This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Specialist Doctor II Nguyen Trung Thanh - Department of Surgical Anesthesia - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalThe most important principle of placing the patient in surgery is "Do not hurt" the patient. Anesthesia often impairs or incapacitates the patient when positioning, so it is the responsibility of the anesthesiologist and other members of the surgical team to ensure that the correct surgical position is achieved. harm the patient.
1. Injury due to surgical position in anesthetized patients

Patients under anesthesia or sedation often lose or reduce sensation due to anesthesia and do not allow the patient to wake up or move. Prolonged immobilization of the affected tissues leads to inflammation and interstitial edema. These two factors exacerbate tension and compression, which over time can cause significant ischemia and tissue damage. The loss of mobility of the anesthetized and sedated patient in response to pain is an important factor in surgical positioning and therefore anesthesiologists are trained in the basics of surgical posture. in your study program.
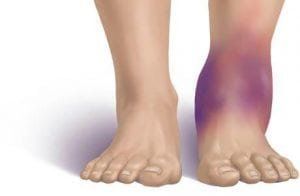
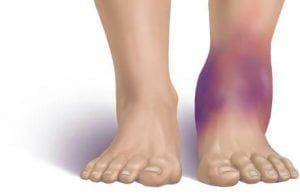
Although common, not all patient postural problems are related to mechanical forces on tissues. For example, an anesthetized patient may be placed in an elevated head position (eg, for shoulder surgery), where blood pressure is insufficient to deliver blood to the brain and overcome the hydrostatic pressure difference between the head and extremities. above can reduce cerebral perfusion pressure. Similarly, anesthetized patients are positioned for bladder or ureteral stone removal, with the legs elevated above the torso, although the patient's blood pressure may be normal but it may not be enough to pump blood upward against gravity because the lower extremities lie higher. Ischemia can cause tissue damage from hypoxia and lead to compartment syndrome.
In many cases the cause is not clearly defined, although many theories have been put forward to explain the suspected lesions due to surgical positioning.
2. Injury mechanism
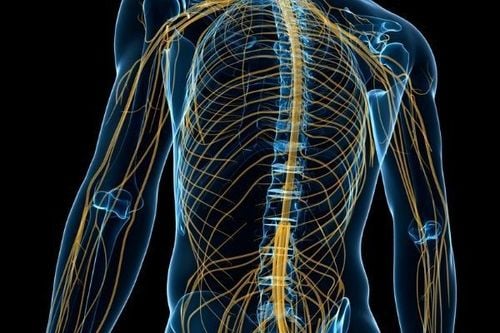
Tissue tension and compression have been implicated in postural problems in sedated or anesthetized patients.2.1 Nerves are nourished from capillaries that divide from the feeding arteries and form a capillary network within them. In the peripheral nerves these small arteries form a continuous network. The network is continuous on the peripheral nerves and rarely a single nerve segment is supplied by a single blood vessel. This network is not common in the CNS. Stretching of nerve tissue, especially beyond 5% of normal length, can twist, or reduce, the diameter of the arterioles and veins. This phenomenon can lead to anemia directly from decreased arterial blood flow or indirectly from venous obstruction. Prolonged anemia can lead to temporary or permanent nerve damage. The lack of capillary networks in CNS tissue leads to poorer tolerance to stretch.
Soft tissues are usually less susceptible to stretch damage than nerve tissues, they are more elastic and do not require the same amount of blood as nerve tissue. However, prolonged stretching can also lead to anemia and tissue damage. The position of the surgical patient can also exert a strain on the soft tissues.
2.2 Compression Direct pressure on soft tissues and nerves can reduce local blood flow and disrupt cellular integrity, leading to tissue edema, anemia, and, if prolonged, necrosis death. This effect is particularly damaging to soft tissues that are susceptible to ischemia (eg, external colostomy).
3. Principles of prevention

Use of padding to distribute compression : although there are few studies showing that wide pads can affect the frequency and severity of perioperative neuropathy, it does have a distributive effect force into many points. Avoid overstretching joints: any nerve that is stretched > 5% of its normal length over a prolonged period of time leads to varying degrees of ischemia and dysfunction. There is a high risk of an anesthetized patient being injured by the surgical position. It consists of mechanical forces caused by the surgical position leading to soft tissue and nerve damage. The immobilized position can also impair a patient's normal physiological function and should be considered for all patients, especially any position other than the supine position. Careful assessment of each patient prior to anesthesia is important to reduce the risk of complications related to the surgical position.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that strictly applies safe surgical anesthesia practice standards according to international guidelines. With a team of experienced anesthesiologists and nurses, along with modern equipment such as nerve detectors, ultrasound machines, Karl Storz difficult airway control system, anesthesia monitoring system GE's comprehensive AoA (Adequate of Anesthesia) including monitoring of anesthesia, pain and muscle relaxation will deliver high quality and safety, helping patients to have adequate anesthesia, not awake, no residual relaxant muscle after surgery. Vinmec Health System is also proud to be the first hospital in Vietnam to sign with the World Anesthesiology Association (WFSA) towards the goal of becoming the safest hospital for surgical anesthesia in Southeast Asia.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.