Thoracic surgery to treat hemothorax - pneumothorax
Hemothorax – pneumothorax is a rather dangerous condition and often occurs in young people. If not handled properly and promptly, this situation will become more and more serious. Among the ways to handle pneumothorax, thoracoscopic surgery is the best way to effectively and definitively deal with this condition.
1. What is pneumothorax? Causes of pneumothorax
Pneumothorax - Primary spontaneous pneumothorax (TKMB TPP) is a condition in which blood gas accumulates in the pleural space. The cause is chest trauma, chest trauma, the source of bleeding is usually from a broken rib, lung parenchyma, or intercostal artery. When the air bubbles in the lungs burst, a condition called hemothorax-pneumothorax occurs. This condition usually occurs in young, healthy patients without pulmonary disease.
Hemothorax - moderate and small pneumothorax will be difficult to diagnose clinically, this case needs to be based on ultrasound results and CT Scanner to determine. As for hemothorax - pneumothorax with a large number can be diagnosed clinically, with severe cases like this, it is necessary to have hemothorax emergency and timely surgery.

Chụp CT chẩn đoán tràn máu màng phổi
2. How to handle hemothorax – pneumothorax?
First, the doctor will appoint pleural drainage >1000ml or 200ml/h for 3 consecutive hours. If pleural drainage has been performed correctly but is not effective, then proceed to CT Scanner after 3 days, there is still blood in the pleural space. Finally, drain the remaining pleural cavity after 7 days.
However, thoracic drainage is only a temporary treatment and is often used in mild cases. After placing a chest drain, the patient must wait for time for the lungs to expand and after the air leak stops for at least 2 days, the patient must have the drainage removed. Therefore, the hospital stay will be prolonged, and this method has a high recurrence rate.
Thoracic surgery is a treatment for severe cases of fluid. When the patient is in a stable systemic and hemodynamic condition, the physician may authorize thoracoscopy. This is a minimally invasive treatment for thoracic diseases, reducing postoperative pain and shortening the postoperative period. Not only helps reduce the rate of disease recurrence but also brings aesthetic effectiveness.
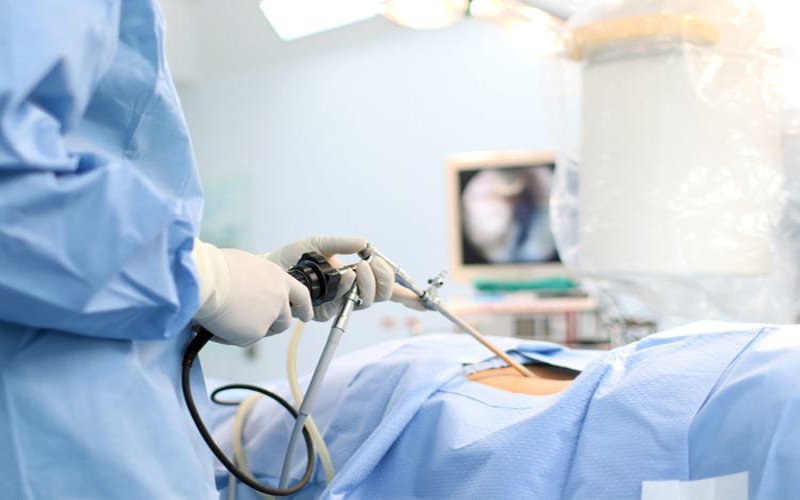
Phẫu thuật nội soi lồng ngực là phương pháp điều trị ít xâm lấn
3. Cases where thoracic surgery is not possible
Thoracic surgery is a minimally invasive and benign method, so there are no absolute contraindications to this method. However, in cases where the patient has a systemic condition or severe co-morbidities, doctors and family members need to be careful before performing thoracoscopy.
4. What should be prepared for thoracic surgery?
Pre-operative preparation is not only important for the patient alone, but the operator also needs to prepare well for his or her work. In addition, surgical aids must also meet the requirements required for this method. The following are specific preparations to be performed prior to thoracoscopy:
4.1 Performer Trained in thoracic surgery. Master the principles of first aid and initial treatment. Explain to the patient and the patient's family about the medical condition and possible risks during and after surgery. 4.2 Facilities Equipment, specialized operating room for cardiothoracic surgery and equipped with endoscopic system.
4.3 Patient Well explained about the disease, risks during and after surgery. Agree to have surgery and sign a written commitment to surgery. Medical records: Prepared according to regulations of the Ministry of Health.

Bệnh nhân được tư vấn và ký giấy cam đoan trước phẫu thuật
4.4 Steps to carry out thoracic surgery Step 1: Check the records, make sure all the papers are in accordance with the regulations of the Ministry of Health.
Step 2: Check that the patient has the right person (name, age, ...), the right disease or not.
Step 3: Perform the technique:
The patient lies in a prone position, with a pillow under his back. General anesthesia, single-lung selective endotracheal intubation. Place Trocar: Place two or 3 trocars. Then place a normal trocar in the DLMP hole. Evaluation of lesions: Number of clots, source of bleeding, has stopped or is still bleeding. Use Pince en coeur to remove all the blood clots, to remove the blood from the endoscope. Hemostasis by electrocautery or hemostasis (if the lesion is still bleeding), suturing torn lung parenchyma... Expanding the lung, checking for air leaks from the parenchyma if enhanced suture is needed. Place pleural drainage (one or two depending on the case). Follow-up after thoracic surgery Patients after surgery need to monitor the following parameters so that they can be handled promptly:
Amount of blood and air out according to drainage. Monitor for complications. Take care of drainage, ensure "sterile, sealed, one-way, continuous suction". The following are possible complications after surgery and how to handle each case:
Bleeding: Heavy bleeding requires surgery to check and stop bleeding. Prolonged gas leak: if more than 7 days, re-examination must be performed. Infection: Treat with antibiotics if pleural deposits are present. If there is pleural effusion, it must be re-operated and cleaned. Above is a detailed introduction about hemothorax - pneumothorax and thoracoscopic surgery methods to handle this condition. Because this is the gentlest and most effective method, it is often chosen by doctors to treat patients. However, it should be done at reputable medical facilities to avoid unfortunate complications.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as customers wishing to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online HERE.






