This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Dr., Dr. Ton That Tri Dung - Head of Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International HospitalCerebral edema is a condition that occurs when fluid accumulates around the brain tissue, causing increased intracranial pressure. Cerebral edema is also known under the name of the complication that it causes, which is increased intracranial pressure. Cerebral edema causes serious complications and causes symptoms.
1. What is cerebral edema, how dangerous is it?
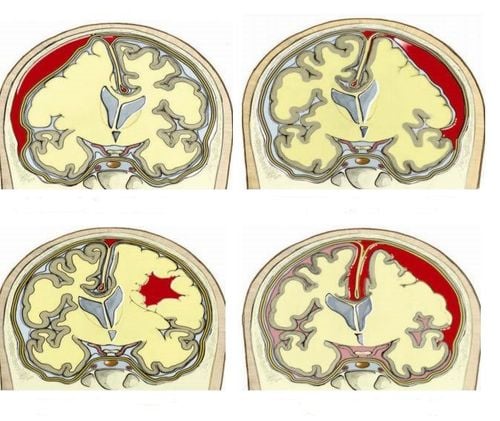
Cerebral edema can occur in specific locations in the brain or in the whole brain, depending on the cause of the brain edema. Cerebral edema will cause pressure inside the skull, restricting blood supply to the brain, increased pressure can compress blood vessels feeding the brain, preventing blood from reaching the brain, limiting oxygen supply to brain cells. work. The lack of oxygen causes serious damage to brain cells, even causing brain death.
In addition, cerebral edema also disrupts the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, making the edema worse.
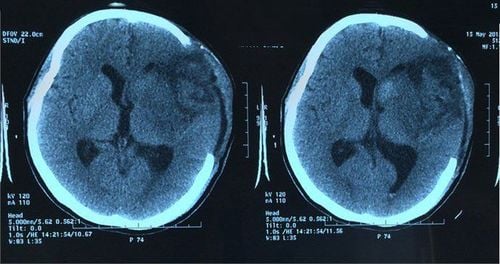
Hình ảnh phù não trên phim X-quang
2. Symptoms of brain edema
Symptoms of cerebral edema can be easily confused with symptoms of many other neurological diseases, making detection and diagnosis somewhat difficult and making patients sometimes subjective to these symptoms. Usually cerebral edema appears with sudden symptoms such as:
Headache, neck Nausea or vomiting Dizziness Loss of memory, consciousness Difficulty speaking, difficulty moving Convulsions Loss of vision

Bệnh phù não gây chóng mặt
3. Causes of cerebral edema disease
Increased intracranial pressure associated with cerebral edema can be caused by one of the following, including:
Traumatic brain : An acute injury such as from a fall or a vehicle accident. Ischemic stroke: Occurs when a blood clot in a blood vessel in the brain restricts oxygen flow to the brain. Lack of oxygen can damage brain cells and cause edema and increased pressure. Brain Tumor: A brain tumor can press on other areas of the brain. Some brain tumors are located near the cerebrospinal fluid drainage holes, when enlarged, they will cover these holes causing increased intracranial pressure leading to brain edema Infection: Bacterial or viral infections can cause brain edema . Encephalitis, for example, is an infection that causes inflammation in the brain and results in elevated intracranial pressure. Brain Hemorrhage: A brain hemorrhage occurs when a blood vessel in the brain bursts and bleeds, causing inflammation and increased intracranial pressure. Altitude: Cerebral edema can also occur at altitudes around 4,000 meters. Other causes: Abuse of stimulants, CO poisoning, poisoning from the bites of some poisonous animals, reptiles or aquatic animals,...
Chấn thương sọ não gây phù não
4. How to treat brain edema?
To effectively treat brain edema, the patient will be prescribed the following treatment methods according to the doctor, depending on the condition and cause of the brain edema. Specifically, these methods include:
Oxygen therapy is a way to provide oxygen to the patient through a ventilator or other means to ensure that oxygen-rich blood is brought to the brain Using drugs to reduce swelling or weight cerebral thrombosis Surgery craniotomy in severe cases to reduce intracranial pressure, ventricular septal defect to drain fluid and reduce intracranial pressure effectively Hypothermia to treat swelling in the brain Osmotic therapy using drugs to pull fluid out of the brain, help increase blood flow to the brain, reduce intracranial pressure. Patients with cerebral edema can be accurately diagnosed as soon as the above symptoms are detected by examining and combining other modern subclinical diagnostic methods such as: physical examination of the head and neck, neurology, radiography. CT or MRI of the brain, blood tests.
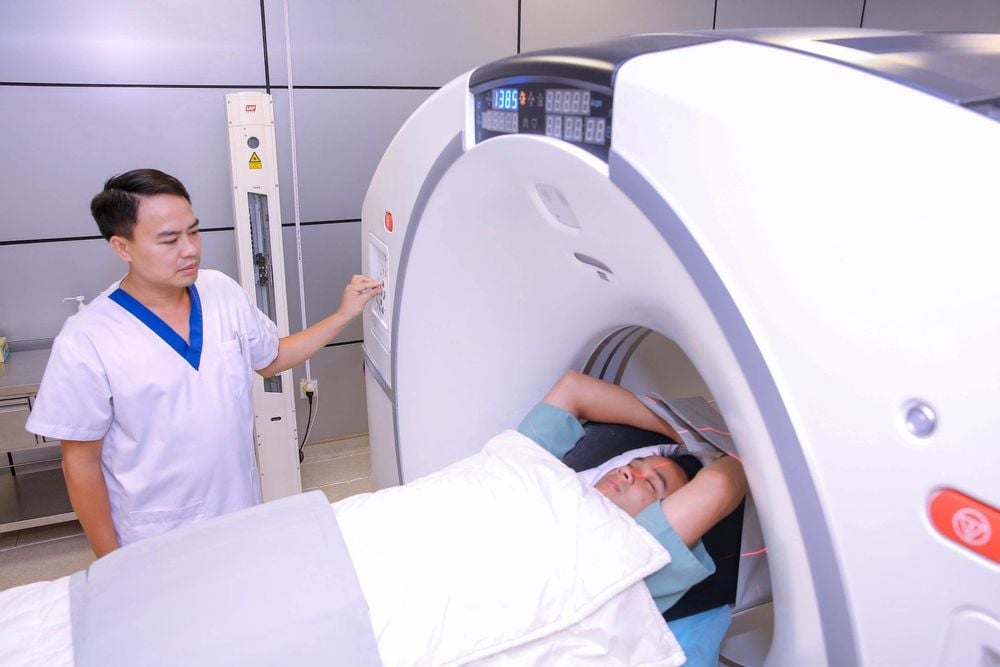
Chụp CT hoặc MRI sọ não giúp chẩn đoán chính xác
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in neurological examination and treatment, patients can completely peace of mind to examine and treat neurological diseases in general and cerebral edema in particular at the Hospital.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.