This is an automatically translated article.
Post written by Master - Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Head of Department of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalPeripheral nerves form a complex network that connects the brain and spinal cord to muscles, skin, and internal organs. Peripheral neuropathy is a condition that occurs when the nerves that transmit messages to and from the brain and spinal cord with the rest of the body are damaged or infected. The following are frequently asked questions about peripheral neuropathy.
1. What is Peripheral Neuropathy?
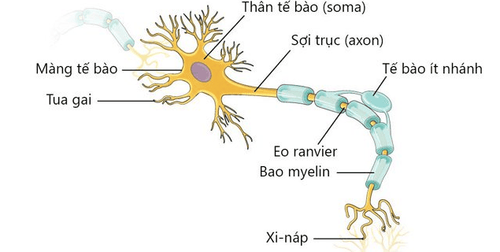
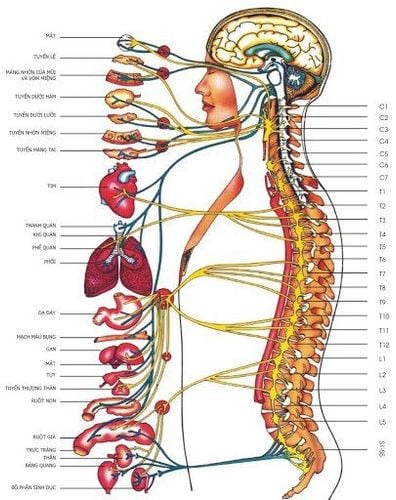
The peripheral nervous system connects nerves from the brain and spinal cord, or central nervous system, to the rest of the body, including:Arms. Hand. Feet. Foot. Internal organs. Mouth. Face. The job of these nerves is to transmit signals about physical sensations back to your brain.
Peripheral neuropathy is a disorder that occurs when these nerves malfunction because they are damaged or destroyed. This disrupts the normal functioning of the nerves. They may send pain signals when nothing is causing pain, or they may not send pain signals even when something is hurting you. For example:
Injury . Whole body disease. Infection . Genetic disorders.
2. What types of peripheral neuropathy are there?
Currently, more than 100 different types of peripheral neuropathy exist. Each type has distinct symptoms and specific treatment options. Peripheral neuropathy is further classified by the type of nerve damage involved. For example, sciatica occurs when only one nerve is damaged. Polyneuropathies, more commonly, occur when multiple nerves are damaged.3. What are the symptoms of peripheral neuropathy?
There are three types of peripheral nerves:Sensory nerves, which connect to your skin. Motor nerves, which connect to your muscles. Autonomic nerves, which connect to your internal organs. Peripheral neuropathy can affect one nerve group or all three.
Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy include:
Tingling in the hands or feet. It feels like you are wearing a glove or a tight sock. Sting. Numbness in hands or feet. feeling of weakness, heaviness in the arms and legs; It can sometimes feel like your legs or arms are locked in place. Frequently dropping objects in hand. Feeling of buzzing or shock. Thin skin. Hypotension . Sexual dysfunction, especially in men. Constipation . Indigestible. Diarrhea . Sweating too much. These symptoms may also indicate other conditions. Be sure to tell your doctor about all of your symptoms.
4. What are the causes of peripheral neuropathy?
People with a family history of peripheral neuropathy are more likely to develop the disorder. However, many underlying factors and conditions can also cause the condition.4.1. Whole body disease
Nerve damage from diabetes is one of the most common forms of neuropathy. This leads to numbness, pain, and loss of sensation in the extremities. The risk of neurological disease is increased for people who:Overweight . Have high blood pressure. Over 40 years old. Have diabetes. According to the University of Chicago's Center for Peripheral Neuropathy (UCCPN), nearly 60 percent of people with diabetes have some type of nerve damage. This damage is usually caused by high blood sugar.
Other chronic diseases that can cause nerve damage include:
Kidney disorders in which high levels of toxins build up in the body and damage nerve tissue. Hypothyroidism, which occurs when the body doesn't produce enough thyroid hormone, leads to water retention and pressure around nerve tissue. Diseases that cause chronic inflammation, which can spread to nerves or damage the connective tissue around nerves Deficiencies in vitamins E, B1, B6 and B12, which are essential for mental health and functioning terrible.
4.2. Injury
Physical trauma is the most common cause of nerve damage. This can include car accidents, falls or broken bones. Inactivity, or staying in one position for too long can also cause neuropathy. Increased pressure on the median nerve, a nerve in the wrist that provides sensation and movement to the hand, causes carpal tunnel syndrome. This is a common type of peripheral neuropathy.
4.3. Alcohol and Poison
Alcohol can be toxic to nerve tissues, putting heavy drinkers at higher risk of peripheral neuropathy.
Exposure to harmful chemicals such as glues, solvents or insecticides, either through chemical abuse or in the workplace, can also cause nerve damage. In addition, exposure to heavy metals such as lead and mercury can also cause this condition.
4.4. Infections and autoimmune disorders
Some viruses and bacteria attack nerve tissue directly.Viruses such as the herpes simplex virus, the varicella-zoster virus that causes chickenpox and shingles, and the Epstein-Barr virus damage sensory nerves and cause severe pain.
Bacterial infections such as Lyme disease can also cause nerve damage and pain if they are left untreated. People with HIV or AIDS can also develop peripheral neuropathy.
Autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus affect the peripheral nervous system in different ways. Chronic inflammation and damage to tissues throughout the body, as well as the pressure caused by inflammation, can both lead to severe nerve pain in the extremities.
4.5. Medicine
Some medications can also cause nerve damage. These include:Anticonvulsants that people take to treat seizures. Medicines against bacterial infections. Certain blood pressure medications. Cancer treatment drugs. Recent research in the Journal of Family Practice also suggests that statins, a drug used to lower cholesterol and prevent cardiovascular disease, can also cause nerve damage and increase the risk of neurological disease.
5. How is peripheral neuropathy diagnosed?
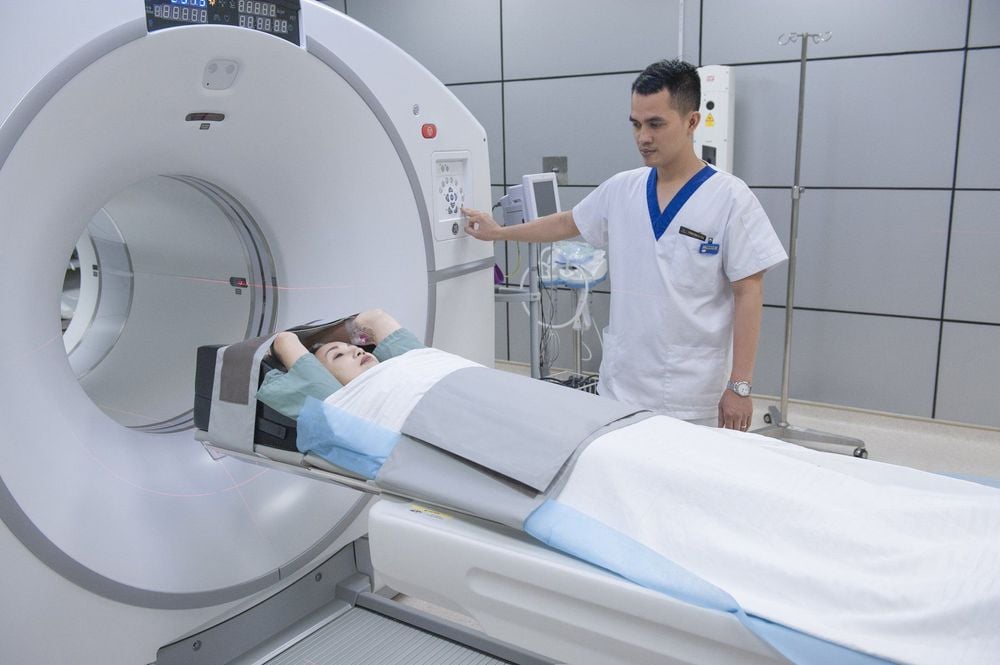
First, your doctor will do a physical exam and ask about your medical history. If they still can't tell if your symptoms are due to peripheral neuropathy, other tests to do include:Blood tests that can measure vitamins and blood sugar levels and identify See if your thyroid gland is working properly. Your doctor may also order a CT or MRI scan to see if anything is pressing on a nerve, such as a herniated disc or a tumor around the nerve. Sometimes your doctor will order a nerve biopsy. This is a minor surgery that involves removing a small amount of nerve tissue, which they can then examine under a microscope. Electromechanical. Electromyography can show problems with the way your body's nerve signals travel to your muscles. For this test, your doctor will place a small needle into your muscle. Then, your doctor will ask you to gently exercise your muscles. The probe in the needle will measure the amount of electricity moving through your muscle. This test may feel like you are receiving an injection. Sometimes, the area becomes sore for a few days afterward. Neurotransmission study. During a nerve conduction study, your doctor will place electrodes on your skin. They then send tiny electrical impulses through your nerves to see if the nerves are transmitting signals properly. The procedure is a bit uncomfortable while it's going on, but it shouldn't be painful afterward.
6. What are the treatment options for peripheral neuropathy?
Treatment is based on treating the underlying disorder. If diabetes is the cause, it is important to ensure that blood sugar is under control. If a vitamin deficiency is causing the problem, treating the deficiency is the way to go. Many treatments can provide relief and help you return to your usual activities. Sometimes, a combination of treatments can work best.6.1. Analgesic
Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as aspirin and ibuprofen, can be very helpful in managing moderate pain. If you take too much, these drugs can affect your liver or stomach function. It is important to avoid using them for long periods of time, especially if you drink alcohol regularly.6.2. Prescription drugs
Many prescription pain relievers can also help control the pain of this condition. These include narcotics, some antiepileptic drugs, and some antidepressants. Other helpful prescription medications include:Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Tramadol . Inject corticosteroids. Seizure medications, such as gabapentin or pregabalin. Cymbalta, is a serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. Prescription medications for sexual dysfunction in men include:
Sildenafil (Viagra). Vardenafil (Levitra, Staxyn). Tadalafil (Cialis). Avanafil (Stendra).
6.3. Medical treatment
Your doctor may use a number of medical treatments to control the symptoms of this condition. Plasmapheresis is a blood transfusion to remove potentially irritating antibodies from your blood stream. If you have a nerve block, your doctor will inject an anesthetic directly into your nerve.6.4. Transcutaneous Electronic Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
Transdermal electronic nerve stimulation (TENS) doesn't work for everyone, but many people prefer it because it's a non-drug therapy. During TENS, electrodes placed on the skin transmit a small amount of electricity into the skin. The goal of this treatment is to interrupt the nerves that transmit pain signals to the brain.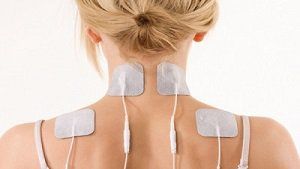
6.5. Fixed brace
A splint can help if neuropathy affects:Legs. Arm. Hand. These bandages or splints will provide support to the part of your body that is uncomfortable and may relieve pain. For example, a cast or brace that holds your wrist in the proper position while you sleep can reduce the discomfort of carpal tunnel syndrome.
6.6. Self care
In addition to over-the-counter pain relievers, many people have found relief from peripheral nerve pain through:Chiropractic care. Acupuncture . Massage. Meditation. Yoga. Regular, moderate exercise can also help ease discomfort.
If you drink or smoke, consider cutting back or stopping. Both alcohol and tobacco aggravate nerve pain and can cause nerve damage with long-term use.
7. How to prevent neuropathy at home?
If you have peripheral neuropathy, you are more likely to have an accident in your home. You can do the following things to improve your safety:Always wear shoes to protect your feet. Check the temperature of the tub or dishwashing liquid with your elbow, not your hand or foot. Fit the handrail to your bath or shower. Use non-slip bathroom mats. Don't stay in one position for too long. Get up and walk a few times every hour. This is especially important for people whose jobs involve sitting for long periods of time at a desk.

8. How to prevent peripheral neuropathy?
Even if you have a family history of this disorder, you can help prevent its onset by doing the following:Avoid alcohol or drink only in moderation. Avoid smoking or quit if you smoke. Eat a healthy diet. Exercise regularly, moderately. You can reduce your risk of peripheral neuropathy by:
Find out if you may be exposed to any toxins at work or school. Protect your feet when playing sports, especially those that involve kicking. Never inhale poisons such as glue. Let them go high. If you have diabetes, take special care of your feet. Wash and check your feet daily and keep the skin moist with a lotion. Here are some frequently asked questions about peripheral neuropathy. You should consult your doctor before deciding on any treatment.
Please follow the website: Vinmec.com regularly to update many other useful information.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference sources: uchicago.edu, galegroup.com