Atelectasis: Diagnosis and treatment
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Nguyen Huy Nhat - Respiratory Doctor - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.
Atelectasis is a condition in which the alveoli in the lungs (lung parenchyma) collapse, which can cause symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, etc., which affects quality of life and can cause many dangerous complications. dangerous.
1. What is atelectasis?
Atelectasis is the complete or partial collapse of the entire lung or an area (lobe) of the lung. It occurs when the small air sacs (alveoli) in the lungs become deflated or may fill with alveolar fluid. Atelectasis is one of the common breathing (respiratory) complications following thoracic surgery. It is also a possible complication of respiratory problems including lung tumor, chest trauma, massive pneumothorax, phlegm plug, obesity, etc. It can also occur when inhaling foreign matter.
Atelectasis can interfere with the airway, especially if there is additional lung disease. Treatment for this condition depends on the cause and severity of the atelectasis.
Atelectasis can interfere with the airway, especially if there is additional lung disease. Treatment for this condition depends on the cause and severity of the atelectasis.
2. Diagnosis of atelectasis
To diagnose atelectasis, the doctor needs to review the medical history, especially the diseases related to the lungs. Next, the specialist will conduct tests to locate the cause of the disease. The first examination done is an X-ray - this is a simple procedure but may be all that is needed for a definitive diagnosis. However, other tests may be done to determine the type or severity of the disease. Diagnostic methods include:
CT scan: Because CT is a more precise technique than X-ray, it can sometimes help better detect the cause and type of atelectasis. Oxygen measurement: This simple test uses a small device placed on your finger to measure the level of oxygen in your blood. It helps determine the severity of atelectasis. Thoracic ultrasound: This noninvasive test can help your doctor tell the difference between atelectasis, pulmonary sclerosis, pneumonia caused by fluid in the air sacs, and pleural effusion. Bronchoscopy: Using a flexible, lighted camera-tipped tube inserted down the throat allows the doctor to see what could be causing the blockage, such as a mucus plug, tumor, or foreign body. This method can also be used to remove blockages.
CT scan: Because CT is a more precise technique than X-ray, it can sometimes help better detect the cause and type of atelectasis. Oxygen measurement: This simple test uses a small device placed on your finger to measure the level of oxygen in your blood. It helps determine the severity of atelectasis. Thoracic ultrasound: This noninvasive test can help your doctor tell the difference between atelectasis, pulmonary sclerosis, pneumonia caused by fluid in the air sacs, and pleural effusion. Bronchoscopy: Using a flexible, lighted camera-tipped tube inserted down the throat allows the doctor to see what could be causing the blockage, such as a mucus plug, tumor, or foreign body. This method can also be used to remove blockages.
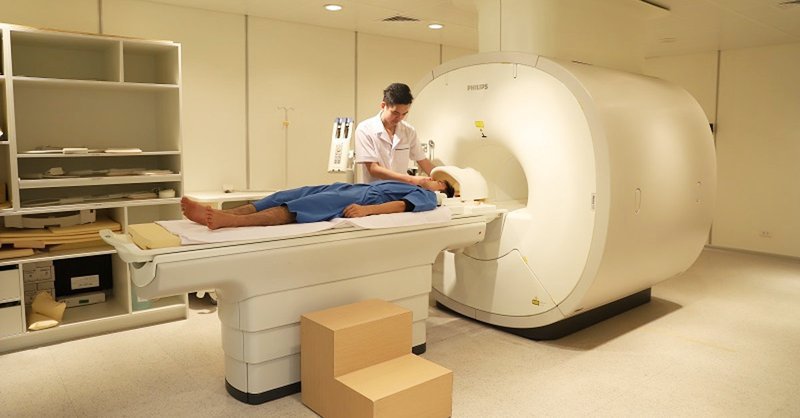
Để chẩn đoán bệnh xẹp phổi, bác sĩ có thể đề nghị bệnh nhân chụp CT
3. Treatment of atelectasis
Treatment of atelectasis depends on the cause. Mild atelectasis may go away without treatment. In some cases, medication will be used to loosen and thin the mucus. If the condition is caused by a blockage, surgery or other treatments may be needed.
3.1 Chest physiotherapy
Techniques that help you breathe deeply after surgery to reopen collapsed lung tissue are important. These techniques are best done before surgery. These include:
Performing deep breathing exercises (spirometry) and using a device to assist with a deep cough can help clear secretions and increase lung volume. Position the body so that the head is lower than the chest (postural drainage). This allows the mucus to better drain from the bottom of the lungs. Tap the chest over the collapsed area to loosen the mucus. This technique is called the typing method. You can also use mechanical mucus cleaning devices, such as an air pulse vibrating vest or hand tools.
Performing deep breathing exercises (spirometry) and using a device to assist with a deep cough can help clear secretions and increase lung volume. Position the body so that the head is lower than the chest (postural drainage). This allows the mucus to better drain from the bottom of the lungs. Tap the chest over the collapsed area to loosen the mucus. This technique is called the typing method. You can also use mechanical mucus cleaning devices, such as an air pulse vibrating vest or hand tools.
3.2 Surgery
Removal of airway obstructions can be accomplished by aspiration of mucus or by bronchoscopy. During a bronchoscopy, the doctor gently guides a flexible tube down the throat to clear the airway.
If a tumor is causing atelectasis, treatment may include surgery to remove or shrink the tumor, with or without other cancer treatments (chemotherapy or radiation).
If a tumor is causing atelectasis, treatment may include surgery to remove or shrink the tumor, with or without other cancer treatments (chemotherapy or radiation).

Phẫu thuật là phương pháp phổ biến để điều trị xẹp phổi
3.3 Breathing treatment
In some cases, using a breathing tube may be necessary.
For children, childhood trauma is often caused by airway obstruction. To reduce the risk of illness, keep small objects out of the reach of children.
In adults, anemia often occurs after major surgery. If surgery is planned, talk to your specialist about strategies to reduce risk. Some research suggests that breathing exercises and muscle training may reduce the risk of disease after certain surgeries. In addition, smoking is also recommended because smoking increases mucus production and affects hair-like structures in the bronchial tubes (hairs).
For children, childhood trauma is often caused by airway obstruction. To reduce the risk of illness, keep small objects out of the reach of children.
In adults, anemia often occurs after major surgery. If surgery is planned, talk to your specialist about strategies to reduce risk. Some research suggests that breathing exercises and muscle training may reduce the risk of disease after certain surgeries. In addition, smoking is also recommended because smoking increases mucus production and affects hair-like structures in the bronchial tubes (hairs).
Để đặt lịch khám tại viện, Quý khách vui lòng bấm số HOTLINE hoặc đặt lịch trực tiếp TẠI ĐÂY. Tải và đặt lịch khám tự động trên ứng dụng MyVinmec để quản lý, theo dõi lịch và đặt hẹn mọi lúc mọi nơi ngay trên ứng dụng.
Article referenced source: mayoclinic.org
Bài viết này được viết cho người đọc tại Sài Gòn, Hà Nội, Hồ Chí Minh, Phú Quốc, Nha Trang, Hạ Long, Hải Phòng, Đà Nẵng.






