This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by MSc Ma Van Tham - Pediatrician - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General HospitalMany TB diagnostic scales have been developed for the diagnosis and prognosis of AFB-negative TB cases. Each scale has advantages and disadvantages as well as different sensitivity and specificity.
1. Current situation of tuberculosis
According to statistics of the World Health Organization 2018, TB causes 2 million deaths each year, of which about 250,000 are children, mainly under the age of 2 years. Children can be infected with all forms of TB, however, the most common are 4 types:
Primary TB; Acute tuberculosis such as meningococcal tuberculosis and millet tuberculosis; Respiratory tuberculosis after primary infection such as pulmonary tuberculosis and pleural tuberculosis; Extrapulmonary TB: there are many types such as lymph node tuberculosis, bone and joint tuberculosis, spinal tuberculosis, peritoneal, pericardial, urogenital - genitourinary, intestinal tuberculosis... Some severe forms of TB such as meningococcal TB, millet TB. .. if it is too late in diagnosis and treatment, it will greatly increase the mortality rate as well as sequelae. However, the diagnosis of TB in children is difficult because the clinical symptoms are atypical and AFB sputum is often negative.
In the diagnosis of TB in adults or children, finding evidence of bacteria is the gold standard by AFB or PCR of TB in sputum, gastric juice, and other specimens. However, this standard is not always found. The rate of finding TB bacteria in the sputum in 2/3 of the samples was only about 6% (Nicol's study on the accuracy of Xpert MTB / RIF in TB diagnosis in South Africa 2011); 4% (Rachow's study in Tanzania in 2012) So how to diagnose AFB negative TB?
2. TB diagnosis by transcript
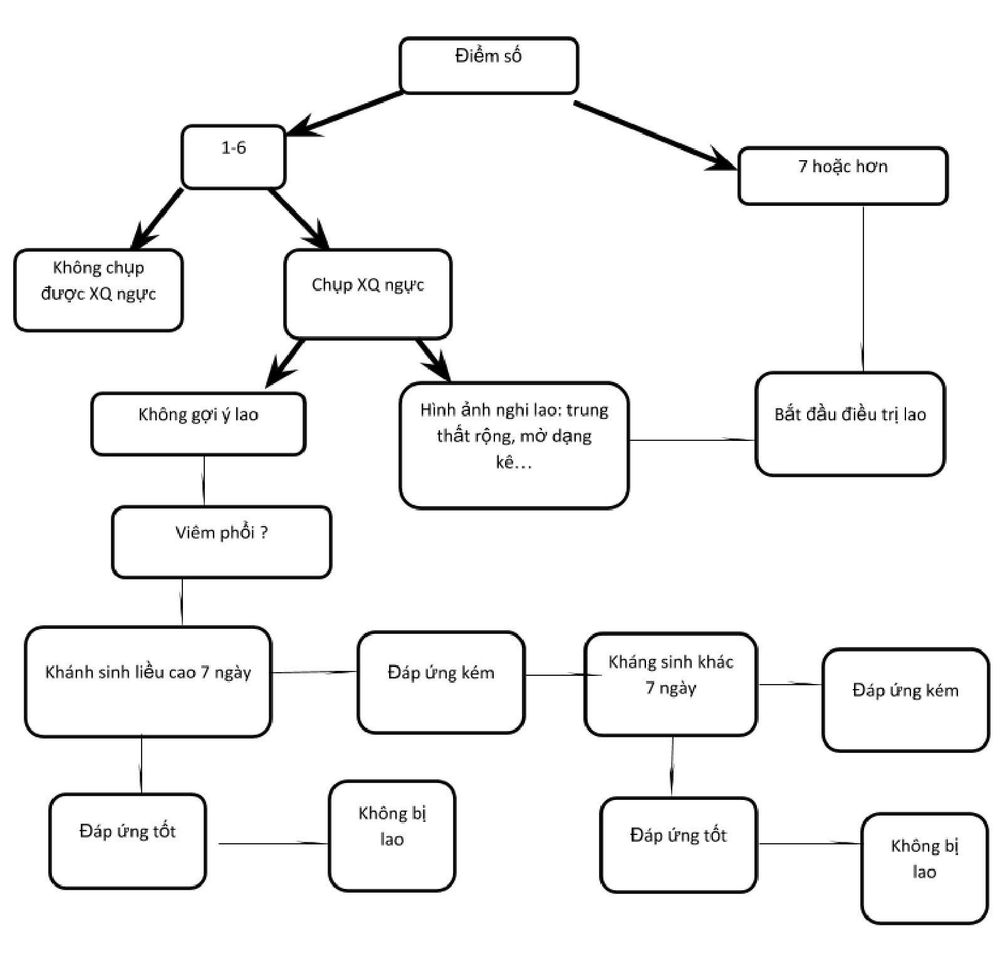
Keith Edwards Scorecard for diagnosing TB in children
This scorecard was created in 1996, developed by Keith Edwards, a lecturer at the University of Papua New Ghine, to diagnose TB in children. This scale has been recognized and recommended by WHO to date.
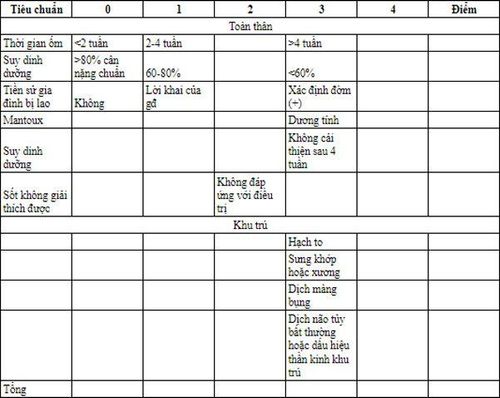
>7 points are positive, treatable. After grading will be handled as follows:
According to research Research by Supriya Sarkar, Dilip Kumar Paul in 2009 on 53 children with a confirmed TB diagnosis, the sensitivity and specificity were 84.9% and 78%.
Research by Dr. Shyam Narayan,. Mahadevan, V. Tiroumourougane Serane in June 2003 performed on 100 children from 2 months to 12 years of age, and showed that the sensitivity and specificity of the scale were 91% and 88%
Study of Mbala L1, Nsibu N2, Mpingiyabo K from 2008-2011 on 161 children, including 100 children with pulmonary tuberculosis and 61 healthy children, showed that the sensitivity and specificity of the above scale were 85% and 67.2%.
In this scale, nutrition and duration of illness are an important factor in the diagnosis. Therefore, the scale is not of high value in diagnosing acute forms of tuberculosis.

Bệnh lao nếu điều trị muộn sẽ để lại nhiều di chứng cho trẻ
3. Some scales of countries
3.1 Kenyan Score Scale| Điểm | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Thời gian ốm | <2 tuần | 2-4 tuần | >4 tuần |
| Tình trạng DD | >80% | 60-80% | <60% |
| TS gia đình bị lao | Không | Được báo cáo | Có bằng chứng (+) |
| TST (+) | 3 |
| Hạch lympho to đau, có rò | 3 |
| Mồ hôi đêm, sốt ko rõ nguyên nhân | 2 |
| Suy dinh dưỡng không cải thiện sau điều trị | 3 |
| Biến dạng cột sống | 4 |
| Sưng khớp không có tràn dịch, không có chấn thương | 3 |
| Chướng bụng/dịch ổ bụng không giải thích được | 3 |
| Thay đổi nhiệt độ, từng cơn hoặc liên tục | 3 |
| X quang phổi bất thường | 2 |
>7 points: definite diagnosis of TB 5-6: likely to have TB 3-4: need to do more tests to evaluate more closely <2: likely not TB 3.2 Diagnostic scorecard Indonesia's child TB
| Điểm | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Tiếp xúc nguồn lây | Không rõ | Tiếp xúc với người bệnh lao có AFB đờm (-) hoặc chưa rõ | Tiếp xúc với người bệnh lao AFB (+) | |
| TST | Âm tính | Dương tính (>10 hoặc >5 ở trẻ có nguy cơ cao) | ||
| Dinh dưỡng | BW/tuổi<80% | Suy dinh dưỡng nặng với BW/tuổi<60% | ||
| Sốt không rõ nguồn gốc | Có | |||
| Ho trên 3 tuần | Có | |||
| Hạch lympho | Nhiều, không mềm | |||
| Sưng khớp (gối, đốt ngón tay) | Có | |||
| X quang phổi | Bình thường | Nghi ngờ lao |
If more than 6 points, the possibility of TB is high.
Diagnosing TB in children as well as adults is always the first priority to find bacteriological evidence. However, because the rate of finding bacteria is not high, especially in children. Waiting for bacterial evidence will miss the diagnosis or delay treatment. The TB diagnostic scale is the solution for TB cases with negative bacteriological evidence. The TB score provides a scientific synthesis of TB risk factors and guides early treatment for TB cases where bacteriological evidence is negative.
However, the TB scales do not give a 100% sure diagnosis of TB. Therefore, in the process of approaching the diagnosis of pediatric TB, in parallel with scoring TB many times, at many times, the search for bacteriological evidence must always be focused.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
To book an appointment for your baby's examination and vaccination at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact HERE.
MORE:
What is the difference between lymph node tuberculosis and pulmonary tuberculosis? How many types of tuberculosis are there? Tuberculosis is not contagious