This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Dinh Hung - Doctor of Radiology - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.
Gastrointestinal X-ray with contrast is an imaging method to evaluate the anatomical structure of the gastrointestinal tract. Contrast-enhanced gastrointestinal X-ray includes: X-ray of the upper digestive tract (gastro-oesophageal) and lower (colon scan).
1. What is an upper gastrointestinal X-ray with contrast?
Contrast X-ray of the upper gastrointestinal tract is an imaging method to evaluate the anatomical structure of the upper gastrointestinal tract. The esophagus, stomach, and duodenum (first part of the intestine) will be highlighted on the X-ray with contrast material. This contrast agent may be a barite solution or a water-soluble contrast agent. If only contrast material is used to evaluate the pharynx and esophagus, this process is called barite swallow. X-rays use invisible electrical energy beams to create images of tissues in internal organs, bones or organs on film. X-ray, which is a procedure that uses X-rays to reconstruct images of organs in the body to help doctors make a diagnosis. During the scan, X-rays pass through your body and hit a shield behind you to produce an image.
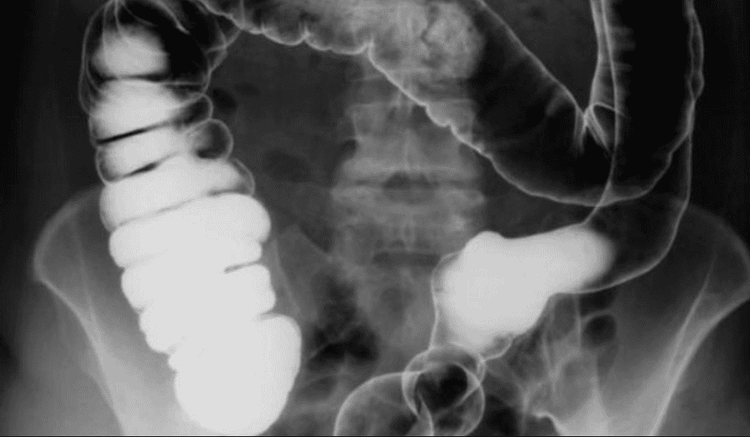
Chụp X-quang cản quang đường tiêu hóa giúp chẩn đoán các bệnh lý về đường tiêu hóa
2. When should you perform a contrast-enhanced upper GI X-ray?
Contrast X-ray of the upper gastrointestinal tract is done while finding some of the following causes:
Finds the cause of gastrointestinal symptoms such as: Difficulty swallowing, vomiting, belching, dyspepsia ... Find out narrowing in the upper intestinal tract due to ulcers, tumors, pyloric stenosis... Find out areas of inflammatory bowel disease, malabsorption syndromes, problems with bowel movement to push food bowel movements (intestinal disturbances) Usually, you won't need a contrast-enhanced upper GI X-ray if you don't have digestive symptoms. You should have this test if:
Difficulty swallowing food. Suspected intestinal obstruction. Abdominal pain that gets better or worse while eating. Heartburn occurs frequently.
3. Things to keep in mind when taking gastrointestinal X-rays with contrast
Today thanks to the development, endoscopy is performed to replace the contrast-enhanced upper gastrointestinal X-ray examination. Endoscopy uses a small, flexible tube to view the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.
Contrast upper gastrointestinal X-ray test:
Cannot show irritation of the stomach lining (gastritis) or esophagus (esophagitis) or ulcers less than 0.25 inches in diameter ( 6mm). Undetectable bacterial infection: Helicobacter pylori (a bacteria that can cause stomach ulcers). When something unusual is found, a biopsy cannot be performed during a contrast-enhanced upper GI X-ray. Before performing this medical technique, the patient should clearly understand the warnings and precautions. If you have any questions, consult your doctor for more information and specific instructions.
4. Procedures performed when taking gastrointestinal X-ray with contrast
4.1. What should the patient prepare before performing a contrast-enhanced upper gastrointestinal X-ray?
The patient will be asked to switch to a low-fiber diet temporarily. Your doctor will also tell you not to eat or smoke after midnight the night before the test.
Before performing an upper gastrointestinal X-ray with contrast, the patient will have to wear a hospital gown and be told to remove all jewelry including breast piercings, navel piercings, dentures, hair clips or Other items may appear on the X-ray if not removed.
The patient should ask the medical staff if the dose of the medications they are taking needs to be changed. It is usually possible to continue taking the medication as usual. Do not change the dose of medication yourself without telling your healthcare provider.
Patients will be asked to remove any jewelry from their neck, chest or abdomen prior to testing.
4.2. What is the procedure for performing a contrast-enhanced upper gastrointestinal X-ray?
The patient will perform an X-ray test before taking the barium compound. The compound is then swallowed several times during the subsequent X-ray. The radiologist will tell you when and how much to drink. Typically, the patient will likely have to drink 1 cup (240 ml) or 2.5 cups (600 ml) of barium during the test.
The radiologist looks at the amount of barium flowing down the digestive tract using fluoroscopy and X-ray imaging. The bed the patient is lying on will be repositioned and the patient will also be repositioned to allow the barium to flow down the body. It is possible that the technician will press lightly on the patient's abdomen with a belt or with the technician's hand. The patient may be asked to cough so that the radiologist can observe the barium flow.
If a gas contrast agent is used, the patient will take sips of barium liquid through a straw with medication that creates gas in the stomach. Thanks to this gas, the doctor can see the lining of the stomach and intestines in more detail.
If the patient has a small bowel test, the radiologist looks at the flow of barium through the small intestine into the large intestine. X-ray images were taken in 30 min.
The test will take about 30-40 minutes. If the test includes the small intestine, it will take from 2 to 6 hours. In some cases, the patient is asked to come back in 24 hours for more X-ray images.
4.3. What should the patient do after performing a contrast-enhanced upper gastrointestinal X-ray?
When done, the patient can eat or drink whatever they like, unless the doctor advises against eating. In addition, the patient may be given a laxative or enema to remove barium from the intestines after the test to prevent constipation. Drink plenty of water for a few days to flush out the barite.
If the patient has any questions about the procedure, please consult your doctor for advice and answers.

Bệnh nhân có thể uống thuốc nhuận tràng sau khi chụp X-quang đường tiêu hóa
5. Contrast X-ray of the lower gastrointestinal tract (colon frame)
Colonic imaging methods have evolved over time, leading to a decrease in the role and number of contrast-enhanced radiographs. However, contrast-enhanced colonoscopy is still used in traditional imaging departments around the world to ensure that patients receive high-quality diagnostic and treatment services.
5.1. Indications and basic shooting techniques
There are two main techniques for performing barium enema colonoscopy, single contrast and double contrast to reveal mucosal lesions, colonic intramural lesions, and compression lesions from the colon. outside. Single-contrast imaging is often used to evaluate colonic obstruction, colonic fistula, for the elderly, and in critically ill or frail patients. Dual-contrast imaging is commonly used to detect small lesions (<1cm), inflammatory bowel diseases, and to evaluate detailed rectal imaging.
Prepare the patient for colon cleansing and the imaging position plays a decisive role in the quality of the scan.
5. 2. Normal x-ray anatomy
The colon is the last part of the digestive tract, 1.4 m to 1.8 m long, consisting of: the cecum and the appendix in the right iliac fossa, followed by the ascending colon, which passes close to the right abdominal wall to the lower face. Right liver, transverse colon turns left to spleen, descending colon goes along left abdominal wall to left iliac fossa, sigmoid colon goes to small pelvis, rectum stands vertically in front of sacrum. The colon has two flexures: the right colic or hepatic flexure and the left colic or splenic flexure. The ascending and descending colon are relatively fixed.
Colonoscopy using contrast is a method often considered by doctors in the diagnosis of many colon diseases, including colon cancer. Before a contrast-enhanced colonoscopy, the colon should be emptied to ensure that the radiographs are not blurred and that there is no confusion between colonic lesions. In addition, for the most accurate scan results, the examiner should also apply a special diet that is a diet that does not cause backlog before 2 days, foods that are not high in fiber, fermented. The patient will also be given a laxative and a thorough enema a few hours before the procedure.
The examiner is taken with many different positions, images of colon segments such as sigmoid, rectum, left splenic angle, hepatic angle, cecum, ascending colon... are recorded for the doctor to assess the condition. injury for each person.
5.3. Some lesions are evaluated in contrast-enhanced colon X-ray
The results of X-ray colonoscopy using contrast may not detect any abnormalities and your doctor will advise you to repeat the scan after a certain time, depending on each specific case.
In addition to observing physical lesions such as abnormalities in size (congenital short, long colon), surface abnormalities... X-ray of the colon with contrast can detect diseases Causes such as:
Colitis
Congenital megacolon (Hirschsprung) is a pathology that causes chronic constipation in children due to colonic lymphadenopathy. X-ray images of the colon using barium contrast media show dilated sigmoid colon, small rectum, elongated colon, uneven absorption in the nodal segment.
Polyp lesions
Small, flesh-like polyps that grow from the lining of the intestine and protrude into the lumen or sometimes grow on the stalk. Some polyps can be flat, some people have several polyps scattered in different parts of the colon... Colon polyps can be hyperplastic polyps, adenomatous polyps or extra tissue polyps. Among them, adenomatous polyps are thought to be the precursors of colorectal cancer.
Lymphoid hyperplasia
Shows small diameter nodules, only 1-3 mm in diameter, of lymphoid cysts characterized by bright defects commonly seen in the terminal ileum and cecum.
Colitis
Colitis is one of the increasingly common digestive tract diseases. X-ray images of the colon using contrast can show colonic tubules, ulcers, pseudo-polyps...
Contrast-enhanced gastrointestinal X-ray is an imaging method to evaluate the structure of the colon. Anatomy of the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, patients should choose reputable medical facilities that have enough modern medical equipment systems to perform this technique.
In order to improve the examination and treatment process, Vinmec International General Hospital has applied X-ray technique of the gastrointestinal tract in examination and diagnosis of many diseases. X-ray technique at Vinmec is carried out methodically and in accordance with standard procedures by a team of highly qualified medical professionals, modern machinery system, thus giving accurate results, making a significant contribution to diagnosis and staging of the disease.
If you have a need for medical examination by modern and highly effective methods at Vinmec, please register here.