This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Duc Thong - Anesthesiologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Danang International Hospital. The doctor has 14 years of experience in the field of Anesthesia.Anesthesia in intraventricular hematoma surgery is an anesthetic method by endotracheal general anesthesia. The purpose of this method is to help control the patient's breathing during surgery for intraventricular hematoma and to resuscitate after surgery effectively. The process of anesthesia - resuscitation needs to ensure that intracranial hypertension and brain edema are avoided.
1. Indications and contraindications of surgical anesthesia to remove intraventricular hematoma
1.1 Indications Surgical removal of acute subdural hematoma Surgical removal of chronic subdural hematoma Surgery to remove hematoma in the sites above the tentacle or below the cerebellar tentacle. 1.2 Contraindications Currently, there are no absolute contraindications for this method. Some factors hindering the process of anesthesia for surgery of intraventricular hematoma include:Patients do not agree with general anesthesia Medical facilities do not have enough facilities, equipment for endotracheal anesthesia and resuscitation after surgery. The operator has not been trained in endotracheal anesthesia.
2. Preparation before anesthesia surgery to remove intraventricular hematoma
Performer Neurosurgeon Anesthesiologist Resuscitation has training in general endotracheal anesthesia.
3. Anesthesia procedure for intraventricular hematoma
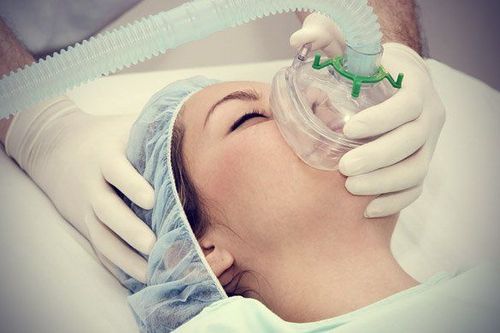
The patient was supine and oxygenated through the nasal cannula at least 5 minutes before induction of anesthesia. Install machines to monitor the patient's vital signs. Establish an intravenous line with 0.9% physiological saline solution. Conduct anesthesia for patients with drugs such as: + Anesthesia: including intravenous anesthetics such as propofol, etomidate...+ Painkillers: fentanyl, sufentanil...
+ Muscle relaxants: rocuronium, vecuronium...
When the patient is in deep sleep with enough muscle relaxation, endotracheal intubation is carried out to control the patient's breathing:
Open the mouth, insert the laryngoscope into the mouth from the right, slide the patient's tongue to the side. On the left, push the light deep and combine with the external cricoid cartilage to find the lid and the glottis. When the glottis hole is visible, insert the endotracheal tube gently through the hole until the balloon of the endotracheal tube passes through the vocal cords 2 - 3 cm. Check the position of the endotracheal tube to enter the correct airway by listening to the lungs and observing the EtCO2 wave. Remove the laryngoscope. Inflate the endotracheal balloon for fixation. Fix the outside with adhesive tape.

Scalp incision Drilling to open the patient's skull Carrying out dural suspension, dural opening. Unfold the brain organizations to enter the ventricles. Suction hematoma in the ventricles, stop bleeding if still bleeding. Clean pump. Seal the dura and place a drain Close the double craniotomy. Maintain anesthesia with intravenous or volatile anesthetics, analgesics, muscle relaxants (if necessary). Pay attention to avoid the occurrence of pros and cons; It is necessary to maintain EtCO2 about 33-35 mmHg to ensure against cerebral edema.
If there is cerebral edema, it is necessary to treat with Mannitol by intravenous infusion quickly, ensuring adequate ventilation.
Monitoring the depth of anesthesia based on heart rate, blood pressure, sweat, tears (PRST); MAC, BIS and Entropy ... and vital signs: heart rate, blood pressure, SpO2, EtCO2, body temperature.
After surgery, it is necessary to pay attention to treat cerebral edema by: mechanical ventilation, osmotic diuretics or corticosteroids.
4. Complications and treatment
Reflux of gastric juice into the airway manifests as the presence of digestive juices in the oral cavity and airways. Need to aspirate immediately, place the patient in a low head position, with the head tilted to the side, quickly insert the endotracheal tube and drain the fluid.Hemodynamic disorders: hypotension or hypertension, arrhythmia.
Accident due to intubation
Misplaced stomach: recognized by auscultation without alveolar murmur, EtCO2 cannot be measured. Vocal - air - bronchospasm: difficult or impossible ventilation, auscultation with rales or silent lungs. Manage by providing adequate oxygen, adding hypnotics and muscle relaxants, ensuring ventilation, giving bronchodilators and corticosteroids. Injuries when inserting tubes such as broken lips, tearing lips causing bleeding, broken teeth, damage to vocal cords, falling foreign objects into the airways...
Respiratory complications: folding, retracting, endotracheal tube deep in one lung, hypo or open respiratory system, out of oxygen, soda has no effect, causing hypoxia and hyperemia.
Complications after extubation: Respiratory failure after extubation, sore throat hoarseness, laryngospasm - trachea - bronchi, inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, laryngotracheal stenosis...
Vinmec Health System is also proud to be the first hospital in Vietnam to sign with the World Anesthesiology Association (WFSA) towards the goal of becoming the safest hospital for surgical anesthesia in Southeast Asia.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.