This is an automatically translated article.
Articles written by MSc, BS. Doan Trung Hiep, Radiation Therapy Center - Vinmec Times City International Hospital
Biomarkers in oncology are used to diagnose and monitor tumor response to treatment, contributing to monitoring and detecting recurrence after treatment. However, biomarkers have a low sensitivity when used alone, so it is often used in combination with other screening therapies to ensure accuracy in cancer diagnosis.
Tumor markers (or tumor markers for short) are protein molecules in the blood and body fluids that provide information to us about the presence of tumor cells in the body. Tumor markers are mainly used in diagnosis, monitoring tumor response to treatment and contributing to monitoring and detecting recurrence after treatment. In people without cancer, tumor markers may play a role in detecting cancer early. An ideal tumor marker should have the following characteristics:
High positive and negative predictive value; The test costs are acceptable, simple, with a clear normal reference value; Accepted by the community; Clinical value has been evaluated in sufficiently reliable studies. Tumor markers are synthesized and excreted into the bloodstream by both malignant and benign cells. Tumor markers can be expressed in blood, urine, body fluids, and on cell surfaces. In this article, we only refer to tumor markers in blood, urine, and body fluids. Tumor markers on the tissue/cell surface should not be used in cancer screening.
1. Using tumor markers in screening/early diagnosis of cancer
Screening is the process of using medical investigations to detect disease at an early stage when the disease has not yet caused clinical symptoms.
Tumor markers in blood and body fluids can be used in cancer screening, with the following advantages:
Easy to implement, no physical harm related to testing for patients/clients. Quick response time (within 1-2 hours). The results are quantitatively reliable. Compared to other cancer screening methods, tumor markers have a much lower cost. However, the cancer marker has the disadvantage that it is low sensitivity if used alone (sensitivity is the ability to detect the disease at an early stage). Therefore, at present, cancer markers should never be used alone for early diagnosis of cancer, they MUST be used in combination with other screening therapies to ensure value in early diagnosis. cancer.
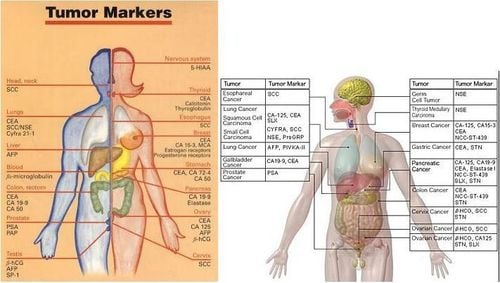
Here, we learn about some common cancer markers used in cancer screening packages.
Trắc nghiệm: Thử hiểu biết của bạn về bệnh ung thư
Ung thư là nguyên nhân gây tử vong hàng thứ 2 trên thế giới. Thử sức cùng bài trắc nghiệm sau đây sẽ giúp bạn có thêm kiến thức về yếu tố nguy cơ cũng như cách phòng ngừa bệnh ung thư.
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
2. CA125 and HE4 in ovarian cancer screening
CA125 alone has a low value in ovarian cancer screening, so Lokich developed a combined formula of 2 tumor markers CA125 and HE4 to assess the risk of ovarian cancer with more confidence (Large scale). ROMA- Risk of Ovarian Malignancy Algorithm score), if the ROMA score is high, it will help doctors to appoint more in-depth exploration such as laparoscopy, sub-frame magnetic resonance imaging... to make the diagnosis.
Normal readings: HE4≤140 pmol/l; CA125 ≤ 46UI/mL.
When you are tested for CA125, HE4, the results are included in the ROMA scoring formula, if a ROMA score <1.14 for menstruating women is low risk, routine screening. ROMA < 2.99 for postmenopausal women is low risk, routine screening. If the ROMA is higher, it will be considered high risk, so it is necessary to move to more intensive therapy evaluation such as pelvic resonance imaging, laparoscopy.
3. Set of 6 tumor markers in lung cancer screening: CEA, CA153, SCC, CYFRA 21-1, NSE, ProGRP
The set of 6 tumor markers used will increase the predictive value of lung cancer in individuals with pulmonary nodules, or heavy smoking.
Normal readings:
CEA, 5 ng/ml; CYFRA 21-1, 3.3 ng/ml; SCC, 2 ng/ml; CA15.3, 35 U/ml; NSE, 25 ng/ml; and ProGRP, 50 pg/ml.
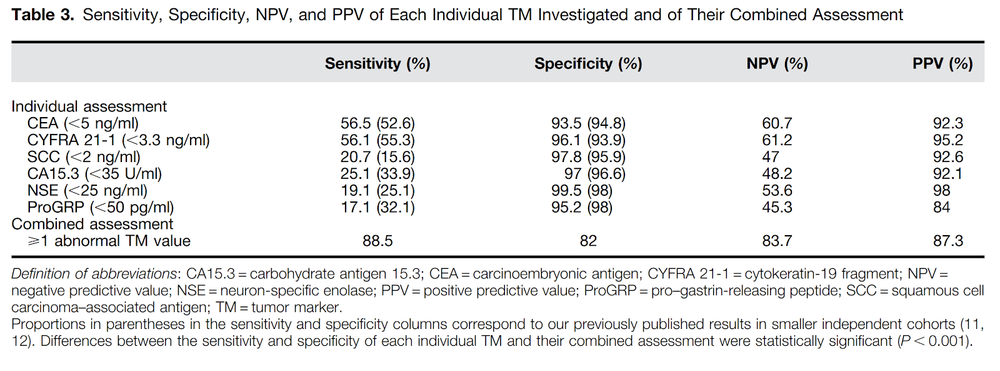
The set of 6 indicators is especially valuable when combined together, to evaluate an incidentally detected pulmonary nodule to predict benign or malignant nature. When used alone, the sensitivity - that is, the ability to detect the disease, each of the 6 cancer markers is only from 17% (ProGRP) to 56% (CEA or CYFRA21-1), however when combined On the other hand, the ability to detect the disease increased to a very high 88.5%. If the test score is mildly abnormal, the test should be repeated after 3-4 weeks to confirm the value of that cancer marker. With these cancer markers, when it increases 2-3 times, all 6 markers are clinically significant.
4. Combo set of 2 tumor markers for primary liver cancer screening: AFP and PIVKA-II
Primary liver cancer is one of the 3 most common cancers in Vietnam, every year tens of thousands of people are infected and die from this disease. Individuals infected with hepatitis virus have a one-third chance of developing cirrhosis within 20 years, of these cirrhosis, about 2-4% develop liver cancer each year. Therefore, the annual rate of liver cancer will increase cumulatively quite large. All current recommendations from Europe and the US agree that people with hepatitis and cirrhosis should be screened every 6 months with liver cancer markers and liver ultrasound.
AFP is a classic marker, widely used in screening for early detection, but the sensitivity-diagnosis ability if used alone is very low, large tumors increase the rate of AFP 40-60%, Small tumor, early stage only 10-20%. Therefore, PIVKA-II was put into use to help increase the sensitivity and predictive value of diagnosis in screening, diagnosis, and post-treatment follow-up. PIVKA-II increased in association with tumor size, degree of vascular invasion, distant metastasis, and recurrence. PIVKA II is very specific for primary liver cancer, it is only increased in cancer, in benign diseases such as cirrhosis, benign liver tumor, this tumor marker does not increase. According to Japanese diagnostic guidelines, liver cancer is confirmed when there is a typical ultrasound image of liver tumor, AFP ≥200 ng/ml, PIVKA-II ≥ 45mAU/ml.
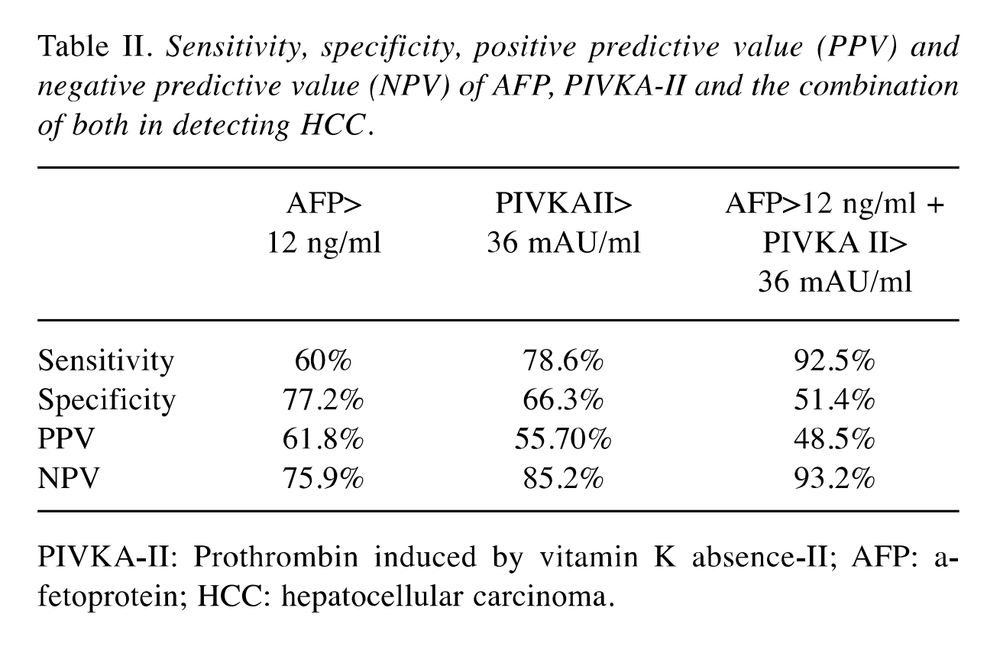
If only AFP is used, the diagnostic ability is only 60%, combined with AFP and PIVKA-II, the rate increases to 92.5%.
5. CA15-3 in breast cancer
The CA15-3 marker is most commonly used in clinical breast cancer. However, the reality is that it has only 10% sensitivity in stage I, 20% stage II, 40% stage III, and 75% stage IV breast cancers. Therefore, it is not enough to use CA15-3 to screen for breast cancer alone, to screen for breast cancer or to use breast self-examination, clinical mammography, mammography, breast ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging. breast. There are 5% of people without cancer also have an increased tumor marker CA15-3, experts note that CA15-3 increases 5-10 times the normal value to have clinical significance.
CA15-3 score has normal value <30-40U/ml. CEA <5 ng/ml. When the tumor index increases by more than 25%, it should be noted, to confirm the value of the second test, repeat after 1 month. CEA in combination with CA15-3 increases the sensitivity insignificantly in breast cancer.
6. Cancer marker CEA
CEA marker used in early diagnosis, differential diagnosis and follow-up after treatment of colorectal cancer with 46.5% sensitivity, using other cancer markers such as CA19-9, CA72-4, CA125, Ferritin also only increases the sensitivity by 50-60%, not much significance. The normal value of CEA is <5 ng/ml.
CEA combined with CA72-4 significantly increased the sensitivity in the diagnosis of colorectal cancer, much higher than the combination of CEA and CA19-9. CEA and CA72-4 showed sensitivity in colorectal cancer diagnosis of 60.6%, the highest compared to other combo combinations such as CEA+CA19-9; CEA+CA125;...
7. Cancer marker CA19-9
CA19-9 is often used in the diagnosis of pancreatic and biliary tract cancers. However, in screening, this indicator has very limited sensitivity. If the patient has clinical symptoms, the diagnostic sensitivity is up to 80%. However, with low specificity, it may be increased in obstructive jaundice. If CA 19-9 increases above 37U/ml, with jaundice with bilirubin increased >51mcmol/l, weight loss, this trio has the ability to diagnose pancreatic cancer correctly to 100%. Therefore, DO NOT use CA 19-9 alone to screen for pancreatic cancer, use tumor markers in the combination of clinical symptoms and imaging to evaluate the diagnosis of pancreatic and biliary tract tumors.
8. PSA Screening for Prostate Cancer
PSA is prostate-specific antigen, used in screening, diagnosis, and evaluation of prostate cancer response to treatment. PSA is a highly sensitive tumor marker used in prostate cancer screening. Although the current normal PSA threshold is ≤4ng/ml, still 20% of men with a PSA of 2.6-4 ng/ml are diagnosed with prostate cancer. In contrast, there are many cases of benign hypertrophy that also have a fairly high PSA, sometimes above 10ng/ml or more. Therefore, at present, in the "Semi-Ham" area, PSA test results of 4.0-10 ng/ml are still controversial because up to 25% of these are diagnosed with prostate cancer. PSA threshold ≥10 ng/ml is the threshold for biopsy indication. To add predictive value, doctors now use many more indicators such as PSA density (taking PSA number/prostate volume), rate of increase of PSA over time, free PSA ratio ( fPSA).
Summary
Early cancer screening is considered a perfect measure in the timely detection and treatment of cancers. Vinmec International General Hospital currently has a high-tech cancer screening and examination package, including genetic testing, imaging, and biomarkers for early tumor detection. A single gene test can assess the risk of 16 common cancers in both men and women (lung cancer, colorectal cancer, breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, cervical cancer) Bowel cancer , stomach cancer , prostate cancer ,....)
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.