This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Nguyen Binh - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.Anesthesia during laparoscopic small bowel resection using endotracheal anesthesia technique for the purpose of breathing control during surgery and postoperative resuscitation.
1. Indications and contraindications for endotracheal anesthesia
Indications in : Laparoscopic surgery to remove the small intestine .
Contraindicated in the following cases:
The patient does not agree to perform. Insufficient means of anesthesia and resuscitation. Not proficient in endotracheal anesthesia techniques.
2. Prepare for endotracheal anesthesia
2.1 The person performing the technique
Anesthesiologists and nurses are trained and proficient in endotracheal anesthesia techniques.
2.2 Means of implementation
Anesthesia machine system with breathing, life function monitor. hand squeeze oxygen source, vital function monitor (ECG, arterial blood pressure, SpO2, EtCO2, breathing rate, temperature) defibrillator, suction machine... Laryngoscope, endotracheal tube of all sizes , straw, mask, oropharyngeal canul, squeeze ball, Magill pliers, soft mandrin. Lidocaine 10% spray, Salbutamol spray. Prophylactic means of difficult intubation such as: Cook tube or laryngeal mask, tracheostomy kit, mouth opener pliers, flexible bronchoscope...
2.3. Requirements for the patient
Anesthesia examination before surgery to detect and prevent risks, explain to patients manipulations and questions to cooperate. Evaluation of difficult endotracheal intubation. Sedation will be administered the night before surgery if needed.
2.4. medical record
Prepare medical records according to the regulations of the hospital as well as the Ministry of Health.
3. Pre-anesthesia steps
Before administering anesthesia, the doctor checks the patient's medical records and checks the patient's condition. Technical operations:

Thực hiện gây mê khi cắt ruột non
3.1 General Procedures
Place patient in supine position, give 100% oxygen 3-6 l/min before induction of anesthesia at least 5 minutes. Install the tracker. Establish effective communication. Perform pre-anesthesia (if necessary).
3.2 Initiation of anesthesia
Sleeping pills: Intravenous anesthetics (propofol, etomidate, thiopental, ketamine...), sevoflurane volatile anesthetics,.... Painkillers: Fentanyl, sufentanil, morphine,... Muscle relaxants (if needed) ): Succinylcholine, rocuronium, vecuronium,... Conditions for endotracheal intubation: The patient sleeps deeply, has enough muscle relaxation (applied in most cases).
3.3 Endotracheal intubation
There are two techniques for endotracheal intubation: oral and nasal.
3.3.1 Oral endotracheal intubation technique
Open the patient's mouth, insert the laryngoscope to the right side of the mouth, then slide the tongue to the left. Push the lamp deeply and then coordinate with the right hand to press down on the cricoid cartilage to find the epiglottis and glottis. Conduct rapid induction of anesthesia and Sellick maneuver in case of full stomach (pressing the cricoid cartilage 20 to 30 kg as soon as the patient loses consciousness until the intubation is complete). Pass the endotracheal tube gently through the glottis, stopping when the balloon of the endotracheal tube passes 2 to 3 cm over the vocal cords. Gently withdraw the laryngoscope and then inflate the endotracheal balloon. Check the correct position of the intubated endotracheal tube by listening to the lungs and EtCO2 results. Secure the tube with adhesive tape. Place the cannula in the mouth to prevent the patient from biting the tube (if necessary).
3.3.2 Nasal intubation technique
Choose the side of the nasal passage and drop the nasal vasoconstrictor (naphazoline, otrivin,...). Select an endotracheal tube size smaller than the oral route and insert the endotracheal tube lubricated with lidocaine ointment through the nostril. Open the patient's mouth, insert the laryngoscope into the right side of the mouth, then slide the tongue to the left. Push the lamp deeply and then coordinate with the right hand to press down on the cricoid cartilage to find the epiglottis and glottis. In favorable cases, proceed to gently intubate the endotracheal tube through the glottis, stopping when the balloon of the endotracheal tube passes through the vocal cords 2-3 cm. Use Magill pliers to guide the tip of the endotracheal tube into the correct glottis; The assistant pushes the endotracheal tube from the outside in case it is difficult to do. Remove the laryngoscope gently and then inflate the endotracheal balloon. Check the correct position of the endotracheal tube with auscultation and EtCO2 results Fix the tube with adhesive tape. In case of difficult intubation, the difficult intubation procedure is applied.
3.4 Maintenance of anesthesia
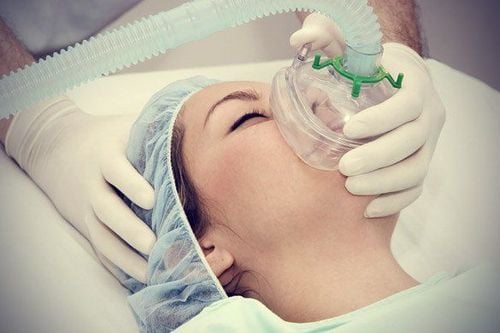
Maintain anesthesia with intravenous or volatile anesthetics, analgesics and muscle relaxants (if necessary). Control breathing by machine or hand squeeze.
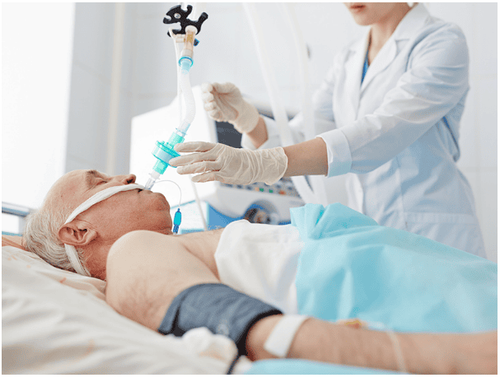
Kiểm soát hô hấp bằng máy cho bệnh nhân
4. Monitoring the patient after anesthesia
Monitoring the depth of anesthesia based on heart rate, blood pressure, sweating, lacrimation (PRST); MAC, BIS and Entropy (if any),... Monitor the patient's vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, SpO2, EtCO2, body temperature. In case the endotracheal tube is in the wrong position or blocked. Criteria for extubation The patient is awake, following orders. Raise the head for more than 5 seconds, TOF > 0.9 (if any). Breathe spontaneously, the patient's respiratory rate is within normal limits. Pulse and blood pressure are stable. Body temperature above 35 degrees Celsius. No complications of anesthesia and surgery.
5. Accidents and handling
5.1. Reflux of gastric juice into airway
There is digestive juices in the oral cavity and airways. Immediately remove the fluid, place the patient in a low position, tilt the head to the side Quickly insert the endotracheal tube and clear the airways Monitor and prevent lung infection after surgery.
5.2. Hemodynamic disorders
Lower or increase blood pressure, arrhythmia manifestations such as: bradycardia, tachycardia, arrhythmia. Treatment depends on symptoms and causes.
5.3. Complications due to endotracheal intubation
Unable to intubate can be managed by difficult intubation procedure or switch to another method of anesthesia. Misplaced endotracheal tube in stomach. Auscultation of the lungs without alveolar murmurs, no measurement of EtCO2. Reinsert the endotracheal tube. Constriction of the larynx, trachea, bronchi. Difficult or impossible ventilation, auscultation with crackles or muted lungs. Provide adequate oxygen, add hypnotics and muscle relaxants, ensure ventilation, and give bronchodilators and corticosteroids. If breathing is not controlled, a difficult endotracheal intubation procedure should be used. Trauma during endotracheal intubation. Bleeding, broken teeth, damage to the vocal cords, falling foreign objects into the airways, ...
5.4. Complications after extubation
Respiratory failure after extubation due to many causes as follows: Sore throat, hoarseness. Constriction of the larynx, trachea, bronchi. Upper respiratory tract infection. Stenosis of the larynx - trachea. The technique of endotracheal anesthesia is widely used in surgery, within the scope of this article this method of anesthesia is used in the small bowel resection. The doctor needs to follow the correct procedure to limit the occurrence of complications after surgery.
Doctor Nguyen Binh has more than 20 years of experience in the field of anesthesia - resuscitation in thoracic surgery, anesthesiology resuscitation for elderly patients... Currently a Doctor of General Surgery, National General Hospital Vinmec Ha Long International.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, for detailed information and to book an appointment for medical examination and consultation, customers can call the hotlines of the hospitals or register for an online consultation with Vinmec International General Hospital HERE.