This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Minh Son - Interventional Cardiologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Nha Trang International General HospitalToday, transesophageal echocardiography is used quite commonly, playing an important role in the diagnostic and treatment process of cardiovascular diseases. Depending on the specific condition of each patient, the doctor will determine whether the patient needs to perform a transesophageal echocardiogram.
1. What is a transesophageal echocardiogram?
Transesophageal echocardiography is a method of using ultrasound waves to record images of the heart's structure and activities. Unlike conventional transthoracic echocardiography, transesophageal echocardiography uses a very small transducer attached to a catheter, the doctor inserts the catheter attached to this probe into the lumen of the esophagus and stomach.
When the ultrasound waves reach the heart chambers, it will reflect specific images of each part of the heart such as: heart valves, heart muscle, pericardium, images of blood vessels leading into and out of the heart. All these images will be transferred to a display screen. Through this screen, the doctor will observe the structure and activity of the heart, diagnose whether you have cardiovascular diseases or not.
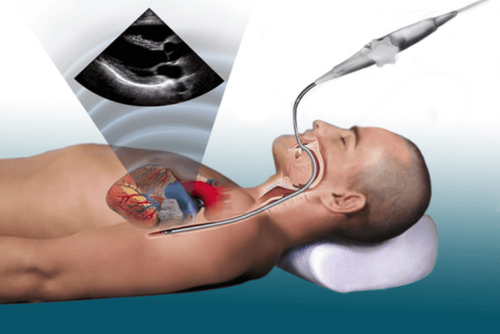
Siêu âm tim qua thực quản là phương pháp chẩn đoán rõ ràng, an toàn cho người bệnh
Transesophageal echocardiography is a fast, accurate and extremely detailed ultrasound method. Transesophageal echocardiography has many advantages such as:
Good image quality because the ultrasound beam is not obstructed by other parts (lungs, fat, chest wall) like transthoracic ultrasound. Ultrasonic transducer has high frequency, high resolution image. The esophagus is very close to the heart, so the probe to the esophagus has reached very close to the heart. Through which, doctors can diagnose diseases such as heart valves, myocardium, aortic diseases, congenital heart disease, pericardium heart, blood vessels near the heart...
However, this method also has certain limitations such as high cost, modern ultrasound machine requirement, sonographer must be trained according to own program. of transesophageal echocardiography, the preparation time is long and may cause some complications (very rare).
2. When is transesophageal echocardiography indicated?
As mentioned in section 1, transesophageal echocardiography results in clearer and more detailed images than transthoracic echocardiography. Through transesophageal echocardiography, the doctor can see very small details of the heart such as heart valves, atria, membranes. From there, it is possible to determine the heart structure, whether the heart function is stable, diagnose the disease and give specific treatment directions. Doctors will prescribe transesophageal echocardiography when transthoracic echocardiography does not meet the desired requirements. Commonly indicated cases of transesophageal echocardiography include:
People with thick chest wall: Due to obesity or geographical location People are using wound dressings, specialized bandages to treat People who have just undergone surgery heart surgery or heart-related surgery
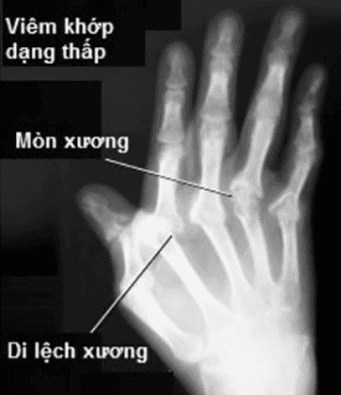
Bệnh nhân mắc viêm khớp dạng thấp chống chỉ định thực hiện thủ thuật này
Transesophageal echocardiography is contraindicated for the following subjects:
People with diseases of the esophagus: tumors, esophageal varices, esophageal dilation, difficulty swallowing... People with severe diseases in cervical vertebra: misalignment, rheumatoid arthritis, hunchback... Patients after mediastinal irradiation... People with unstable hemodynamics.
3. Transesophageal echocardiography
3.1. Specialized staff
Transesophageal echocardiography is a complex exploratory technique, so it requires 1 team to perform:
1 doctor directly ultrasound 1 nurse 1 anesthesiologist (if the patient needs anesthesia) Both Both doctors and nurses must have a separate training in transesophageal echocardiography.
3.2. Transesophageal echocardiography
To conduct transesophageal echocardiography, medical equipment is required:
Color ultrasound machine, with Cardiology program and transesophageal ultrasound software program and a video recorder. Transesophageal echocardiogram transducer Blood pressure monitor Blood oxygen saturation monitor Throat anesthetic, sedative Oxygen source and breathing mask

Hình ảnh đầu dò siêu âm tim qua thực quản
3. Patient prepares
Patients need to fast for at least 4 hours before conducting transesophageal echocardiography. Patients are examined to determine the condition of the esophagus, diseases of the esophagus, teeth...
4. Conduct transesophageal echocardiography
Transesophageal echocardiography takes about 30 - 60 minutes. The patient is lying on a special table and anesthetic is sprayed into the throat to numb, reduce discomfort during the ultrasound The nurse puts an intravenous line for the patient Some patients will be sedated to stay calm Small electrodes will be placed on the patient's chest, followed by wire electrodes that will be attached to an electrocardiogram (ECG) recorder to monitor the patient's electrocardiogram

Bệnh nhân có thể được tiêm thuốc an thần để tránh bị kích động
The doctor will put a catheter with an ultrasound probe (soft, flexible) through the mouth, into the patient's throat to the esophagus The ultrasound probe will send ultrasound waves to the heart and record the echoes back. The echoes will display images of the heart structure and parts of the heart on a pre-connected video screen The doctor will record these ultrasound images. After obtaining all the necessary images, the catheter will be removed and the electrode removed. The patient will be monitored until he or she regains consciousness. At this point, the patient can stand up and finish the ultrasound.
4. Notes after transesophageal echocardiography?
Many patients often feel anxious when doctors order transesophageal echocardiography. This method is more complicated than normal ultrasound and there will be some discomfort when the doctor inserts the catheter into the esophagus. However, a transesophageal echocardiogram will not affect the patient's larynx or pharynx.
After transesophageal echocardiography, the patient should note:
Immediately after the ultrasound, the throat may be numb. Don't worry too much because this feeling will go away quickly (about 1-2 hours after the ultrasound). Do not eat or drink anything until the numbness disappears, otherwise it is very easy to choke. The patient may feel difficulty swallowing after the ultrasound for a few hours. The patient may have a mild sore throat for 1-2 days after the ultrasound. Do not drink alcohol, beer, stimulants for 1-2 days after the ultrasound
Siêu âm tim qua thực quản gây đau họng cho người bệnh trong 1 - 2 ngày sau siêu âm
To protect cardiovascular health in general and detect early signs of myocardial infarction and stroke, customers can sign up for Cardiovascular Screening Package - Basic Cardiovascular Examination of Vinmec International General Hospital . The examination package helps to detect cardiovascular problems at the earliest through tests and modern imaging methods. The package is for all ages, genders and is especially essential for people with risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.