This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Dr., Doctor Tran Nhu Tu - Head of Diagnostic Imaging Department - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.
Spine X-ray technique plays a very important role in the diagnosis and treatment of spinal injuries.
1. What is an X-ray?
X-ray is a commonly used method in diagnostic imaging. This is a method of imaging using X-rays (Roentgen rays) to build and reconstruct images of the internal structures of the body. These captured images are valuable information in the diagnosis of medical imaging as well as the treatment of disease.
Patients need to take X-rays when prescribed by a doctor.
2. X-ray methods of the spine
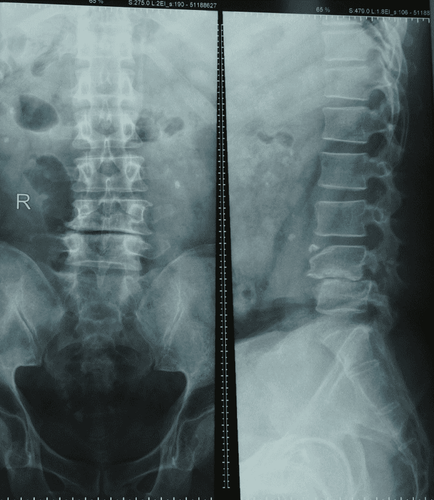
Take X-rays of each area of the spine including: neck, back, sacrum, on both straight and inclined planes. Take X-rays of the spine with special positions such as:
Take C1 and C2 cervical vertebrae in an upright position and open mouth. This X-ray method is intended to detect changes in the apex and the mandibular joint. Scan 3/4 of the spine to detect graft-hole changes. Myelography is used to detect narrowing of the canal, especially due to myeloma. Radiography of the nerve roots, especially due to herniated discs in the lumbar spine. Computed tomography: scan to evaluate bones of the spine, often applied in trauma Magnetic resonance imaging: is currently considered the most valuable method in the field of medical imaging of the spine and spinal cord. living. This method is indicated in cases of suspected myeloma and disc herniation.
3. Evaluation of pathological lesions of the spine on X-ray film
3.1 Changes in the physiological curve of the spine May be caused by congenital or acquired causes leading to kyphosis, curvature, spondylolisthesis, or the straightened spine loses its physiological curvature.
3.2 Change in vertebrae shape and height of intervertebral disc space On the myelogram, it is necessary to inject contrast agent into the spinal canal to allow assessment of stenosis, compression, and changes in the canal.
4. Some X-ray anatomical features of the spine
4.1 Physiological curve Physiological curve, which is recognized by X-ray film of the spine in the inclined position, is a continuous curve connecting the anterior or posterior border of the vertebral bodies.
At the neck: The curve is slightly curved forward. Back segment: Back curve. Waist segment: Curve slightly forward. Truncated segment : Backward curve. 4.2 Vertebral body and intervertebral disc gap 4.2.1 Vertebral body In young people, the vertebral body is rectangular in shape. In the elderly, the upper and lower margins of the vertebral body are slightly concave towards the vertebral body.
4.2.2 Disc Located in the intervertebral disc space is the space between 2 vertebral bodies. Normally, discs do not require contrast and are not visible on radiographs.
4.3 Joints in the spine Articularis intervertebralis, also known as Luschka joints, is found only in the cervical vertebrae in each intervertebral space. The normal semicircle has rose thorns and is easily recognized on radiographs of the cervical spine in the upright position..
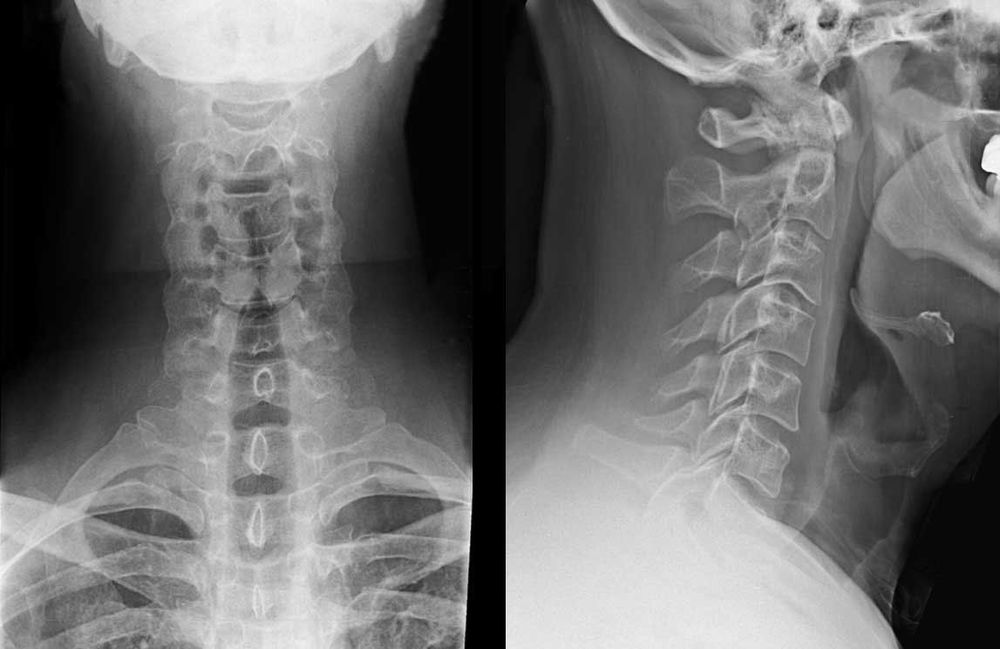
5. X-ray diagnosis of some common diseases in the vertebrae
Normally the cervical spine will have 7 vertebrae, the thoracic spine has 12 vertebrae, the lumbar spine has 5 vertebrae, 5 sacral vertebrae and 3-4 coccyx. Changes in the number of vertebrae can occur as follows:
There are 8 cervical vertebrae. There are ribs in the 7th cervical vertebra. May be only on one side or both sides, causing compression of the brachial nerve root. The coccyx of vertebra D12: The coccyx of D12 is atrophied. Lumbalisation S1 (Lumbalisation): The 1st sacrum protrudes into the lumbar segment to form the 6th lumbar vertebra.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.