This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Vo Thi Thuy Trang - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International General HospitalToday's modern diet and lifestyle lead to an increasing rate of people with fatty liver disease. If not detected and treated early, it will lead to severe fatty liver, seriously affecting health and quality of life.
1. What is fatty liver?
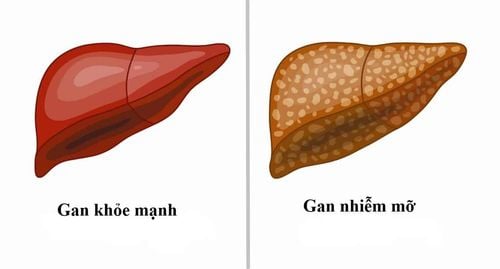
In a healthy person without fatty liver, the structure of the liver will have about 3-5% of its weight as fat. Therefore, if the percentage of fat accumulation in the liver exceeds 5%, it will lead to fatty liver disease.
Severe fatty liver is the end stage of this disease, equivalent to stage 3 of the disease. Fatty liver disease grades are classified based on the percentage of excess fat in the liver structure.
2. What is the cause of severe fatty liver?
Currently, severe fatty liver is caused by many factors, including many factors in daily life, living habits as well as diet.
Besides, the late detection of the disease, making the disease progress silently to the end stage is the most important factor leading to severe fatty liver. Some common causes of fatty liver:
Improper nutrition, using a lot of fat and grease, especially animal fat. Unscientific living habits, sluggishness, physical inactivity. Regular use of stimulants such as smoking, drinking a lot of alcohol.

Chế độ dinh dưỡng ảnh hưởng lớn đến gan
Abnormal weight such as overweight, obesity or malnutrition. Infection with viruses that cause hepatitis. Complications of other diseases such as dyslipidemia, diabetes... Genetics or endocrine disorders.
3. Grading, signs and treatment of severe fatty liver
3.1 Grade 1 fatty liver Grade 1 fatty liver is when excess fat accumulates in the liver accounting for 5 - 10% of the liver weight, equivalent to mild fatty liver. This is considered the first stage, the onset of the disease, so the signs are very poor, non-specific and sometimes no specific symptoms.
Therefore, mild fatty liver is difficult to detect clinically and cannot be checked through laboratory tests. At this stage, the disease has not affected much to health, but the patient must not be subjective. Periodic and regular health check-ups will help detect grade 1 fatty liver, from which there are specific treatment options, good prognosis and complete cure.
Treatment of grade 1 fatty liver is mainly to change living habits, find out the cause of the disease to avoid progressing to a more severe level. Treatment methods include changing the diet, not using alcohol, avoiding eating a lot of fat and fat (especially animal fat) and increasing regular and regular physical activity.

Gan nhiễm mỡ cấp độ 1 chưa ảnh hưởng nhiều đến sức khỏe
3.2 Grade 2 fatty liver Grade 2 fatty liver is when the amount of fat in the liver structure accounts for 10 - 25% of the weight of the liver, equivalent to a moderate fatty liver. At this stage, adipose tissue is already present on the surface of the liver parenchyma and sometimes in the diaphragm. Although the disease at this stage has progressed more severely than grade 1, the signs and symptoms of the disease have not yet shown clearly, making it easy to misdiagnose with other liver diseases.
Nonspecific signs of the disease include gastrointestinal disturbances (loss of appetite, loss of appetite, dyspepsia), fatigue, lethargy, sometimes feeling pain in the right lower quadrant, a few there are signs of biliary obstruction such as skin and eye conjunctiva turns pale yellow...
Because the symptoms are not clear and specific, it is similar to grade 1 fatty liver, at this stage it is difficult to detect the disease. if not check your health regularly and perform liver function tests. Grade 2 fatty liver can progress quickly, progress to severe fatty liver and complications begin to appear.

Gan nhiễm mỡ cấp độ 2 gây cảm giác chán ăn
There is no radical treatment for grade 2 fatty liver, the main treatment is maintenance treatment, avoiding aggravation, and improving the patient's condition. Doctors recommend that patients should use more foods that contain a lot of fiber and vitamins such as vegetables and fruits, and replace animal fats with unsaturated fats found in avocados, walnuts, and flaxseeds. ... Increase physical activity and sports and minimize drinking too much alcohol.
3.3 Grade 3 fatty liver Grade 3 fatty liver is when the percentage of excess fat in the liver structure accounts for more than 30% of the liver weight, equivalent to severe fatty liver. This is the most dangerous of the three stages of fatty liver disease, the disease has progressed to the end stage and complications due to liver failure will occur.
Severe fatty liver has obvious symptoms, more typical include: the patient will feel pain in the right lower quadrant, the liver is enlarged, can be palpable from the skin, when pressed, it is painful. cholestasis syndrome such as jaundice and yellow eyes, frequent gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, dyspepsia, poor appetite and anorexia. Severe fatty liver, if the patient is not detected and treated promptly, will rapidly progress to cirrhosis or liver cancer.

Gan nhiễm mỡ độ 3 có nguy cơ dẫn đến xơ gan
At this stage, it is impossible to treat severe fatty liver for a completely healthy liver. The methods of treating severe fatty liver are mainly to support the body, support the functions of the liver and slow down the progression to cirrhosis, liver cancer.
Treatment methods include: adjusting the diet in a scientific way, doing regular exercise regularly, using oral drugs to support liver function as prescribed by the doctor to help limit complications, improve liver function and health status of patients.
Should be examined periodically 3-6 months or when there are signs such as liver pain, weight loss, fatigue, jaundice, fever. Vinmec has a system of high-class ultrasound, CT, and MRI machines with a team of highly qualified doctors, thorough consultation and service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.