This is an automatically translated article.
Banana is extremely good for human health and easy to use. Bananas contain several essential nutrients and offer benefits for digestion, heart health, and weight loss. In addition to being very nutritious, bananas are also a very convenient snack. In this article, we will provide useful information for you to better understand 6 important nutrients found in bananas.
1. Nutritional value in banana
The scientific name of the banana is Musa, belonging to the family Musaceae - a tropical flowering and fruiting plant that grows in clusters at the top of the tree. Bananas are so nutritious, even dubbed the first "superfood," that were endorsed by the American Medical Association in the early 20th century as a health food for children and a treatment for celiac disease.1.1. 6 important nutrients found in bananas include:
Calories:89 Protein: 1.1 grams Carbs: 22.8 grams Sugar: 12.2 grams Fiber: 2.6 grams Fat: 0.3 grams

Trong chuối có nhiều nhóm dưỡng chất quan trọng
1.2. Energy level
Bananas are a rich source of carbs, mainly in the form of starch in unripe bananas and sugar in ripe bananas.
The carb composition of bananas changes drastically during ripening. An unripe banana has starch as its main ingredient. Green bananas contain up to 80% starch by dry weight. During ripening, the starch is converted to sugar and less than 1% remains when the banana is fully ripe.
The most common sugars in ripe bananas are sucrose, fructose and glucose. In ripe bananas, the total sugar content can amount to more than 16% of the fresh weight.
Bananas have a relatively low glycemic index (GI) of 42–58 due to their high content of resistant starch and fiber, depending on their ripeness. GI is a measure of how quickly the carbs in a food enter your bloodstream and raise blood sugar.
1.3. Fiber
Most of the starch in unripe bananas is resistant starch, which passes through your intestinal tract without being digested. In your large intestine, this starch is fermented by bacteria to form butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid that has beneficial effects on gut health.
Bananas are also a good source of other types of fiber, such as pectin. Some pectins in bananas are water soluble. As bananas ripen, the percentage of water-soluble pectin increases, which is one of the main reasons why bananas become soft as they age. Neither pectin nor resistant starch raise blood sugar levels after a meal.

Trong chuối có hàm lượng chất xơ cao
1.4. Vitamins and minerals
Bananas are a good source of many vitamins and minerals, especially potassium, vitamin B6 and vitamin C.
Potassium: Bananas are a good source of potassium. A diet rich in potassium may lower blood pressure in people with high levels and is beneficial for heart health. Vitamin B6: Bananas are rich in vitamin B6. One medium-sized banana can provide up to 33% of the Daily Value (DV). Vitamin C: Like most fruits, bananas are a good source of vitamin C.
1.5. Other plant compounds
Fruits and vegetables contain a wide variety of bioactive plant compounds, and bananas are no exception.
Dopamine . Although it is an important neurotransmitter in your brain, dopamine from bananas does not cross the blood-brain barrier to be able to affect mood. Instead, it acts as an antioxidant. Catechin. Several antioxidant flavonoids are found in bananas, most notably catechins. They have been linked to various health benefits, including a reduced risk of heart disease
Dopamine từ chuối hoạt động như một chất chống oxy hóa.
2. Health Benefits of Bananas
2.1. Heart health
Heart disease is the most common cause of death in the world.
Bananas provide an excellent amount of potassium – an important mineral and electrolyte in the body that carries a small electrical charge. These charges cause nerve cells to send signals to the heart to beat steadily and the muscles to contract. Potassium is also needed to maintain a healthy balance of water in the cells and offset the effects of excess dietary sodium. An imbalance in the diet with too little potassium and too much sodium can lead to high blood pressure. Too much sodium can lead to a buildup of fluid in the blood, which puts pressure on the walls of blood vessels and eventually causes damage. Potassium helps the body get rid of excess sodium through the urine and calms the tension of the blood vessel walls. Potassium and fiber-rich, low-sodium bananas are an important component of a heart-healthy diet such as DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) which aims to provide about 4,700 mg. potassium in the daily diet. In addition, bananas contain antioxidant flavonoids that are also associated with a significant reduction in the risk of cardiovascular disease.
2.2. Digestive Health
Unripe green bananas contain significant amounts of pectin and resistant starch - a type of carbohydrate that "fights" digestion in the small intestine. It is absorbed slowly and does not cause a sharp spike in blood sugar. Starch acts as food for the growth of beneficial bacteria in the digestive tract. Microorganisms break down and ferment starch as it enters the large intestine, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that may play a role in preventing chronic diseases including digestive disorders. Clinical studies have demonstrated the potential use of SCFAs in the treatment of ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, and antibiotic-associated diarrhea.
Bananas are included in the BRAT (an acronym for Bananas, Rice, Applesauce, Toast) diet, a regimen commonly prescribed to patients with diarrhea or who require a bland diet, easy to digest after stomach disease. Not only are they easy to eat, bananas can help replenish electrolytes such as potassium lost with diarrhea or vomiting, and contain resistant starch (especially if cooked unripe green bananas are used) which can aid in healing. intestinal healing.
Tăng cường chuối trong chế độ ăn giúp hỗ trợ sức khỏe tiêu hóa
2.3. Support weight loss
Bananas are a low calorie food with lots of fiber that helps support weight loss goals. With about 3 grams of fiber for every 100 calories, bananas are a great choice to feel satisfied without overeating.
One meta-analysis estimated that adding 14 grams of dietary fiber (or reducing calories by 10%) per day could result in 2 kg of weight loss in 4 months. Bananas as a snack or breakfast option can help you achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
2.4. May support wound healing and strengthen resistance
The vitamin C content in a medium-sized banana will provide about 10% of your daily vitamin C needs. Vitamin C in bananas helps your body heal cell and tissue damage; support the body to absorb iron; Supports brain health by producing serotonin – a hormone that affects sleep cycles, mood and the experience of stress after pain.
Banana peels contain phytochemicals in the form of antioxidants, which have long been used in traditional and folk medicine as an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory to promote the healing of wounds such as wounds. bites, minor burns and sunburn. This is considered a simple home remedy, you apply the inside of a banana peel to the wound for a few minutes.

Một công dụng của chuối có thể hỗ trợ chữa lành vết thương và tăng cường sức đề kháng
2.5. Skin Health
One medium-sized banana provides about 13% of your daily manganese needs. Manganese helps the body make collagen and protects the skin and other cells against the damaging effects of free radicals.3. Disadvantages of bananas
Bananas contain a lot of starch and sugar, which can cause your blood sugar to rise. But because of the low GI, moderate banana consumption won't raise blood sugar nearly as much as other high-carb foods. Therefore, people with diabetes should avoid eating a lot of ripe bananas. It's best to monitor your blood sugar carefully after consuming a lot of sugar and carbs.
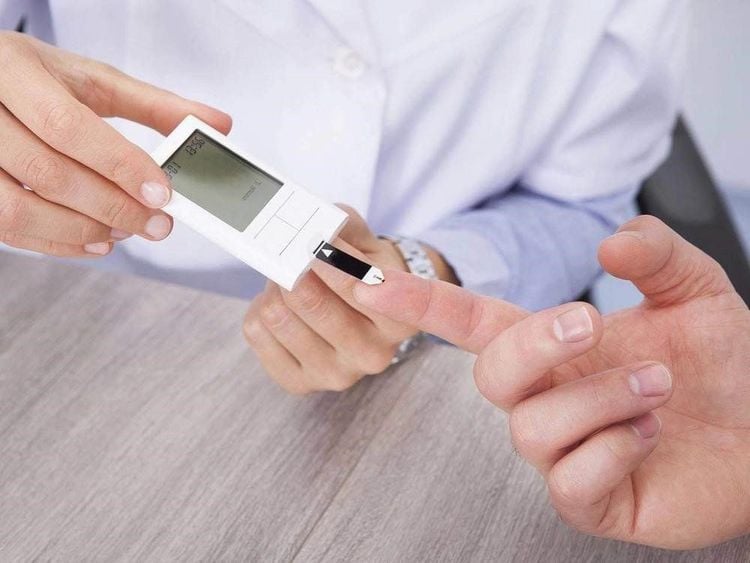

Chuối có thể làm tăng lượng đường trong máu
4. Preservation
Store at room temperature away from direct sunlight Do not refrigerate green bananas as this may damage the normal ripening process. To speed up ripening, store in a brown paper bag or near ripe fruit, which releases ethylene gas which causes ripening. On the other hand, if you want to slow down the ripening process, store bananas away from bananas or other ripe fruit. Do not store in a plastic bag as this holds excess moisture and can cause rotting. Fully ripe yellow bananas can be stored in the refrigerator in an airtight product drawer. The refrigerator will preserve the flavor for another week, even if the skins continue to darken. If the banana peel is ripe to almost brown, peel it and chop or puree it for baking or freeze it to add to smoothies. Please follow the website: Vinmec.com regularly to update many other useful information.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: healthxchange.sg, hsph.harvard.edu, healthline.com, verywellfit.com