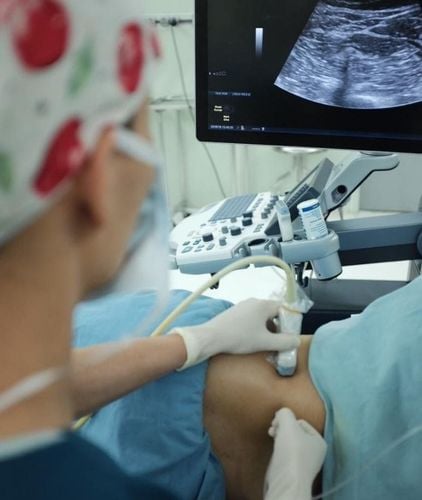
Gây tê đám rối thần kinh cánh tay có thể gây tê tuỷ sống
3. Indications and contraindications for brachial plexus anesthesia
Indications for brachial plexus anesthesia in the following cases:
Performed when performing surgery on the upper extremities For patients with contraindications to general anesthesia Treatment of pain due to neuritis, pain between the stumps, pain in the hand during exercise. Cases of ischemia of the limb causing pain Surgery from the elbow to the hand Surgery performed on the lower third of the arm or lower of the hand Surgery on the shoulder and down the hand Contraindication of brachial plexus anesthesia in cases of:
The patient has pre-existing central or peripheral nerve damage of the upper extremities. Infection at the needle puncture site The patient has coagulopathy and is being treated with anticoagulants. Patients with cardiac arrhythmias, with atrioventricular conduction disturbances Patients with hepatic impairment Patients with malignant hyperthermia or a history of porphyria Patients with a history of or current pneumothorax, patients with severe respiratory failure.
4. Brachial plexus anesthesia procedure
Step 1: The patient lies on his back, his arms are extended and close to the axis of the body, the hand is supine, the head is turned to the opposite side, and a thin pillow is placed under the shoulder so that the neck is slightly bent. Step 2: Disinfect the skin and prepare the head for ultrasound Step 3: The ultrasound probe after applying the gene will be wrapped in a sterile glove and placed at the patient's neck at the level of the cartilage. From this view, the doctor observing on the ultrasound screen will see: the thyroid gland, the anterior and middle scalene muscles, the internal carotid artery, and two muscle bundles, located between the anterior and middle scalene muscles. is the brachial plexus. After clearly seeing the nerve structure, blood vessels in the brachial plexus capsule and nearby tissues, the doctor will insert the needle into the nerve capsule to administer precise anesthesia.
Gây tê đám rối thần kinh cánh tay cần được thực hiện đúng quy trình
5. Advantages and disadvantages of brachial plexus anesthesia
Advantages:
Brachial plexus anesthesia does not affect heart rate, blood pressure and oxygen saturation. This is a simple, easy to do, low-toxic, low-impact technique for the patient's physiological function. Follow-up, care during and after surgery is gentle, good postoperative pain relief, low cost, and anesthesia. Brachial nerve disorders under ultrasound guidance will be safe, with little effect on physiological function. Disadvantages
In essence, brachial plexus anesthesia is still anatomical puncture, the path and destination of the needle is not clear, so the rate of complications such as nerve penetration, pulse Blood often pokes at the top of the lung, causing paralysis of the diaphragm, pneumothorax or hemothorax, and the scariest complication is a puncture in the cervical spinal cord, causing the patient to die...
To register for examination and treatment at the Hospital Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE
SEE MORE
Distinguishing between epidural and spinal anesthesia Pain management - "Specialty" at Vinmec Any solution for persistent pain after surgery?