This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Specialist Doctor I Vu Thi Hanh - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital
Placental hemangioma is the most common non-trophoblastic vascular tumor of the placenta, with an incidence of about 1%. Accordingly, ultrasound of placental hemangioma helps doctors detect abnormalities in many organs of the fetus for early treatment.
1. What is placental hemangioma?
Chorioangioma is the most common non-trophoblastic vascular tumor of the placenta, with an incidence of about 1%. Although its exact causes are not fully elucidated, they are thought to result from abnormal growth of blood vessels during different stages of differentiation in the stromal fibrous tissue. together.
2. Ultrasound image of placental hemangioma
Prenatal diagnosis of placental hemangioma is based on observation of an echogenic, round, well-margined mass, homogeneous or not, located toward the surface of the placenta. Use of color Doppler ultrasound allows visualization of blood vessels entering the placenta and diffuse angiogenesis around the tumor. In most severe cases, signs of hyper-output heart failure, including enlarged heart, polyhydramnios, increased midcerebroventricular peak velocity, and polyhydramnios, may be associated with the tumor. Tumor size, presence of polyhydramnios, and gestational age at the onset of heart failure have been reported to be major determinants of perinatal outcomes in pregnancies complicated by placental hemangiomas.
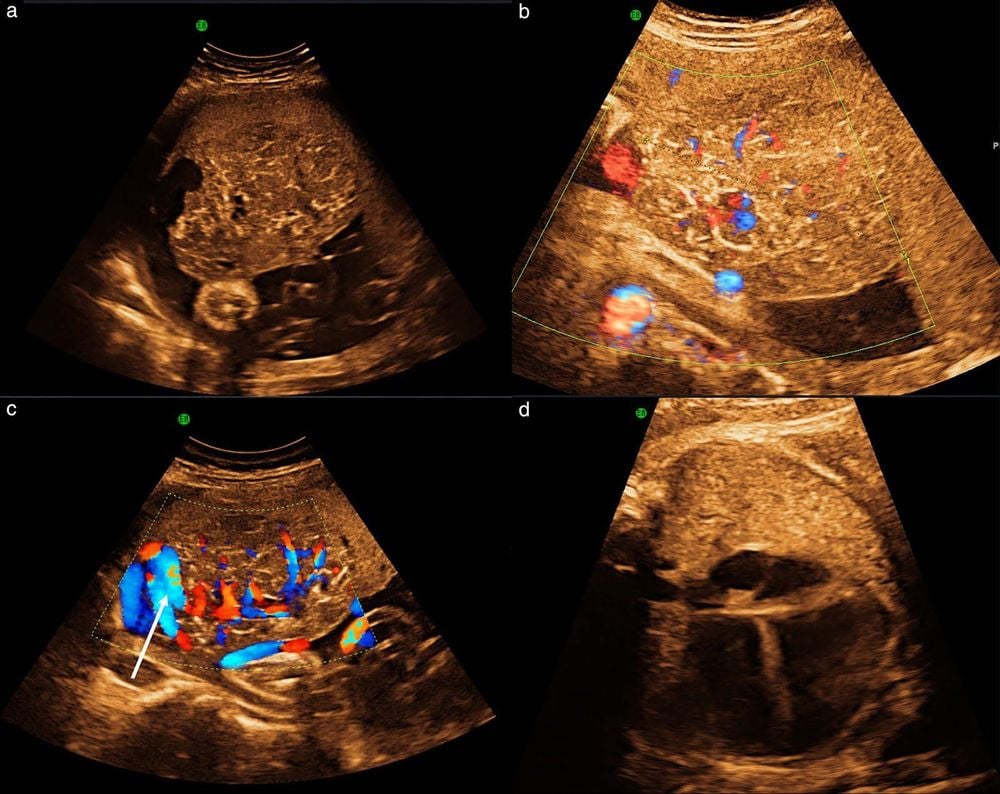
Hình ảnh siêu âm u máu bánh nhau
3. Based on what characteristics to manage blood tumors?
Most of the time, hemangiomas are small and asymptomatic lesions that are only found postpartum after slicing the placenta. In contrast, large tumors are often associated with adverse perinatal outcomes, including intrauterine growth retardation, preterm birth, stillbirth, and neurodevelopmental abnormalities.
A systematic review of 28 studies (161 pregnancies) found that, in pregnancies with non-interventional placental hemangiomas, the rate of intrauterine fetal death was 8.2%, while the neonatal mortality rate and perinatal events occurred in 3.8% and 11.1%, respectively. Small fetuses account for 24% of cases. Preterm birth before 37 weeks accounted for 34.1% of pregnancies. Illness occurred in 12% of cases.
4. What to do when ultrasound chorioangioma?
4.1. For a transabdominal ultrasound You will lie on your back on an examination table with the entire abdomen exposed. Next, the doctor will apply a special gel to the area to be examined and move the transducer back and forth to record the necessary images. Meanwhile, look up at the screen. You should be able to see the placenta of the fetus appearing on top. 4.2. For a transvaginal ultrasound You will be asked to change into a special gown or remove clothing from the waist down. Adjust your posture: you step on the examination table and put your feet on the pedals (similar to when doing a gynecological exam). First, your doctor will wrap the transducer in a plastic cover (like a condom) and lubricate it with a gel. Then put it in the vagina and move it to different positions to survey and record the necessary information. Depending on your baby's location and developmental stage, you may see different stages of the placenta. Finally, when that's done, the transducer will be removed from the vagina. Ultrasound of placental hemangioma helps doctors detect abnormalities in the placenta for timely treatment.

Đầu dò âm đạo được bọc bao cao su trước khi tiến hành siêu âm qua ngã âm đạo
Vinmec International General Hospital system currently uses the most modern generations of color ultrasound machines in examining and treating patients. In addition, a team of experienced doctors and nurses will greatly assist in the diagnosis and early detection of abnormal signs of the body in order to provide timely treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.