This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master. BSCK II Phan Thi Minh Huong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.Peritonitis is a fairly common emergency with many different causes. But in general, all of them have a serious effect on the patient's health and require treatment as soon as possible. So how to recognize an peritonitis? Who is at high risk for peritonitis?
1. Acute peritonitis
Peritonitis is an inflammation of the tissue lining the inside of the abdominal wall and covering most of the abdominal organs (called the peritoneum) caused by pathogens (bacteria, fungi, ..) or not caused by bacteria. bacteria (stomach acid, pancreatic juice, ...).Infection of the peritoneum is often severe because the patient has easy access to the existing pathogens and easily spreads to the entire peritoneal cavity. This is a serious and urgent condition that requires immediate treatment.
2. Why is it dangerous?
Peritonitis is a very serious disease in surgery, if not treated promptly, the mortality rate can be up to 60-70%, because acute peritonitis is the final stage of the bacterial infection in the body. Abdominal cavity, there are many types of bacteria, their toxicity is very high, while the area of the peritoneum (peritoneum) is very large, so the ability to absorb toxins from empty organs (stomach, intestines...) Infiltrated, toxins (secreted by bacteria) very quickly lead to shock and poisoning (septic shock).Severe disease is also due to the ease of spreading throughout the abdomen by peristalsis (colic contractions push the dirt into the abdomen). Therefore, when peritonitis is suspected, it is necessary to diagnose it early and treat it properly and promptly in order to minimize mortality.
3. Causes of peritonitis
Acute peritonitis can be caused by primary, that is, caused by an infection in the peritoneum such as peritoneal tuberculosis, pneumococcal or gonococcal peritonitis (low rate). Besides, secondary peritonitis accounts for the highest rate, which is peritonitis due to gallbladder perforation, bile will seep into the peritoneum causing inflammation (biliary peritonitis), intestinal perforation, intestinal obstruction, gastric perforation, ruptured appendicitis, abdominal trauma (due to bullets, landmines, labor accidents, traffic accidents...).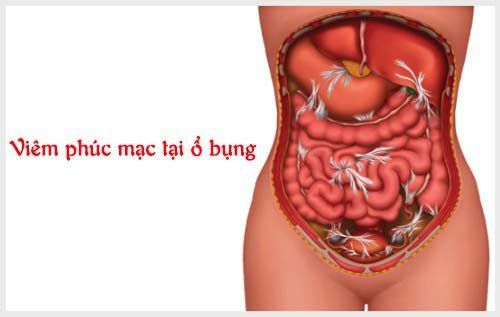
Viêm phúc mạc là một bệnh lý rất nặng trong ngoại khoa, cần được chẩn đoán và điều trị kịp thời
The cause of peritonitis can be bacterial or chemical. Bacterial peritonitis is caused by bacteria entering the abdominal cavity by a blood vessel, either by spread from an infection in the abdominal cavity or by perforation of a hollow viscera (intestine, stomach, bladder, etc.) ) fluid and dirt from those organs carry bacteria into the peritoneum causing inflammation. Bacteria can be tuberculosis bacteria (due to peritoneal tuberculosis), intestinal bacteria such as: E.coli, Proteus, Klebsiella, blue pus bacilli, anaerobic bacteria (C. difficil), if perforated hollow viscera (C. difficil) stomach, intestines, bladder, etc.).
4. Symptoms of acute peritonitis
Abdominal pain is the earliest and always present symptom in peritonitis, the location of the pain depends on the cause of the disease (gastric perforation, severe abdominal pain and hard as wood, ruptured appendix, primary pain). weakness of the right iliac fossa and epigastrium...), accompanied by nausea and vomiting. When the peritoneum is infected, the fever will be high or very high (39 - 40oC). Patients are tired, emaciated, listless, pale skin, sweaty, cold limbs. More severe can be lethargy, semi-consciousness or coma, tachycardia, low blood pressure due to dehydration, electrolytes (vomiting, fever) and due to water retention in the intestinal lumen and abdominal cavity, causing bacterial toxicity.Necessary tests such as complete blood count (high white blood cell count and neutrophil count), erythrocyte sedimentation rate, elevated blood urea, urinalysis, abdominal ultrasound, X-ray- Abdominal radiograph...
Consequences of peritonitis, if severe, if not detected early and treated properly, in time can be fatal, if cured, treated aggressively, later may cause intestinal adhesions, Intestinal obstruction is complex. Therefore, after being cured and discharged from the hospital, patients should always pay attention if there are signs of abdominal pain, constipation, defecation, nausea, vomiting, they must urgently go to the hospital immediately.
5. Diagnosis and Treatment
5.1 Diagnosis 5.1.1 Definitive diagnosis is based on: Systemic infection syndrome. There is a muscle reaction of the abdominal wall. Abdominal muscle spasticity is evident (early arrival, young patient in good health). Positive Blumberg sign. On rectal examination, the vaginal sac is distended and painful. 5.1.2 Diagnosis should be differentiated from diseases Early arrival with pain:Peptic ulcer disease. Renal colic. Liver writhing.
Khoa Ngoại tổng hợp - Bệnh viện Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec là địa chỉ uy tín và chất lượng.
Diagnosis of the cause should be based on:
History. The nature of pain and the initial location of pain ... It is necessary to pay attention to common clinical causes first (acute appendicitis rupture, perforation of peptic ulcer, biliary obstruction due to stones ...). 5.2 Treatment The principle is that surgical treatment must be combined with active surgical resuscitation.
5.2.1 Surgical resuscitation: Fluids, electrolytes to rehydrate, electrolytes. Adjust acid-base balance (Natribicarbonate). Strong, broad-spectrum antibiotics, preferably by antibiogram. Ensure respiration, cool down... 5.2.2 Surgical treatment: The principle of surgical treatment is surgery as soon as possible on the basis of active resuscitation. There are cases where both resuscitation and surgery are required.
Surgical content:
Solve the cause: Cut the appendix, stitch the perforation .... Clean the abdominal cavity, pay attention to the low areas, the pits. Effective drainage (location, size, ... of the drain, early withdrawal, no adhesions, infection). 5.2.3 Some notes: Anesthesia: Endotracheal anesthesia. Incision: into the direct line or the middle white line above and below the navel. Leave the skin open, when the abdominal wall is closed. Acute peritonitis is a dangerous disease, leaving severe sequelae and having a high risk of death. Therefore, if you see any unusual symptoms, you should immediately seek medical attention.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.