G6PD deficiency is a fairly common genetic yeast disease in humans. G6PD deficiency can lead to hemolysis, jaundice, yellow eyes and kidney failure. Newborn screening plays an extremely important role in early detection of disease for effective prevention and treatment.
1. What is G6PD deficiency?
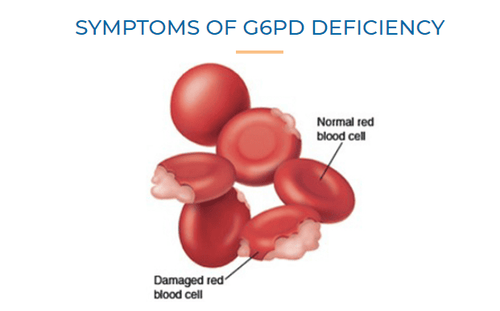
G6PD is an acronym for Glucose-6-phosphate Dehydrogenase. The enzyme G6PD is produced in all normal human cells. It serves as an important catalyst for metabolic reactions in cells, especially red blood cells.
G6PD deficiency leads to a deficiency of glutathione - an antioxidant that protects red blood cell membranes against oxidizing agents in certain drugs, foods or infectious disease agents. If glutathione levels are depleted, enzymes and proteins are damaged by oxidation, leading to red blood cell dysfunction and rupture (hemolysis). Prolonged hemolysis can lead to anemia. In addition, broken red blood cells also lead to hemoglobin breakdown in an excessive amount, which accumulates in the kidneys and leads to kidney failure.
On the other hand, when red blood cells break down, they release free bilirubin into the blood. Newborns lacking G6PD enzyme will cause liver cell activity to decline, unable to metabolize bilirubin to excrete bilirubin, causing symptoms of jaundice and yellow eyes. If the free bilirubin accumulates too much in the blood, it will seep into the brain, causing irreversible neurological complications and seriously affecting the child's brain development later on.
2. Causes of G6PD . deficiency disease
G6PD deficiency disease is an inherited recessive disease on the X chromosome. Children get the disease by receiving an abnormal recessive gene on the sex chromosome from their parents. Because men have only one X chromosome, they are more susceptible to G6PD deficiency than women (who have 2 X chromosomes).
3. Symptoms of G6PD . deficiency

Most cases of G6PD deficiency are asymptomatic. Some patients had neonatal jaundice, a history of infection, or drug-induced hemolysis. There are cases with many gallstones, enlarged spleen.
When hemolysis occurs, the amount of oxygen is not enough to supply the body's activities, the patient shows fatigue, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeat and dark yellow urine.
If a patient with G6PD deficiency eats lentils or takes drugs, foods with antioxidants, suddenly symptoms such as headache, fever, abdominal pain, low back pain, heart palpitations, shortness of breath, etc. splenomegaly, jaundice, gray-brown hemoglobin in urine,... These symptoms usually occur in about 1-2 days, the urine fades, the patient is very tired, severe anemia, jaundice, yellow eye. There are cases of complications of acute kidney failure, which is easy to die if blood transfusion is not timely.
On the contrary, if detected and treated correctly, G6PD deficiency symptoms disappear very quickly, usually within a few weeks. In case of mild symptoms, no treatment is necessary, but patients should avoid using lentils and oxidizing drugs and foods. If symptoms worsen, the patient needs to be hospitalized for treatment.
4. Is G6PD deficiency curable?
Currently G6PD deficiency disease cannot be cured. However, the consequences of hemolytic anemia due to G6PD deficiency can be prevented and patients can live as normal healthy individuals. Ways to prevent complications are as follows:
When taking drugs, consult a doctor, avoid using some recommended drugs such as: pain relievers, antipyretics containing aspirin or phenacetin; taking antibiotics of the sulfonamide and sullfone groups; antimalarial drugs such as quinine, chloroquine, primaquine; using vitamin K, methylene blue to treat urinary tract infections,...; Avoid eating lentils and their products; Patients need to avoid conditions that can adversely affect health such as illness caused by bacterial infections, viral infections; When suffering from an infection, the patient needs to see a doctor for timely treatment; If parents are deficient in G6PD enzyme, special care should be taken for the child such as: do not use drugs that can cause hemolysis; do not put mothballs in wardrobes, blankets, bedding to prevent cockroaches (because mothballs contain naphthalene, which is an oxidizing agent); be careful with some herbal medicines, Oriental medicine because they may contain oxidants; Breastfeeding mothers should not use foods or drugs that must be avoided in people with G6PD deficiency because these substances can enter the baby's body through breast milk; Blood transfusion if G6PD-deficient children have severe anemia; dialysis in case of acute renal failure; People with G6PD deficiency should not donate blood to others.
5. Newborn screening detects G6PD deficiency disease
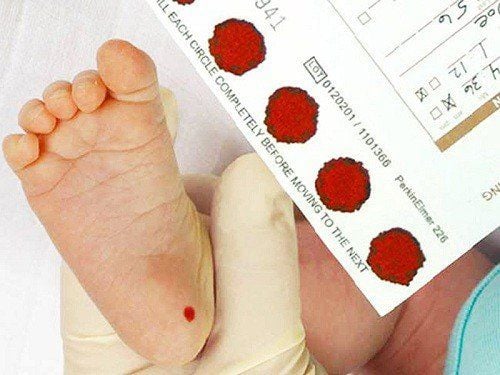
Newborn screening test is a routine screening program for newborn babies to detect endocrine diseases and metabolic disorders early. Early detection, diagnosis and treatment of health problems, especially G6PD deficiency, can help children grow up healthy and normal. Conversely, if not detected and treated early, the child's health can be seriously and irreversibly affected.
After birth, about 36 - 48 hours after birth, the baby will have blood from the heel or hand, soaked in blood sample paper to send to the testing center for screening test for G6PD enzyme deficiency. Results will be announced within 24 hours of testing. Children with G6PD deficiency will be consulted and issued a G6PD deficiency card.
*Note: in case the first blood sample is not enough or gives unclear results, the medical staff will take a second blood sample of the child and explain it clearly to the parents.
Heel blood test is one of the newborn screening methods under the Maternity Care Program implemented at Vinmec International General Hospital. In addition to taking heel blood, Vinmec also performs a full range of other antenatal, intrapartum and postpartum screening tests according to international standards, helping to best protect the health of mother and baby.
As a key area of Vinmec Health system, Pediatrics Department always brings satisfaction to customers and is highly appreciated by industry experts with:
Gathering a team of top doctors and nurses in Pediatrics : consists of leading experts with high professional qualifications (professors, associate professors, doctorates, masters), experienced, worked at major hospitals such as Bach Mai, 108.. Doctors All doctors are well-trained, professional, conscientious, knowledgeable about young psychology. In addition to domestic pediatric specialists, the Department of Pediatrics also has the participation of foreign experts (Japan, Singapore, Australia, USA) who are always pioneers in applying the latest and most effective treatment regimens. . Comprehensive services: In the field of Pediatrics, Vinmec provides a series of continuous medical examination and treatment services from Newborn to Pediatric and Vaccine,... according to international standards to help parents take care of their baby's health from birth to childhood. from birth to adulthood Specialized techniques: Vinmec has successfully deployed many specialized techniques to make the treatment of difficult diseases in Pediatrics more effective: neurosurgery - skull surgery, stem cell transplantation. blood in cancer treatment. Professional care: In addition to understanding children's psychology, Vinmec also pays special attention to the children's play space, helping them to have fun and get used to the hospital's environment, cooperate in treatment, improve the efficiency of medical treatment. Doctor Dang Thi Ngoan used to be a lecturer in the Department of Pediatrics - Hai Phong University of Medicine and Pharmacy. Having been granted certificates in Pediatrics at home and abroad such as: Westmead Hospital, Australia; Hai Phong Medical University. Currently, Doctor Ngoan is a Pediatrician - Neonatologist at the Neonatal Department of Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital
Để đặt lịch khám tại viện, Quý khách vui lòng bấm số HOTLINE hoặc đặt lịch trực tiếp TẠI ĐÂY. Tải và đặt lịch khám tự động trên ứng dụng MyVinmec để quản lý, theo dõi lịch và đặt hẹn mọi lúc mọi nơi ngay trên ứng dụng.