This is an automatically translated article.
Aciclovir, also known as acyclovir, is an antiviral medicine. It is mainly used to treat acute shingles, herpes simplex and chickenpox. Other uses include preventing post-transplant cytomegalovirus infection and serious complications of Epstein-Barr virus infection. In this article, we will provide useful information for you to better understand the uses, indications and precautions when using Aciclovir.
1. What is Acyclovir?
Acyclovir belongs to the group of antiviral drugs used to treat diseases caused by viral infections. This medicine does not cure the herpes infection, but only reduces the ability of the herpes virus to multiply in your body, helping to treat the symptoms of the infection. Medication can reduce the severity and duration of flare-ups, keep new sores from growing, and relieve pain and itching.
1.1. Indications for use of Acyclovir Use Acyclovir for the treatment of some of the following diseases:
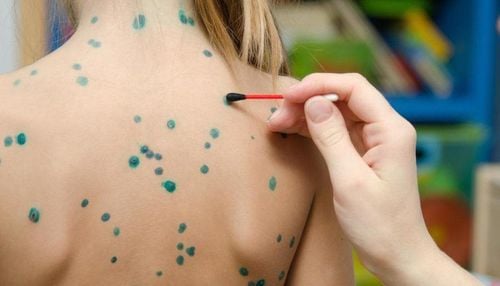
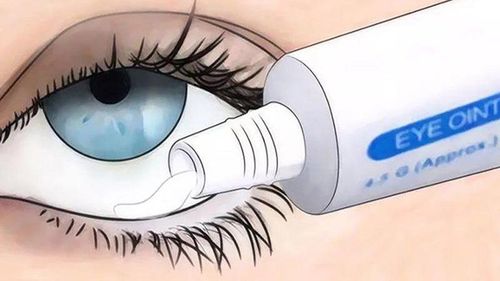
Herpes simplex virus infection type 1 and Herpes simplex type 2 in the skin and mucous membranes, Herpes simplex encephalitis. Herpes zoster virus infection in adults. Genital herpes. Hemorrhagic varicella, varicella in immunocompromised people, varicella in infants. 1.2. Drug forms Acyclovir Tablets strength 200mg, 400mg, 800mg. Oral suspension; 200mg/5ml (473ml). Topical medicine: 3g, 15g ointment. Cream tube 2g, 10g. Acyclovir ophthalmic ointment. 4.5g . Additionally, Acyclovir is available as an intravenous drug, but is for use only by physicians in medical settings.
Solution for injection: 50mg/ml (10ml, 20ml).
2. Dosage of Acyclovir
The dosage information for Acyclovir oral tablet depends on:Age. Disease condition. Other comorbidities. Response to the first dose. 2.1. How to use In pill form, drink directly with plenty of water. With liquid suspension, remember to shake well before taking and use the measuring device provided by the manufacturer to measure the most accurate amount of medicine. With topical creams apply a thin amount directly to the lesion site. Injectable form as prescribed by the doctor. This medication works best at the start of the first sign of a flare-up, as directed by your doctor. Medicines work best when the amount of medicine in your body is kept constant. Therefore, take this medicine at fixed times of the day during the treatment period. Do not arbitrarily change the dose of the drug or stop the drug without the consent of the doctor.
Thuốc Acyclovir dạng viên nén
2.2. Dosage 2.2.1. Tablet form (for shingles, genital herpes or chickenpox): Adult dosage (18 - 64 years old):
Dose for shingles: 800 mg every 4 hours without morning medicine night, 5 times daily for 7-10 days. For patients with severe immunodeficiency (e.g., following bone marrow transplantation) or intestinal malabsorption, intravenous administration should be considered. It should be started as soon as possible after infection, with good results if started at the onset of the rash. Dosage for genital herpes: + Typical initial dose: 200mg every 4 hours x 5 times daily, for 10 days.
+ Typical dosage to prevent recurrent herpes: 400mg x 2 times/day, for up to 12 months. Other possible dosing indications include doses ranging from 200 mg 3 times daily to 200 mg 5 times daily. Your doctor will decide how long you should take this medicine to avoid flare-ups of infection.
+ Typical dosage for reinfection (infection flare): 200mg every 4 hours, 5 times daily, for 5 days. You should take this medicine as soon as the first signs of a flare appear.
Usual dose of chickenpox: Take 800mg x 4 times daily for 5 days. There are no clinical studies to prove that the medicine works if you start taking it more than 24 hours after the first sign of chickenpox.

Người bệnh cần uống Acyclovir theo đúng chỉ định của bác sĩ
Dosage for children (ages 2 - 17 years):
Typical dose for chickenpox:
+ Children weighing 40 kg or less: 20 mg/kg body weight x 4 times daily for 5 day.
+ Children weighing more than 40 kg: 800 mg x 4 times / day for 5 days.
There are no clinical studies to prove that the medicine works if your child starts taking it more than 24 hours after the first sign of chickenpox.
Pediatric dosage (ages 0 - 1 year):
It has not been confirmed that acyclovir is safe and effective for children under 2 years of age.
Dosage for the elderly (65 years of age and older):
The kidneys of the elderly may not work as well as they used to, the total body clearance of acyclovir decreases in parallel with the clearance of creatinine. This can cause their body to process the drug more slowly. As a result, many drugs stay in their system longer, increasing their risk of side effects. Rehydration should be maintained for patients receiving high doses of acyclovir.
Your doctor may start treatment with a lower dose or a different dosing schedule
Note: reduce dose in patients with chronic renal failure
In the management of herpes simplex infection in patients with renal impairment, the recommended dose Oral administration did not result in accumulation of acyclovir above levels determined to be safely administered intravenously.
However, in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 10ml/min) the dose should be adjusted to 200mg twice daily 12 hours apart.
In the treatment of shingles (herpes zoster) 800 mg twice daily 12 hours apart in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/min) and 800 mg 3 times daily 8 hours apart hourly for patients with moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance between 10-25ml/min).
2.2.2. Cream form: Dosage for both adults and children, should be applied 5 times a day about 4 hours apart, continuously for 5 days, if not, can extend the treatment to 10 days, do not use at night. Acyclovir cream should be applied to the lesion or the site of the lesion as soon as possible after infection.
Treatment of particularly severe recurrent episodes should be initiated during the prodromal phase or as soon as lesions begin to appear.
2.2.3. Acyclovir Ophthalmic Ointment Dosage for both adults and children, apply to the sac and conjunctiva an extruded amount of about 10 mm x 5 times / day 4 hours apart. Continue treatment for at least 3 days after healing.
Thuốc Acyclovir dạng kem bôi
3. Acyclovir side effects
3.1. Common side effects Nausea or vomiting. Diarrhea. Headache. Tired. 3.2. Serious side effects Behavioral changes or unusual mood swings such as:
Aggressive behavior or extreme fatigue. Slow, fast, or irregular heartbeat. Trembling. Confusion. Distorted voice. Hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that are not real). Convulsions. Comatose. Decreased red blood cells and platelets, manifesting fatigue symptoms Muscle pain. Skin reactions, symptoms include:
Hair loss. Easy bruising and bleeding. Rash. Loose skin texture. Stevens-Johnson syndrome (acute atopic dermatitis) is very rare. Change in your vision. Symptoms of kidney failure include:
Kidney or lower back pain. There is blood in your urine. Allergic manifestations:
Difficulty breathing. Swelling of your throat or tongue. Rash. Drugs affect each person differently. Call your treating doctor right away or go to the nearest medical facility if you have any of the above symptoms.

Sau khi dùng thuốc Acyclovir, một số trường hợp có thể xuất hiện biểu hiện dị ứng như khó thở
4. Notes when using Acyclovir
4.1. Warning to certain populations For people with kidney problems: If you have kidney problems or a history of kidney disease, this medicine may also decrease your kidney function, tell your doctor so they can Adjust your dose depending on how well your kidneys are working. For pregnant women: Acyclovir is a category B pregnancy drug which means: Studies in pregnant animals have shown no hazard to the fetus. But there aren't enough studies done in pregnant women to show whether the drug poses a risk to an unborn baby. Tell your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
For women who are breastfeeding: Acyclovir can pass into breast milk and may cause side effects in a nursing infant. Talk to your doctor about whether you are breastfeeding. For children: This medicine has not been studied in children under 2 years of age. For the elderly: The renal filtration rate in the elderly is often lower. The doctor will consider the appropriate dose for this group of subjects. 4.2. Follow the guidelines If you stop taking your medicine suddenly or don't take it at all: Your infection symptoms may not improve or may get worse. If you miss a dose or don't take it on schedule: Your medicine may not work as well or it may stop working altogether. If you are taking this medicine to prevent outbreaks of an infection, then you need to have a certain amount in your body at all times. You should not stop taking this medicine without first talking to your doctor. What to do if you miss a dose: Take it as soon as you remember. But if you remember just a few hours before your next scheduled dose, take only one dose. Never take two doses at the same time. This can lead to dangerous side effects. If you take too much: You may experience more serious side effects. Go to the nearest doctor or medical facility immediately. 4.3. Drug Interactions Some products that may interact with this drug include: other drugs that can cause kidney problems (including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs-NSAIDs such as ibuprofen, naproxen).
Acyclovir is very similar to valacyclovir. Do not use medicines containing valacyclovir while using acyclovir.

Người bệnh có thể nhờ sự tư vấn từ dược sĩ để có cách dùng thuốc Acyclovir an toàn
4.4. Storage Store this medication at room temperature. Keep the temperature between 15 °C and 25 °C. Keep away from sunlight. Do not store this medicine in damp or humid places, such as the bathroom. The drug in suspension or cream has been used up after the course of treatment must be discarded and not reused in the next session (if relapse occurs). 4.5. Sensitivity to the sun Acyclovir can make your skin more sensitive to the sun. This increases the risk of sunburn. Limit direct sun exposure as much as possible. If you can't, be sure to wear protective clothing and apply sunscreen.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference sources: webmd.com, healthline.com