This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Master, Doctor Mai Vien Phuong - Department of Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
If you were recently diagnosed with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), chances are you have been told that you need to improve your eating habits. A healthy diet won't cure COPD, but it can help your body fight infections, including chest infections that can lead to hospitalization. Eating healthy can also make you feel better.
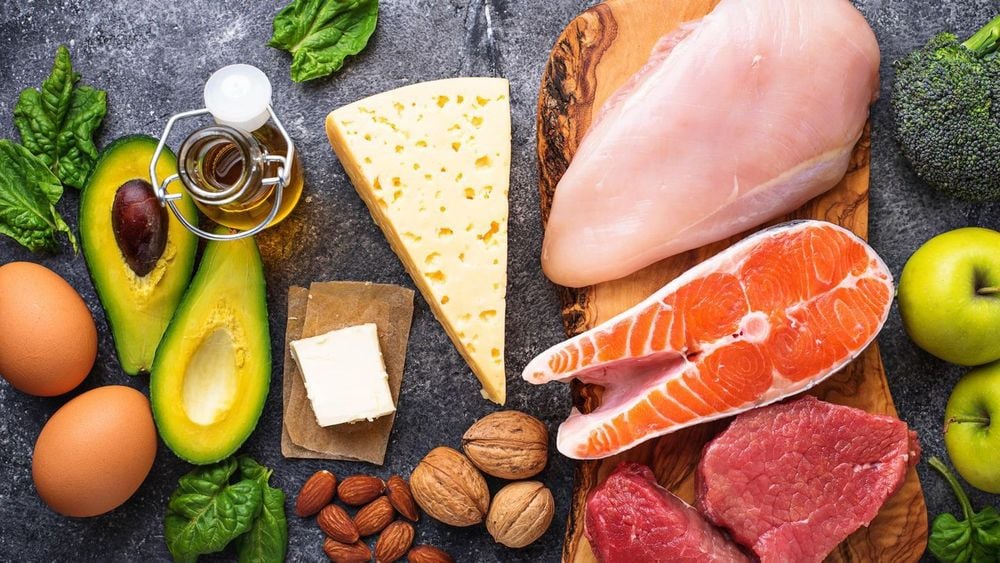
1.High-fat, lower-carb diets may be best. Low-carbohydrate diets lead to lower carbon dioxide production. This can help people with COPD take better control of their health.
According to a study in the journal Lung in 2015, healthy individuals following a ketogenic diet had lower carbon dioxide output and end-tidal partial pressure (PETCO2) than those following the Mediterranean diet. Sea .
Additionally, research from 2003 showed improvement in people with COPD who took a low-fat, low-carb supplement instead of eating a high-carb diet.
Even with reduced carbohydrate intake, a healthy diet includes a variety of foods. Try to include them in your daily diet.
Protein foods Eat high-quality, high-protein foods, such as grass-fed meats, poultry and eggs, and fish - especially oily fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines.
Complex carbohydrates If you include carbohydrates in your diet, choose complex carbohydrates. These foods are high in fiber, which improves digestive system function and blood sugar management.
Foods to include in your diet include:
Peas Bran Potatoes Lentils Quinoa Beans Oats Barley Fresh produce Fresh fruits and vegetables are packed with essential vitamins, minerals and fiber . These nutrients will help keep your body healthy. Non-starchy vegetables (except peas, potatoes, and corn) are low in carbohydrates, so they can be included in all diets.
Some fruits and vegetables are more suitable than others - see the list of foods to avoid in the next section to learn more.
Potassium-rich foods Potassium is important for lung function, so a potassium deficiency can cause breathing problems. Try to eat foods that are high in potassium, such as:
Avocados Dark green Tomato Asparagus Radish Potatoes Bananas Oranges Potassium-rich foods can be especially helpful if a dietitian or Your doctor prescribes you a diuretic.
Healthy fats When choosing a high-fat diet, instead of choosing fried foods, choose snacks and meals that contain fat like avocados, nuts, seeds, coconut and coconut oils, olives and olive oil olives, fatty fish and cheese. These foods will provide more overall nutrition, especially in the long run.

2. Foods to Avoid Certain foods can cause problems like bloating and gas or may have little or no nutritional value. Foods to avoid or minimize include:
Salt
Too much sodium or salt in your diet causes water retention, which can affect your ability to breathe. Take the salt shaker off the table and do not add salt to your dishes. Instead, use unsalted herbs and spices to flavor foods.
Check with your dietitian or healthcare provider about low sodium salt substitutes. They may contain ingredients that can negatively affect your health.
Despite what many people believe, most of the sodium consumed does not come from the salt shaker but from what is already in the food.
Be sure to check the labels of the foods you buy. Your snacks should contain no more than 300 milligrams (mg) of sodium per serving. A whole meal should have no more than 600 mg.
Certain fruits
Apples, stone fruits like apricots and peaches, and watermelon can cause bloating and gas in some people due to their fermentable carbohydrates. This can lead to breathing problems in people with COPD.
Instead, you can focus on low-fermentation or low-FODMAP fruits like berries, pineapple, and grapes. However, if these foods are not an issue for you and your carbohydrate goals allow for fruit, you can include them in your diet.
Certain vegetables and legumes
There is a long list of vegetables and legumes known to cause bloating and gas. What matters is how your body works.
You may want to track your intake of the foods below. However, you can continue to enjoy them if they don't cause you problems:
Cabbage Brussels Cabbage Cauliflower Corn Leeks Some lentils Onions Peas Dairy products
Some people found that dairy products, such as milk and cheese, make phlegm thicker. However, if dairy products don't seem to make your phlegm worse, you can keep eating them.
Chocolate
Chocolate contains caffeine, which may affect your treatment Check with your doctor to find out if you should avoid or limit your consumption.
Fried foods
Fried, fried, or greasy foods can cause bloating and indigestion. Spicy foods can also cause discomfort and affect your breathing. Avoid these foods when possible.

3. Don't forget to see what you drink?
People with COPD should try to drink plenty of fluids throughout the day. It is recommended to have about 6 to 8 glasses of non-caffeinated beverages per day. Staying hydrated will help thin your mucus and make it easier to cough up.Limit or avoid caffeine altogether, as it can affect your medications. Caffeinated beverages include coffee, tea, soda, and energy drinks, such as Red Bull.
Ask your doctor about alcohol. You may be advised to avoid or limit alcoholic beverages, as they can interact with medications. Alcohol can also slow your breathing and make it harder for you to cough up phlegm.
Likewise, talk to your doctor if you have been diagnosed with heart problems as well as COPD. Sometimes people with heart problems need to limit their water intake.
4. Track your weight - in both directions
People with chronic bronchitis tend to be obese, while people with emphysema tend to be underweight. This makes diet and nutritional assessment an important part of COPD treatment.If you are overweight
When you are overweight, your heart and lungs have to work harder, making breathing more difficult. Excess body weight can also increase oxygen requirements. Your doctor or dietitian can advise you on how to achieve a healthier body weight by following a customized eating plan and an achievable exercise program.
If you are underweight
Some symptoms of COPD, such as loss of appetite, depression or feeling unwell in general, can cause you to be underweight. If you're underweight, you may feel weak and tired or be more susceptible to infections.
COPD requires you to use more energy when breathing. A person with COPD can burn 10 times more calories while breathing than someone without COPD. If you're underweight, you need to include healthy, high-calorie snacks in your diet. Items to add to your grocery list include:
Oatmeal custard, quinoa and beans Cheese Avocado Nuts and nut butter Rolled Oat oil

5. Prepare for a meal
COPD can be a difficult condition to live with, so it's important to make food preparation a simple and stress-free process. Make mealtimes easier, encourage your appetite if you're underweight, and follow a healthy eating program by following these general principles:Eat small meals
Try to eat five to six small meals a day instead of three large ones. Eating smaller meals can help you avoid getting too full and give your lungs enough room to expand, making breathing easier.
Eat meals early
Try to eat meals early in the day. This will boost your energy levels for the whole day.
Choose foods that are quick and easy
Choose foods that are quick and easy to prepare. This will help you avoid wasting energy. Sit down when preparing meals so you don't get too tired to eat, and ask family and friends to help with meal prep if needed.
You may also be eligible for home meal delivery.
Be comfortable
Sit comfortably in a high-backed chair when eating to avoid putting too much pressure on your lungs.
Make enough for leftovers
When cooking a meal, portion a larger portion so you can refrigerate or freeze later and have healthy meals when you feel too tired to cook .
Conclusion
It is important to be mindful of your overall health when you have COPD, and nutrition is an important part of that. Planning healthy meals and snacks while emphasizing higher fat intake can help you manage symptoms and minimize complications.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
ReferencesAlessandro R, et al. (2015). Effects of twenty days of the ketogenic diet on metabolic and respiratory parameters in healthy subjects. researchgate.net/publication/282248189_Effects_of_Twenty_Days_of_the_Ketogenic_Diet_on_Metabolic_and_Respiratory_Parameters_in_Healthy_Subjects Nutrition. (2018). lung.org/lung-health-and-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/copd/living-with-copd/nutrition.html Nutritional guidelines for people with COPD. (2011). my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/9451-nutritional-guidelines-for-people-with-copd The importance of good nutrition for chronic lung condition patients. (n.d.). emphysemafoundation.org/index.php/healthy-habits/nutrition/91-nutrition-articles/198-the-importance-of-good-nutrition-for-chronic-lung-condition-patients Ferreira IM, et al. (2001). Nutritional intervention in COPD. journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(15)38208-8/fulltext