This is an automatically translated article.
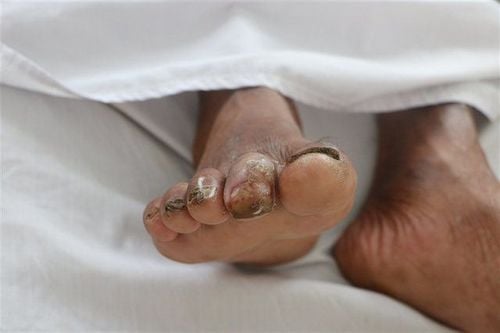
Melioidosis, also known as Whitmore's disease, is an infectious disease caused by the Gram-negative bacillus Burkholderia pseudomallei. Bacilli are found in soil and water environments. This is an important health issue in endemic areas, particularly Vietnam and northern Australia. The disease exists in acute and chronic forms with symptoms of back pain, pain in bones and joints, severe cough, skin infections, lymph nodes in the lungs and pneumonia.1. How dangerous is Whitmore's disease?
A 2016 statistic shows: the incidence is 165,000 cases per year (95% confidence interval), of which 138,000 cases occur in Southeast Asia and the Pacific. About half of the patients who get the disease will die. In particular, Northeast Thailand is home to the highest incidence of melioidosis in the world (average rate is 12.7 cases/100,000 people/year).Melioidosis has also been reported in animals, including cats, goats, sheep and horses. Cattle, water buffalo and crocodiles are thought to be resistant to Melioidosis despite their constant and direct exposure to mud. B. pseudomallei is commonly found in soil and water, so patients with melioidosis have a history of soil or water exposure. People with Whitmore's disease are also infected by inhaling dust contaminated with bacteria or coming into contact with contaminated soil through skin abrasions. Infection usually occurs during the rainy season.
Whitmore's disease often presents with pulmonary involvement. If whitmore's disease is not treated promptly, it can lead to death. With antibiotic treatment, severe conditions have a 50% chance of recovery, but overall mortality remains high, around 40%.
2. Whitmore disease in Vietnam
Whitmore's disease was discovered in Vietnam in the 50s of the last century, the disease appeared sporadically in some southern provinces and was classified as a "forgotten" dangerous infectious disease.However, Whitmore's disease is at risk of re-emergence in Vietnam after many years of absence. People with diabetes, lung disease and chronic kidney disease are at risk for Whitmore's disease with diverse clinical manifestations: high fever, muscle pain, skin infections, muscle abscess, liver and spleen abscess , pneumonia...
About 5 - 10 years ago, there were only 20 cases of Whitmore, from the beginning of 2019 until now, 20 cases have been recorded, mainly patients from the Northern and Northern provinces. Central. The clinical picture of Whitmore's disease is complex, often misdiagnosed with other diseases such as pneumonia, tuberculosis, muscle abscess, sepsis caused by other bacteria such as staphylococcus and streptococcus. ..
The disease usually occurs in the rainy season, mainly from July to November every year. Persons with characteristics of working that have to be exposed to a lot of soil and water environments need to have labor protection equipment. If there are scratches on the skin, they need to be treated early and thoroughly.
3. Diagnosis of Whitmore's Disease

Chẩn đoán whitmore có thể dựa trên xét nghiệm máu
Blood tests: useful for early detection of acute cases of the disease, however However, a negative result cannot completely rule out the possibility of having Whitmore. Other commonly used tests are: indirect hemagglutination (IHA), complement fixation (CF) and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) tests.
4. Treatment of whitmore disease?
Treatment includes the use of antibiotics, depending on the location and extent of the disease.For mild disease, antibiotics such as imipenem, penicillin, doxycycline, amoxicillin - clavulanic acid, ceftazidime, ticarcillin - clavulanic acid, ceftriaxone and aztreonam are recommended. For more severe patients, a combination of two of the above antibiotics is needed, for up to 12 months. In the attack phase, doctors treat with a specific regimen of antibiotics. After the general condition begins to stabilize, the patient still needs to continue to receive prolonged antibiotic treatment, combined with specialized ENT therapies such as: wound washing, control and treatment of the lesions in the nose - throat.
If Whitmore's sign is present in the lung and the culture is still positive after 5 months, the patient should be considered for lobectomy to remove the lung abscess.
5. Whitmore's disease has a high risk of treatment failure

Nếu không được điều trị đúng liều, đúng phác đồ, đúng thuốc và theo dõi sát sao, bệnh Whitmore rất dễ tái phát
The process of monitoring and treating the disease is long and expensive, so many patients have given up. This is one of the causes leading to treatment failure and high mortality rate of more than 40%.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.