This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Anal fissure in children is a common condition in children aged 6 to 24 months, less common in older children. It often causes discomfort in children because anal fissures cause pain and bleeding, but most cases heal on their own and can be treated at home. If the symptoms do not improve or the fissure does not heal for a long time, it may lead to a chronic condition, so parents need to take the child to a doctor and take care under the guidance of a specialist.
1. What is an anal fissure?
An anal fissure is the term used to describe a small tear in the lining of the anal canal in a child. Although it is only a small lesion in the mucosal area, it is easy to cause inconvenience, even fear in children's daily activities when defecation is difficult, or there is blood in the stool, causing confusion for parents.2. What are the causes of anal fissures in children?
Anal fissures in children have a variety of causes, but are mainly the result of constipation, leading to a large and hard stool mass when passing through the anal canal. fracture wound. Besides, the anal fissure causes pain when having a bowel movement, which makes children afraid of defecation. This increases the risk of chronic constipation, forming a pathological spiral that affects the entire digestive system of the child.In addition, there are a number of other causes leading to anal fissures in children, including:
The habit of pushing during bowel movements causes strong force to push stool through the anal canal, causing increased pressure to form tears; anorectal inflammation or ulcerative colitis; Up to 80% of children have anal fissures within the first year of life, with no known cause.
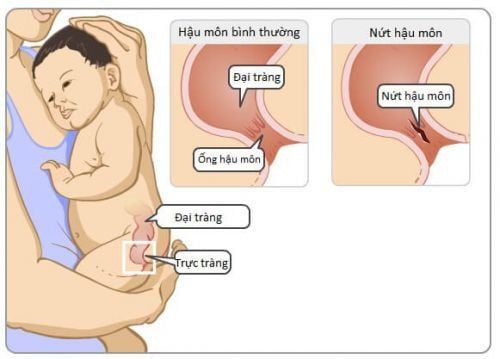
Có đến 80% trẻ em bị nứt hậu môn trong năm đầu đời
3. Symptoms of anal fissure in children
Anal fissures in children have fairly obvious symptoms and are easy to check. Parents need to pay attention to the following symptoms in children:The child is fussy or uncomfortable when having a bowel movement; When the child has finished defecation, he will produce a large and hard stool with fresh blood on the outside; For older children, they often try to hold back their bowel movements to avoid pain; It is most obvious when a parent examines the child's anus that a tear is found along the skin of the anal canal; Children may also experience itching or irritation around the anus. If an anal fissure does not heal and persists for more than 6 weeks, there is a high risk of becoming chronic. This is the most common complication of anal fissures in children. Cracks after healing are still prone to recurrence and continuous histological damage. In addition, if the tear penetrates to the inner anal sphincter, it will cause the muscle to contract, which can easily lead to a larger tear and difficult to heal, requiring specialist treatment.
4. Treatment of anal fissures in children
As mentioned, anal fissures are quite common in children and most of them heal on their own or with non-surgical treatment. Symptoms usually disappear after 2 weeks, but it takes up to 8 weeks to fully heal. If after that time the crack persists, specialist treatment may be needed.The first thing to do to cure anal fissures in children is to change the child's living habits and diet, namely:
Change diapers regularly and keep the anal area clean;
Thay tã thường xuyên và giữ cho vùng hậu môn sạch sẽ
Surgery is the last resort to treat anal fissures in children when the course of the disease tends to become chronic. Surgery involves removing part of the anal sphincter to relieve spasms and pain to promote healing, and may include removal of the fissure and surrounding fibrous tissue. Children after surgery need hospital care, although this surgery rarely causes incontinence complications.
5. How to prevent anal fissures in children
Changes in living habits and lifestyle will help your child avoid an anal fissure or ease its symptoms and heal faster. Preventive measures include:Eat plenty of fiber, preferably 20-35 g of fiber per day. The increase in fiber should be done slowly because eating a lot can cause bloating and gas; Adequate water intake is important to prevent constipation - which is also the main cause of the disease; Regular exercise will help increase bowel movements, blood circulation to facilitate bowel movements and quick healing of tears; Soak the anus in warm water for 15-30 minutes, 2-3 times a day to help relieve pain and itching; Instruct your child to avoid straining when having a bowel movement because it will create pressure, tear or create new cracks in the anus. Parents can take children with anal fissures to Vinmec International General Hospital for examination and treatment. There is a team of well-trained and experienced gastroenterologists; system of medical equipment is complete, modern, professional service quality, for high efficiency in diagnosis and treatment.