This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by MSc Ma Van Tham - Pediatrician - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.The diagnosis of AFB-negative TB will be based on the exposure history, clinical and radiological suspicions. Thus, the diagnosis of tuberculosis or non-tuberculosis will rely heavily on the clinician's experience. Tuberculosis in children is a serious disease with complicated long-term treatment, so TB vaccination is the safest and most effective method of prevention.
1. Characteristics of tuberculosis in children
The majority of cases occur in children under 5 years of age and the majority of cases occur within 2 years of exposure to TB bacteria.
Tuberculosis in children is still mainly pulmonary tuberculosis. But extrapulmonary TB is also very common and varies with age.
After TB infection, the younger the child, the higher the rate of disease development and the higher the rate of severe forms of TB. Migraine TB and meningococcal TB are two very common forms of severe TB in young children. While children over 2 years old, this rate decreased to very low. Therefore, when tuberculosis is suspected in children under 2 years of age, especially children under 1 year of age, finding BK in gastric juice and in cerebrospinal fluid are two very necessary tests.

Trẻ nhỏ dưới 2 tuổi dễ mắc bệnh lao
2. Diagnosis of TB in young children
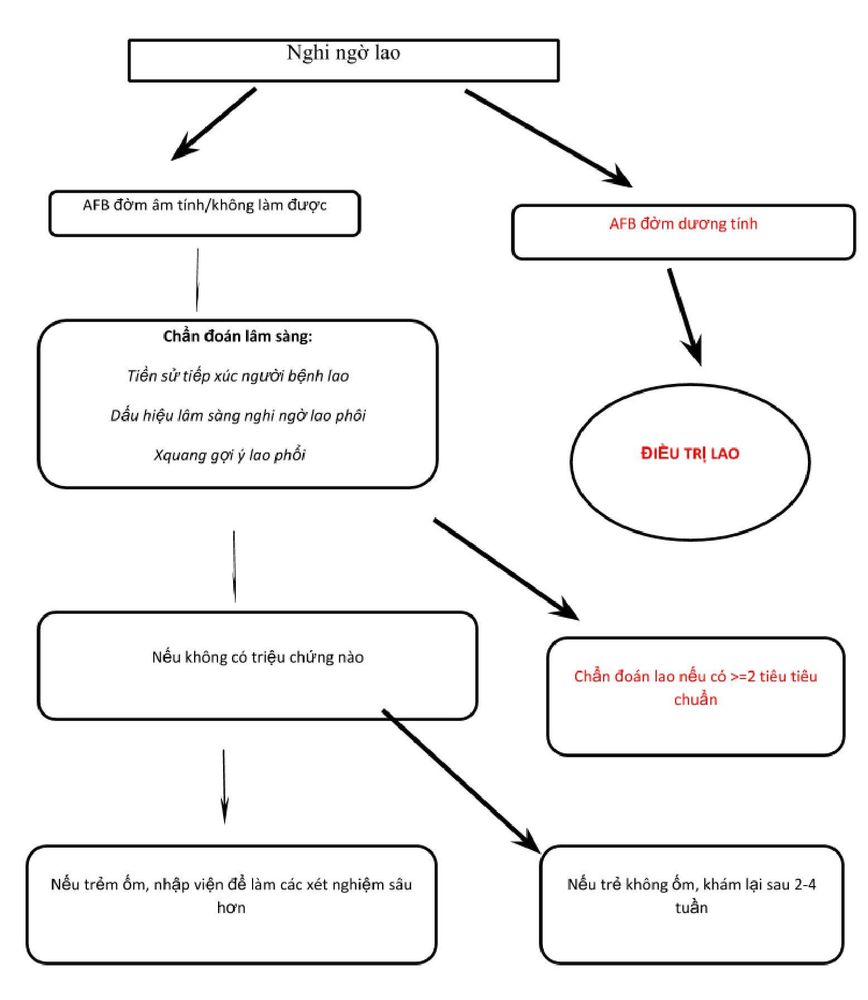
2.1 WHO Recommendations 2012 on approach to diagnosis of TB in young children Consists of 6 steps:
Step 1: Take a detailed medical history: history must include exposure history and suspected symptoms
Money contact history: people in contact with the child include family members, neighbors who have contact with the child, other children, friends at school, teachers... anyone with tuberculosis, or a persistent cough , or chronic lung disease. If there is a need to carefully examine the patient's disease, chest x-ray and AFB sputum test. Contact time is also important. Children usually develop TB within 2 years of exposure and 90% of them within the first year. Step 2: Clinical examination
The most important thing is to assess the physical development, malnutrition status and symptoms of disease in the lungs as well as outside the lungs. Children with TB often show signs of poor appetite, poor play, slow or no weight gain. If severe or persistent undernutrition is a useful factor in the diagnosis of TB, malnutrition increases the risk of TB and TB infection will facilitate malnutrition. Depending on TB, the clinical manifestations will vary. Common symptoms include: Cough, especially cough that is persistent and does not improve with treatment Weight loss or failure to gain weight Fever or night sweats Fatigue, poor play or activity.
Especially if symptoms persist for more than 2 weeks and do not improve with routine treatments (antibiotics for coughs, antivirals for feverish children, or dietary changes for malnourished children)
Step 3 : Test mantoux
Test Mantoux Method: inject 0.1 ml of a solution with 10 units of PPD (Purified Protein Derivative) into the skin of the front forearm to create a lump on the skin from 5-6mm in diameter Read the results: after 72h False positives and false negatives:
A positive Mantoux test is a contributing factor to the diagnosis of TB, but does not mean that the child is sick. However, a strong positive reaction, including blistering at the injection site, is an important suggestion for a child with TB.
Step 4: Find TB bacteria in the specimens
This is a decisive factor in the diagnosis of TB. But the rate of finding bacteria is so low that it is difficult to diagnose. Specimens used include: + For primary pulmonary tuberculosis, pulmonary tuberculosis: sputum specimens (older children), gastric lavage fluid (young children) because young children do not yet have a cough reflex, but often swallow phlegm.
+ Cerebrospinal fluid, pleural fluid, peritoneal fluid, joint fluid.
+ Urine if a urinary tract infection is suspected.
Tests that can be done to identify bacteria include: sputum AFB staining, TB bacilli culture (MODS TB, BACTEC...), TB PCR. AFB sputum, if positive 2/3 of the sample, has diagnostic value, usually positive in older children. Tuberculosis culture tests and TB PCR are both diagnostic if positive in a specimen.
Vi khuẩn lao được tìm thấy trong các mẫu bệnh phẩm
Step 5: Further tests if tuberculosis is suspected
Chest X-ray: essential. When TB is suspected in any subject, chest radiograph is mandatory, contributing to the diagnosis and deciding the direction of treatment. Imaging suggestive of TB on X-ray in children includes: mediastinal lymph nodes, diffuse opacities in both lungs (tuberculosis), cavernous forms of tuberculosis, tubercular nodules are more rare. have suggestive symptoms such as: meningeal syndrome, mental disturbances, cranial nerve palsies, hydrocephalus... suspected cause of tuberculosis, lumbar puncture test for biochemical changes and Cell culture as well as tuberculous cultures are required. CT scan of spine, bones if suspected tuberculosis, spinal tuberculosis.
Step 6: Routine HIV testing
HIV infection is often asymptomatic. In addition, HIV greatly increases the risk of tuberculosis. When HIV-infected patients develop TB, treatment attitudes and prognosis change.
Because of the very common association of HIV and TB, if the patient has HIV, it is recommended to try tests for TB and vice versa.
WHO Recommendations on Access to Diagnosis of TB in Children 2013.
For Children Without HIV
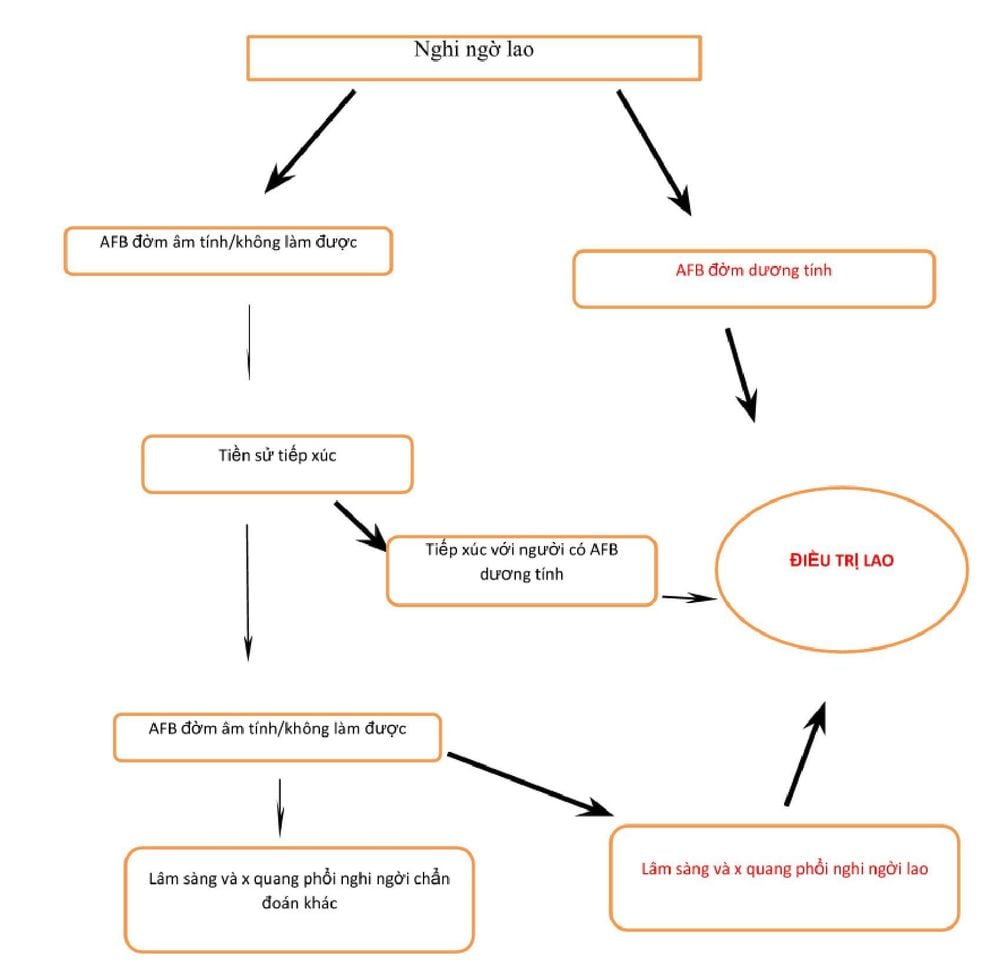
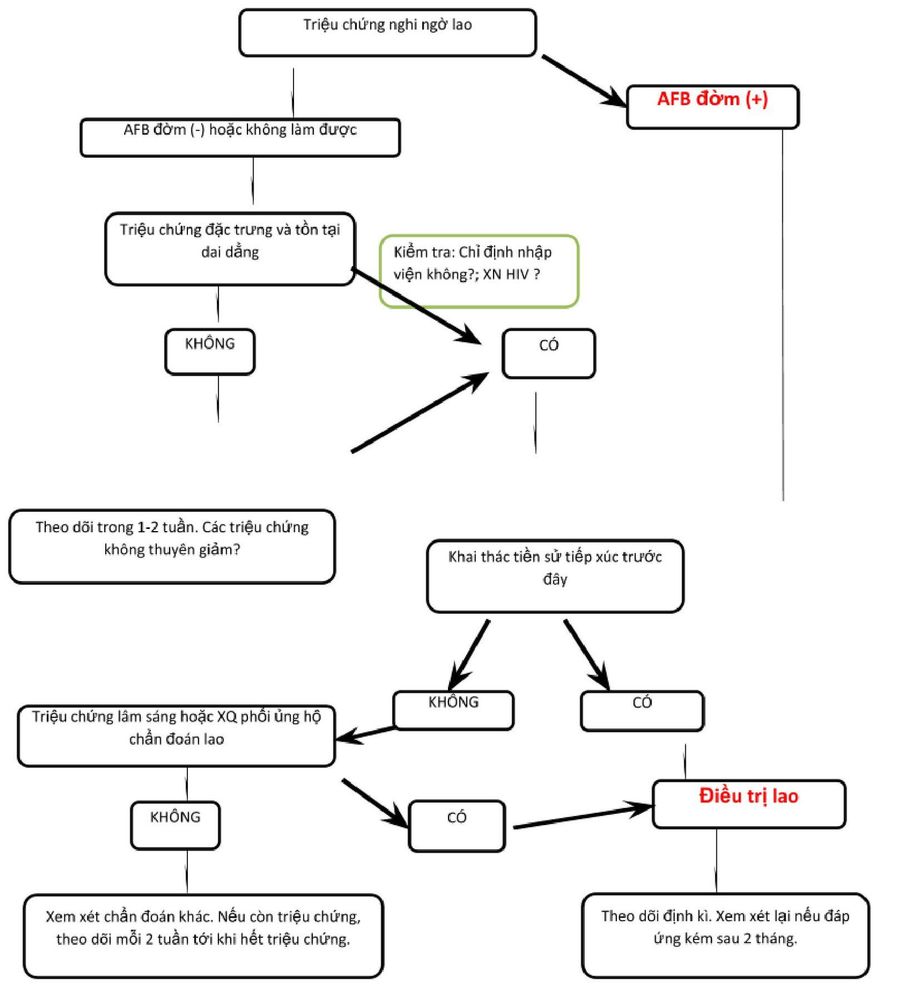
Tuberculosis in children is a serious disease with complicated long-term treatment, so TB vaccination is the safest and most effective method of prevention.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
To book an appointment for your baby's examination and vaccination at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact HERE.