The 500-calorie diet is a very low-calorie diet designed to help you lose weight. Doctors may recommend this diet for severely overweight or obese individuals with a BMI over 30, especially if their health is at risk. It’s important to note that this diet is not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women. Here’s everything you need to know about the 500-calorie diet:
1. What is the 500-Calorie Diet?
The 500-calorie diet is an extremely strong and strict plan. It limits your daily calorie intake to an exceptionally low level, often replacing normal eating habits with liquid supplements, meal replacement products, or snack bars for a specific period.
With fewer calories, the body burns stored fat for energy, leading to fast weight loss. It is sometimes known as the 5:2 intermittent fasting plan, where calorie intake is restricted to 500 calories on two non-consecutive days each week while maintaining normal calorie consumption on the other five days. On fasting days, calorie intake typically covers only 20-25% of energy needs.
Studies suggest that intermittent fasting may help overweight and obese individuals lose weight. However, findings remain inconclusive, and more research is needed to confirm these claims.
While the 500-calorie diet can aid in rapid weight loss, it is not suitable for everyone.
The benefit of the 500-calorie diet lies in its ability to promote rapid weight loss. Following this diet can enhance metabolism, accelerate fat oxidation, and support effective weight loss. This diet is often recommended for individuals who need to lose weight quickly to prevent potential health risks associated with excess weight.
However, the 500-calorie diet is not suitable for everyone, as long-term adherence can lead to severe nutritional deficiencies. A study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that extremely low-calorie diets, such as the 500-calorie diet, can cause significant micronutrient deficiencies.
The study revealed a significant decrease in levels of vitamin D, vitamin C, and zinc in obese individuals following the 500-calorie diet for more than 12 weeks. Additionally, this diet may lead to side effects such as nausea, fatigue, diarrhea, increased sensitivity to temperature, menstrual irregularities, and hair loss. The lack of dietary fiber can also result in constipation. Furthermore, the immune system may be weakened, making the body more susceptible to various illnesses.

2. Seven Key Points About the 500-Calorie Diet
The 500-calorie diet is an extreme form of very low-calorie diets (VLCDs). It requires individuals to significantly cut calorie intake, up to 800 calories per day. This method relies on meal replacements such as drinks, shakes, and pre-packaged foods to substitute at least two meals a day. As mentioned, this diet is also suitable for individuals who are severely overweight and have not succeeded in losing weight after trying multiple diet plans. However, this diet can be dangerous and requires medical supervision. Here are 7 things you need to know about the 500-calorie diet.
2.1. Don’t Attempt It Without Medical Supervision
Doctors may prescribe the 500-calorie diet if they determine that weight loss is necessary for your health. The decision whether to use it is based on the concern of the patient against the potential risks and complications. If a doctor doesn’t recommend this diet, you should not attempt it on your own. It requires close medical supervision.
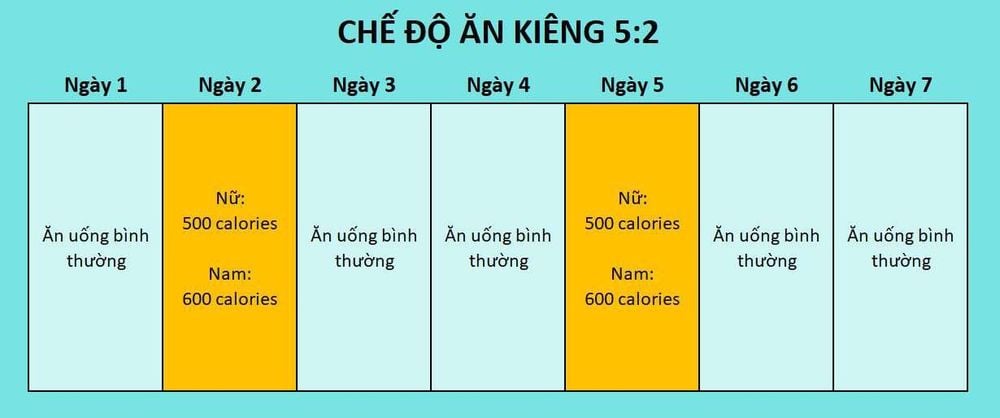
2.2. 5:2 Diet Plan
Recently, some people use the 500-calorie diet into the 5:2 intermittent fasting plan. This involves eating a balanced Mediterranean-style diet of approximately 2,000 calories on five days of the week and then restricting calorie intake to 500 on the other two daday(Two days of "fasting" in a cycle are usually not consecutive.). However, there is little scientific evidence to support the benefits of the 5:2 approach so you should carefully consider before adopting this diet.
2.3. How much is 500 calories?
You absolutely can perfectly tell what 500 calories are when considering the calorie intake of common foods. The U.S. Department of Agriculture calculates that:
-Two handfuls of peanuts or a slice of pepperoni pizza = ~250 calories
-One apple = ~80 calories
-Two pieces of fried chicken = ~400 calories
Additionally, you can consider how many calories you burn. For instance, a person weighing 84 kg burns about 72 calories by simply sitting in a one-hour meeting.
2.4. Nutritional Balance Is Essential
A major issue with this diet is the lack of control over fat and carbohydrate intake. For instance, consuming a chocolate bar and a glass of milk may total 500 calories but won’t provide the vitamins and minerals your body needs. A balanced diet includes fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Your body's health isn't just calculated by numbers that represent regular calorie levels.
2.5. Risk of Nutritional Deficiencies
The greatest risk of this diet is vitamin and mineral deficiency, which can harm overall health. Most people cannot meet their nutritional needs with less than 1,200 calories daily. For example, according to the Mayo Clinic, a diet lacking zinc, found in pumpkin seeds and beef, may lead to hair loss. Low iron intake can cause anemia, while chronic deficiencies in calcium and vitamin D may result in osteoporosis later in life. Additionally, insufficient niacin, present in tuna and dates, could increase the risk of heart attacks due to arterial blockages. Therefore, it’s crucial to focus on the complete nutritional profile of the foods you eat, not just their calorie content.
2.6. Muscle Loss
The 500-calorie diet can also put you at risk of muscle loss. Dr. Sharon Palmer, a nutritionist and author of Plant-Powered for Life, explains that "once your body has used up its fat reserves, it will also start burning healthy muscle." Initially, losing muscle may appear as rapid weight loss, but remember that not all body weight is bad. To maintain a healthy body, you need the ability to build and preserve muscle. A healthy diet is one that burns fat, not muscle.
2.7. Metabolic Changes
Another health risk to consider with the 500-calorie diet is how it affects the body’s metabolism. Prolonged calorie restriction significantly slows down the metabolism, causing the body to burn fewer calories over time. Additionally, as weight is lost, the body may require fewer calories to maintain the new weight compared to the original weight.
Dr. Mindy Haar from the New York Institute of Technology’s School of Health said, "Many people believe they can stick to a restrictive diet for a short time, lose weight, and then return to their usual eating habits. However, doing so often results in regaining the weight until reaching the original level." Typically, weight loss includes both fat and lean mass, but when they regain weight is primarily fat, which can lead to increased long-term fat accumulation.
The 500-calorie diet is not suitable for everyone and should only be undertaken under strict medical supervision. While it may lead to rapid weight loss, it also carries risks such as malnutrition and micronutrient deficiencies. A healthy weight-loss diet focuses on providing a variety of nutrients from different food sources, controlling portion sizes, and burning more calories than consumed. Therefore, the key to sustainable weight management is portion control and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.

For more health, nutrition, and beauty tips, visit Vinmec International General Hospital to safeguard the health of yourself and your loved ones.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.