This is an automatically translated article.
The article is written by Resident Doctor of Pediatrics - Neonatology, Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Amniotic band is a congenital abnormality, can be seen with an incidence from 1:12000 to 1/15000 babies, boys and girls have the same risk; manifest in the extremities (legs, arms, and trunk).
1. Risk factors for amniotic band syndrome
Mom smokes; living in highland...
Cause of the disease is not clear, the pathogenic mechanism is believed to be rupture of membranes in early pregnancy leading to the development of many amniotic bands from the chorion side of the amniotic membrane entangled into the embryo or germ disc.
This restricts the blood supply and creates a tight ring, affecting the structure of the organ. Some other mechanisms such as vasomotor disorders, mechanical disorders, genetic disorders ...
2. Early detection signs and symptoms
From the time of the baby in the fetus, can be screened through ultrasound based on:
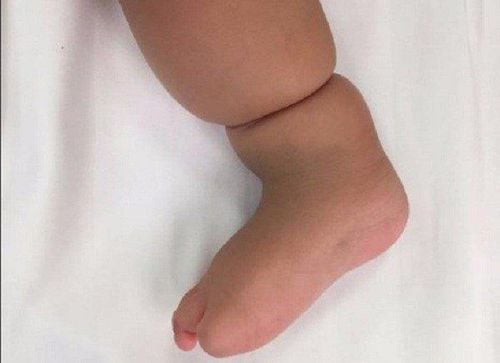
Image of the constriction of the limbs Deformity: loss of distal end of one or more fingers, fusion of fingers, lack of limbs, amputation, table clubfoot...

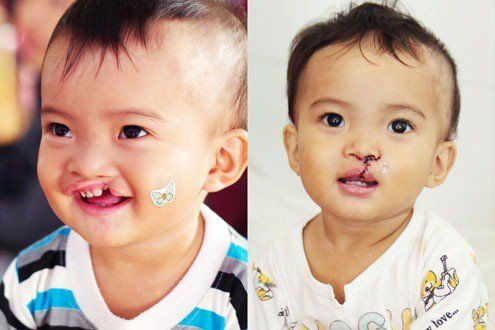
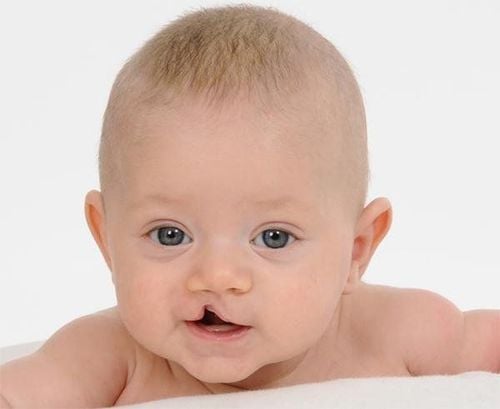
Abdominal wall deformities: thoracic cavity, abdominal hernia, scoliosis... Nerve defects: brain and spinal cord Craniofacial abnormalities: cleft palate and skull. In which the most common (80%) is the image of limb loops and deformities. These loops can be limited to the skin/soft tissues, can also penetrate deep tissues: blood vessels, nerves or bones, leading to lymphedema, neuropathy, fractures or even is amputation. Some other serious deformities: facial deformity, cleft lip, cleft palate, nasal deformity, spine deformity, pulmonary hypoplasia. Limbs include: loops of limbs without distal parts of fingers, toes, fractures.
3. Diagnosis of amniotic band syndrome
Prenatal diagnosis: diagnosed in the first 3 months, ultrasound can detect torsion, amputation, body wall defects or craniofacial defects, edematous distal extremities. An accurate prenatal diagnosis is usually in severe cases: there are many major abnormalities such as in the limbs and trunk (short umbilical cord, amniotic band). In the last 3 months of pregnancy, 3D ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging are complementary techniques that can provide information and help confirm the diagnosis. On T2 magnetic resonance imaging the amniotic bands are observed as thin bands. Postpartum diagnosis: suspected in children with amputations, trunk malformations and skull defects in abnormal positions. It is very important to check the amniotic membrane and placenta. Finding amniotic fibers will aid in the diagnosis. Differential diagnosis: + Before birth: differentiate with amniotic cavity septum and body complex abnormalities.
+ Postpartum: Chi in chubby babies...
4. Prognosis of amniotic band syndrome
This pathology is associated with an increased risk of miscarriage and stillbirth, the postpartum prognosis depends on the severity of the abnormalities, may not occur immediately after birth except in the case of marked vascular occlusion due to The narrow band causes progressive edema at the constriction.
5. Management of amniotic band syndrome
Prenatal assessment and counseling: Doctors should talk to parents about possible risks during pregnancy and postpartum risks. Amniocentesis may be performed if the indication is relevant to the decision to keep the fetus. Prognosis should be discussed with pediatricians, neurologists, orthopedic surgeons. Some patients may be able to have a antenatal hysterectomy. Intrauterine ligation must be performed before severe, irreversible vascular damage affecting the extremities leads to amputation. The effectiveness of this method has not been proven nor is there a consensus in the selection of criteria for selecting patients for intervention. For amniotic bands involving a limb, a reasonable criterion is that the limb must have normal blood flow.

Interventions in the fetus need to weigh the benefits and risks. The frequency of maternity monitoring or delivery method has not been specific, depending on the lesion. If vasospasm occurs, fetal intervention should be considered. With babies after birth, some babies with amniotic band syndrome can be mistaken for chubby babies. The release of the constriction rings relieves venous congestion, lymphedema, which can save some limbs. Surgery can be delayed from weeks to months unless the vasospasm requires emergency surgery. In addition, children receive palliative care including functional enhancement surgery or cosmetic, prosthetic, and physiological purposes for children with limb abnormalities. Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consulting services. and comprehensive, professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.