This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Dr. Ngo Dac Thanh Huy - Cardiologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.The circulatory system has an important function, maintaining the life of the body. To ensure that circulatory system function is maintained, three important factors are required: circulatory volume, blood vessels, and heart. Only one change in any of these factors can affect circulatory system function.
1. What is the function of the circulatory system?
The circulatory system contains important components of the body, whose main functions include:Transporting nutrients and oxygen to cells. Transport substances that are products of excretion out of the cell. Role in the immune system to help the body fight infections. Transport hormones to target organs. Regulating body temperature due to the hot blood source heating the organs and doing the job of removing heat from the body, stabilizing the pH level and maintaining homeostasis. The circulatory system consists of the large circulatory system and the small circulatory system:
Pulmonary circulation: Blood, after exchanging oxygen in the cells, has been deoxygenated into the right atrium, from where the blood is transferred to the ventricle right and is pumped into the pulmonary artery to ascend to the lungs. In the lungs, the blood releases CO2 and absorbs oxygen and returns it to the heart through the pulmonary veins. Systemic Circulation: Blood from the pulmonary circulation through the pulmonary veins is oxygen-rich blood into the left atrium, and then from the left atrium to the left ventricle. Blood is pumped by the heart from the left ventricle into the aorta for distribution throughout the body. After metabolism with cells in tissues in the body, blood returns to the right atrium through the superior and inferior vena cava ending the great circulation. Circulatory system function is extremely important for the body, maintaining life for the body. To ensure these functions, it is necessary to have important factors to maintain and ensure the best operation of the circulatory system.
2. Factors that ensure circulatory system function
To ensure the operation and ensure the functions of the circulatory system, it is necessary to have the completeness of 3 factors including heart, vascular system and circulatory volume.2.1 Circulatory volume
Circulatory volume also known as blood, used to transport oxygen and nutrients, O2 gas to cells, carry waste from cells back and out by excretory organs such as respiratory tract, through the kidney.
When there is a cause leading to hypovolemia, it will cause hypovolemic shock. Hypocirculatory shock is a life-threatening condition caused by circulatory failure, which results in an inadequate oxygen supply to meet the metabolic needs of cells causing cellular and tissue hypoxia.
Circulatory volume may decrease with dehydration, blood loss, diarrhea, fever...
If the loss of body fluids is rapid or prolonged, it will lead to shock. orally or by infusion to ensure circulatory function.
2.2 Heart
The heart is located in the chest, has a left axis deviation, is a hollow muscle, weighs about 300 grams, is divided into 4 chambers including 2 atria and 2 ventricles:
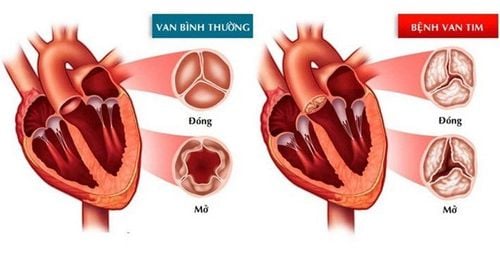
Right atrium and left atrium, thin wall, receiving blood veins, to the ventricles. The right and left ventricles, thick-walled, pump blood into the arteries at high pressure. The wall of the left ventricle is twice as thick as the wall of the right ventricle, due to the great pressure that brings blood into the aorta. The two atria are separated by the interventricular septum and the two ventricles are separated by the interventricular septum. Between the ventricles and the atria is blocked by the atrioventricular valves. The left side has a mitral valve separating the left atrium and the left ventricle, and the right side has a tricuspid valve separating the right ventricle from the right atrium. It helps blood flow in one direction from the atria to the ventricles. The main function of the heart is that when the heart contracts, it creates pressure to push blood into the arteries, from there to nourish the body. The heart is operated by an automatic mechanism, regulated by the autonomic nervous system and nourished by the coronary artery system.
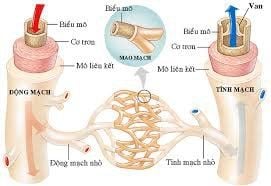
2.3 Circuit system
The vascular system is responsible for transporting blood to the organs and from the organs to the heart. The vascular system includes arteries, arterioles, capillaries, veins, and venules.
Arteries have the function of carrying blood from the heart to the organs, the function of transporting blood under great pressure, so the artery wall consists of 3 layers of very strong muscles and has the ability to stretch to create contraction pressure. squeeze blood circulation. As the arteries move away from the heart, they divide into small branches that carry nutrients and oxygen to nourish the organ tissues. Arterial blood pressure is the pressure of blood in the arteries, the blood flowing in the arteries is the result of two opposing forces, the force of the heart pushing the blood and the resistance of the artery walls. Arterial blood pressure is maintained stable, blood from the arteries can come to nourish the organs, on the contrary, if low blood pressure leads to blood not being able to nourish the organs, it can lead to death. If the arterial blood pressure is too high, causing great pressure on the vessel wall, there is a risk of vessel wall rupture. vessels, act as valves to regulate blood flow to the capillaries according to the blood needs of that organ. Vessel walls can close off blood flow or widen to allow more blood to pass through by the strength of the arteriole walls. Capillaries: Capillaries are thin-walled and permeable to small molecules. At the capillaries nutrients, when, hormones... are exchanged with tissues. Veins: From the capillaries, blood flows into thin-walled blood vessels called venules. Veins: Venules gather into large veins. The wall of a vein has three layers, like an artery, but is thinner and more easily dilated. The layers of the venous wall include: The innermost layer is the endothelial cell layer with each protrusion forming semicircular folds opposite each other to form the venous valve, the purpose of which is to direct the blood to flow one way to the heart. . Venous valves are present in the veins of the extremities and are absent in the small veins, veins from the brain, or veins from the viscera. The middle layer is composed of connective and muscle fibers. The thin outer layer consists of elastic connective fibers. Has good stretchability. Thus, to ensure circulatory function, three important factors are needed: heart, vascular system and circulatory volume. An abnormal change in one of the three factors causes a decline in the function of the circulatory system, which can be life-threatening.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, a system of modern equipment and technology. The hospital provides comprehensive, professional medical examination, consultation and treatment services, with a civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References source: Vietnam Heart Association