This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Specialist Doctor II Dinh Van Loc - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.The subdural pus accumulation is a rather dangerous condition, it is a sign of diseases related to the brain. Therefore, the patient must undergo surgery to drain the pus collection.
1. Information about the subdural pus accumulation
The source of subdural pus may be sinusitis or mastoiditis, in the majority of cases from frontal sinusitis. Other causes include previous trauma with a superinfected subdural hematoma, following craniotomy, or complications of meningitis. Patients may present with fever, headache, seizures, and focal neurological deficits. Subdural empyema is a surgical emergency and often requires neurosurgical intervention.The subdural space is the space between the inner surface of the dura and the arachnoid membrane. This space is opened by a subdural hematoma or by a subdural hygroma. Mucus collection due to cerebrospinal fluid entering through a tear in the arachnoid membrane.
Subdural hematomas can be acute, subacute, or chronic. A subdural hematoma is said to be chronic when it has been present for at least 2 weeks. At this time, the hematoma changes from a blood clot, the fluid turns yellow-brown. In the mucus, there may be little fresh blood as fresh blood pours into the liquefied blood. Over time, a chronic subdural hematoma forms a capsule: a vascular-rich capsule that arises from the vascular tissue on the inner surface of the dura; The relatively vascularized inner capsule originates from the arachnoid membrane. This capsule-forming hematoma may be divided by septums.
2. Method used to treat subdural pus accumulation.
Currently, there are many methods to treat subdural pus accumulation, in which the most popular is the method of craniotomy and drainage of the pus accumulation.This is the most commonly used surgical procedure in the world for chronic subdural hematoma through craniotomy with or without a closed drainage system.
How to do it
Usually 2 drill holes are enough, 1 in the attachment, 1 right in front of the rim joint, 3 cm from the midline. Sometimes a drill hole in the lower temple is also needed. Skin openings and perforations can be converted into craniotomy if necessary.
If both sides of the hematoma need to be opened at the same time, otherwise the patient may become worse after surgery due to brain displacement. It is possible to perform a large craniotomy, slit the pericardium with many blood vessels, and stop bleeding carefully to have a large space to place the drain.
Pump out the hematoma with saline solution and suction. Rinse until the fluid comes out clear and colorless. Saline can be pumped through a flexible drain to dislodge the clot at the edge of the hematoma, taking care not to cause brain damage.
Many surgeons place a closed subdural drainage system after pumping out the hematoma. A flexible drainage tube is placed in the subdural space, through a drilled hole, the tube runs under the scalp and protrudes into the skin through another small skin incision. The tube is connected to a closed drainage system, placed 10 - 15 cm below the head position, drained after 24 - 48 hours.
3. When to perform craniotomy to drain subdural pus?
On computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, there is a thick subdural pus collection. The patient's consciousness gradually worsens. Localized neurological signs appear. Pustules gradually increase in size on examination films. Intracranial pressure increases gradually (from over 20 mmHg) Diagnosis of chronic DMC hematoma. When there are clinical symptoms: headache, vomiting, hemiplegia ... On the film: Hematoma has the effect of pushing. In case of chronic subdural hematoma with rapid loss of consciousness, coma, emergency surgery is indicated as quickly as acute hematoma.
4. Anesthesia for craniotomy to drain subdural pus accumulation?
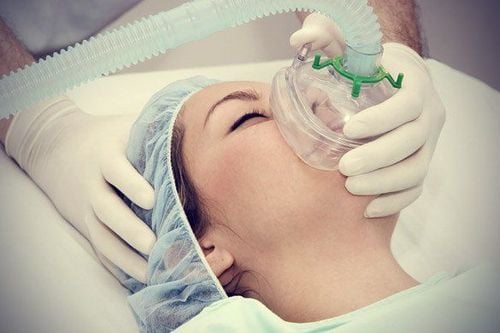
Surgery is a very effective way to remove pus accumulations or clear pus from the skull. The surgery can be performed under local or general anesthesia. Use anesthesia when the patient's condition is bad. Anesthesia can be difficult when it takes a long time to remove the clot and completely stop the bleeding. And for the surgery to be successful, anesthesia is a very important job. Therefore, the technique in anesthesia will directly determine the surgical outcome of the patient. In which, the most prominent technique is general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation.Endotracheal anesthesia is a technique of general anesthesia with intubation for the purpose of breathing control during surgery and postoperative resuscitation.
Pre-anesthesia (rarely used)
TCI sedation combined with local anesthesia
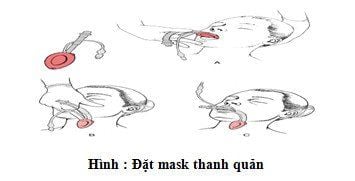
Laryngeal mask anesthesia
All anesthetic methods are selected depending on the patient's condition and type of surgery...
4.1.Usually used equipment during anesthesia
Anesthesia machine system with breathing, hand squeeze oxygen source, vital function monitor (ECG, arterial blood pressure, SpO2, EtCO2, breathing rate, temperature) defibrillator, suction machine... Sound bar endotracheal tube, endotracheal tube of various sizes, suction tube, mask, squeeze balloon, oropharyngeal cannula, Magill forceps, soft mandrin. Lidocaine 10% spray. Salbutamol spray. Prophylactic means of difficult intubation: Cook tube, laryngeal mask, flexible bronchoscope, tracheostomy kit, mouth opener...
4.2.Steps to conduct anesthesia for craniotomy to drain the subdural pus collection
The anesthetic process includes the following steps:*Preparation
Position: supine, breathing 100% oxygen 3-6 l/min at least 5 minutes before induction of anesthesia. Install the tracker. Establish effective communication. Pre-anesthesia (if necessary) *Initiation of anesthesia
Sleeping pills: intravenous anesthetics (propofol, etomidate, thiopental, ketamine...), volatile anesthetics (sevoflurane...). Painkillers: fentanyl, fentanyl, morphine... Muscle relaxants (if needed): (succinylcholine, rocuronium, vecuronium...). Conditions for endotracheal intubation: the patient sleeps deeply, with sufficient muscle relaxation (in most cases). There are two techniques for endotracheal intubation: oral and nasal.
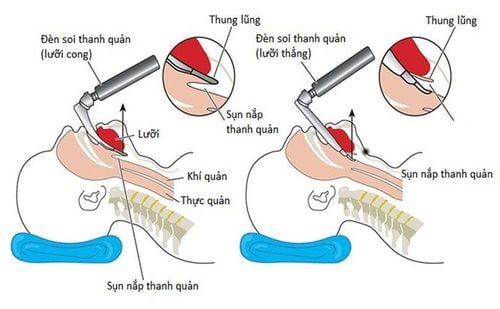
Oral intubation technique: -Open the mouth, insert the laryngoscope to the right of the mouth, move the tongue to the left, push the lamp deep, coordinate with the right hand to press the thyroid cartilage to find the epiglottis and the laryngeal foramen. subject.
-Initiate rapid induction of anesthesia and perform the Sellick maneuver in case the stomach is full (press the cricoid cartilage 20-30kg as soon as the patient loses consciousness until the intubation is completed).
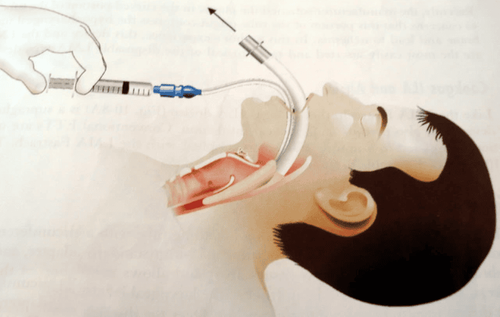
-Insert the endotracheal tube gently through the glottis, stopping when the balloon of the endotracheal tube passes 2-3 cm through the vocal cords.
- Remove the laryngoscope gently.
-Inflate the endotracheal balloon.
-Check the correct position of the endotracheal tube with auscultation and EtCO2 results
-Fix the tube with adhesive tape.
-Put the canul in your mouth to avoid biting the tube (if necessary).
Techniques for nasal intubation: -Select the side of the nose and drop a vasoconstrictor drug (naphazoline, otrivin...).
-Choose an endotracheal tube size that is smaller than the oral one. Insert an endotracheal tube lubricated with lidocaine ointment through the nostrils.
-Open the mouth, insert the laryngoscope to the right of the mouth, move the tongue to the left, push the lamp deep, coordinate with the right hand to press the cricoid cartilage to find the epiglottis and glottis.
-Favorable case: insert the endotracheal tube gently through the glottis, stopping when the balloon of the endotracheal tube passes through the vocal cords 2-3 cm. Use Magill pliers to guide the tip of the endotracheal tube into the correct glottis; The assistant pushes the endotracheal tube from the outside in difficult cases.
- Remove the laryngoscope gently.
- Inflate the endotracheal balloon.
-Check the correct position of the endotracheal tube with auscultation and EtCO2 results.
-Fix the tube with adhesive tape.
Maintain anesthesia
Maintain anesthesia with intravenous or volatile anesthetics, analgesics and muscle relaxants (if needed). Control breathing by machine or hand squeeze. In people with chronic subdural pus accumulation, it is easy to confuse with other brain diseases such as dementia, cerebrovascular accident, especially patients often forget the history of traumatic brain injury from previous day and month. Therefore, it is necessary to have a thorough clinical examination, perform computed tomography or cranial magnetic resonance imaging early for timely diagnosis and surgical intervention.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures high professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, a system of modern technological equipment, but also stands out for its outstanding medical examination and treatment services. , comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe, effective and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.