This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Hoang Thi Hoa - Cardiologist - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine - Vinmec Ha Long International General Hospital.Echocardiography is an important imaging method in the examination, examination, screening and treatment of heart diseases. Depending on the operating principle or location on the body, there will be different echocardiography methods such as: transthoracic echocardiography, transesophageal echocardiography, fetal echocardiography...
1. Why need echocardiography?
Performing an echocardiogram will help the doctor accurately and objectively diagnose the patient's medical condition. When using an echocardiogram, doctors can perform an echocardiogram to look at a patient's heart. The ultrasound waves from the ultrasound machine allow doctors to see how the patient's heart is beating and pumping blood. Through these images, the doctor can find many abnormalities in the heart muscle and heart valves.
Besides, echocardiography is important, helping doctors check for heart abnormalities including:
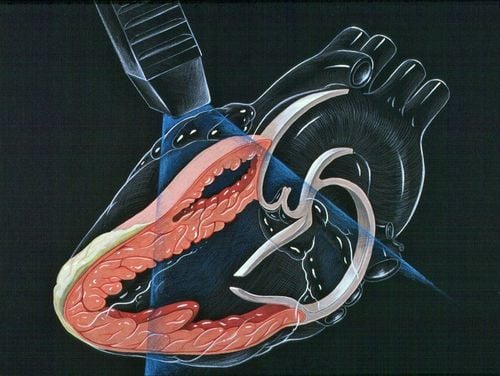
Heart valve problems such as regurgitation can be detected because this technique helps to shape the heart. Capturing the movement of your heart valves. Measures the velocity of blood flow in different areas of the heart. This is useful in measuring impaired blood flow in conditions such as aortic stenosis. Echocardiography evaluates congenital heart disease during pregnancy, infancy and infancy. Echocardiography is commonly used to measure left ventricular ejection fraction to evaluate the effectiveness of various cardiac treatments in conditions such as heart failure. If you have an arrhythmia, an ultrasound can assess the movement of your heart, which can help determine the exact cause and best treatment. Assess the direction of blood flow through the heart; pumping action of the heart; changes in the electrical current in the heart; locate the thrombus or tumor.
2. 6 commonly used echocardiographic methods
Transthoracic echocardiography: This is the most common type of echocardiogram. This form is painless and non-invasive. A transthoracic echocardiogram is performed by your doctor using a device called a transducer and placing it on your left chest, where your heart is. Then, the doctor will apply a gel to the chest to help the sound waves travel better. The transducer uses ultrasound waves through the chest and creates a live image of the heart that is displayed on a connected computer screen.
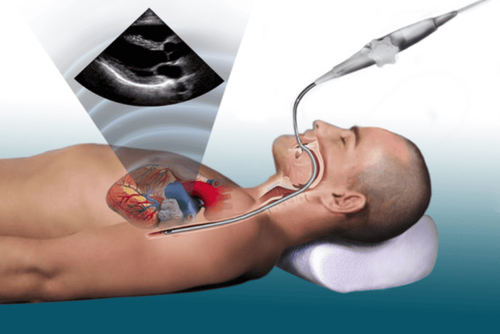
Transesophageal echocardiogram: If an echocardiogram does not produce a clear picture, your doctor may recommend a transesophageal echocardiogram. With a transesophageal echocardiogram, your doctor will use a smaller probe down your throat through a thin catheter. This tube is guided through your esophagus and with a transducer that records the ultrasound waves and reproduces a more detailed image of your heart on a computer screen.
Fetal echocardiography: Fetal echocardiography is used with pregnant women between 18 and 22 weeks of pregnancy. An ultrasound device is placed on a pregnant woman's abdomen to check for heart problems in her unborn baby. Fetal echocardiography is considered safe for the fetus because it does not use radiation, unlike X-rays.
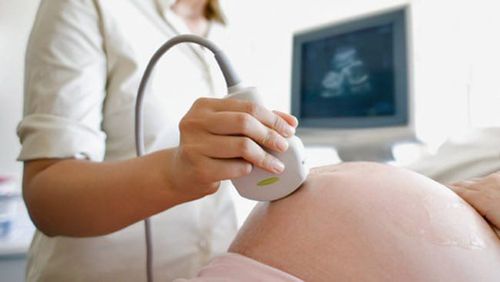
Siêu âm tim thai
Doppler ultrasound: Doppler ultrasound helps check blood flow; Pulmonary arterial pressure measurement; mapping the direction and speed of blood flow in the heart; check, detect some heart diseases, blood vessels and evaluate cardiac output.
Three-dimensional echocardiography: Three-dimensional echocardiography, also known as 3D echocardiography, helps doctors evaluate heart valve function in people with heart failure; heart problems in infants and children; reconstruction of structures in the heart; assessment of heart function; preoperative evaluation
Stress echocardiogram : Stress echocardiogram means that the patient has to exercise (such as running or walking on the machine. After that, the doctor will monitor the heart rate, pulse activity, etc.) Electrocardiogram to determine if you have conditions such as: ischemic heart disease, heart failure, heart valve problems.
3. Echocardiography procedure
3.1. Before performing an echocardiogram If a stress echocardiogram or a transesophageal echocardiogram is performed, the physician may ask the patient not to eat for several hours and during the stress echocardiogram the patient must run or walk on a treadmill so wear comfortable shoes.
For the remaining echocardiographic methods, the patient does not need to prepare anything and can live and eat as usual.
3.2. The echocardiogram procedure typically takes less than an hour, but the time can vary depending on the patient's condition.
Step 1: The patient will lie on the bed for an ultrasound, the doctor will attach patches (electrodes) to the body to help detect and monitor the electrical currents of the heart. Step 2: The doctor will apply a special gel on the patient's chest to increase the transmission of sound waves and eliminate air between the skin and the transducer. Step 3: The doctor will move the transducer back and forth across the chest and the sound waves that create an image of the heart are recorded on an observation screen. Patient You can hear the sound of blood flowing in the heart recorded by the ultrasound machine. If you have a transesophageal echocardiogram, you will be numbed with a spray of water or gel to make it easier for the transducer to be inserted into your esophagus. Step 4: During the transthoracic ultrasound, the person may be asked to breathe in a certain way or lie on their left side.
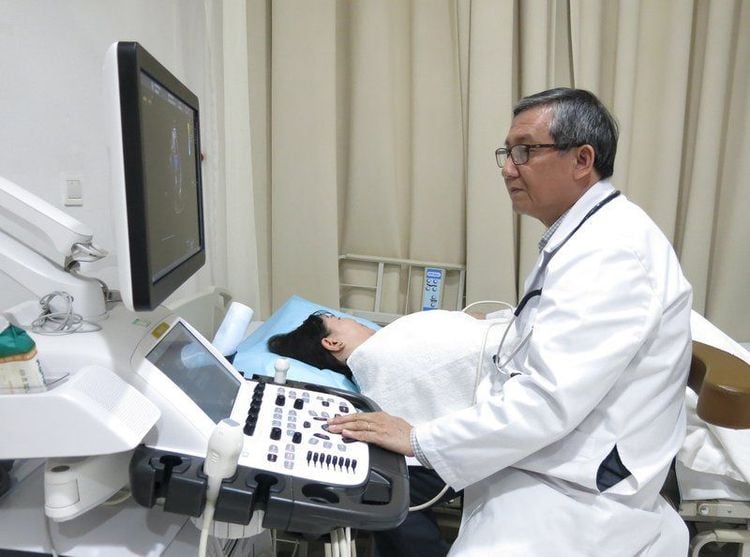

Siêu âm tim tại Bệnh viện Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec
3.3. After the Echocardiogram Usually, the patient can resume normal daily activities immediately after the echocardiogram.
If echocardiogram results are normal, no further tests are needed. If the results are worrisome, you may be referred to a cardiologist for further testing.
Treatment depends on what the doctor finds on the physical exam, the specific signs and symptoms. The person may need a repeat echocardiogram in a few months or other diagnostic tests such as cardiac computed tomography or coronary angiography.
To protect heart health in general and detect early signs of myocardial infarction and stroke, customers can sign up for Cardiovascular Screening Package - Basic Cardiovascular Examination of Vinmec International General Hospital . The examination package helps to detect cardiovascular problems at the earliest through tests and modern imaging methods. The package is for all ages, genders and is especially essential for people with risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Master. Hoang Thi Hoa has more than 10 years of experience in the field of Cardiology, especially in the field of cardiovascular emergency and echocardiography. Doctor Hoa used to be the Deputy Head of Cardiology Department of Quang Ninh General Hospital before working at Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.