This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master, Doctor Nguyen Van Huong - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.X-rays are highly effective for diagnosis with bone and joint tissue. Therefore, in cases of suspected bone and joint trauma, radiography is the first imaging tool required to diagnose fractures, joint displacement or structural abnormalities on musculoskeletal radiographs. quickly intervene for the patient.
1. What is a musculoskeletal X-ray?
An X-ray is a non-invasive medical test that helps doctors diagnose and treat medical conditions. X-ray imaging is a technique that exposes a part of the body to a small amount of ionizing radiation to create images of structures inside the body. This is the oldest and most frequently used form of medical imaging, which is simple, fast and widely available.Of all tissues, bone tissue has the highest ability to block X-rays. Therefore, a bone X-ray can create an image of any bone in the body, including the hand, wrist, arm, elbow, shoulder, spine, pelvis, hip, thigh, knee , leg, ankle or foot.
Besides, at the junction between the ends of bones is a joint, this structure is often examined for anatomical stability under radiographs. Unlike bone, because this is a dynamic structure, a comprehensive radiograph of the joint requires two films of flexion and extension. In addition, because joint trauma is not only joint deformity, joint displacement or bone damage alone, but also affects other components in the joint such as cartilage, bursa, ligaments, tendons and muscles. Meanwhile, these tissues do not show up on radiographs. Therefore, joint magnetic resonance imaging is sometimes indicated as a follow-up to the initial initial radiographic evaluation of the joint.
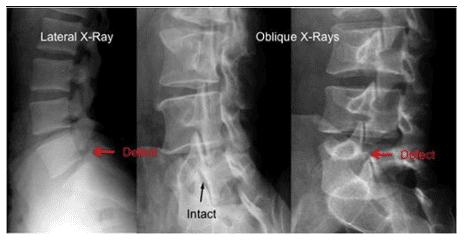
2. X-ray diagnosis of bone trauma
When approaching a patient with a bone injury, one of the first things a doctor wants to know is the signs of a fracture, its location, type, and extent. To determine the severity and length of treatment or recovery, doctors will usually perform an X-ray as this is the most universal and effective tool. In some difficult, complicated bone injuries, other imaging techniques will also be used to aid in the diagnosis, such as computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging, especially in cases of Suspect a pathological fracture rather than a simple bone injury. Accordingly, this is a type of fracture that is not caused by trauma but is the result of an underlying health or medical condition that causes poor bone quality.3. Objectives of Bone Trauma Radiology
Bone radiographs are used for the purposes of bone trauma including:Diagnosis of fractures or dislocations Evaluation of appropriate alignment and stability of bone fragments after splint immobilization Direction Lead orthopedic surgery, such as spinal repair or fusion, joint replacement and fracture risk reduction Look for injuries, infections, secondary osteomyelitis, and abnormal bone growth or changes general bone after a traumatic event Locating a foreign body in the surrounding soft tissues or in the bone during bone trauma
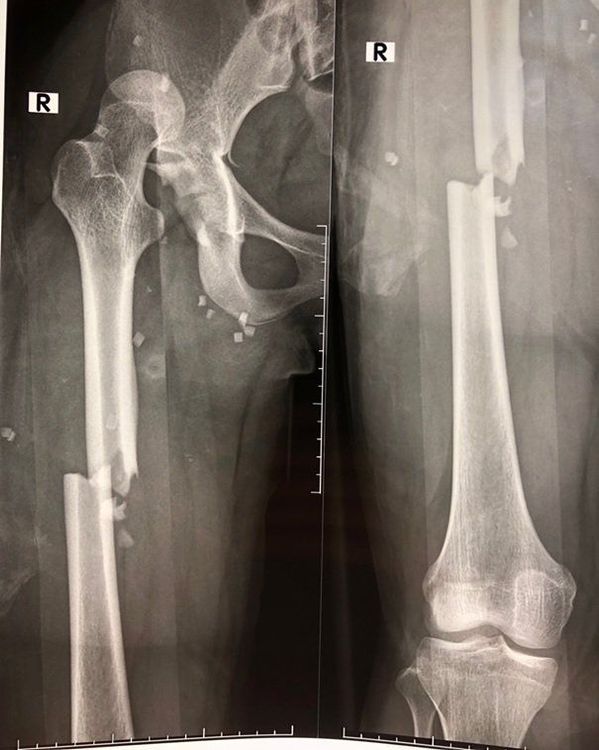
4. Describe the fracture location on the X-ray film of bone trauma
The anatomical location of the fracture is not only the location of the fracture, but also describes the structural features that disrupt the stability of the bone tissue. To describe this, doctors will often use the following diagnostic terms for fractures:Body: The middle (central) part of the bone Head of the bone: Located on one end of the bone but not at the top of the bone. Joint Peri-articular: Belonging to the joint area at the end of the bone In the joint: In cases of fracture extending into the joint socket through the articular cartilage When it is found on radiographs of bone trauma, there is a fracture involving the joint surface, Patients should be treated aggressively because loss of bone-to-joint connection can lead to more rapid joint inflammation.
5. Describe the type of fracture on the X-ray film of bone trauma
The displacement of the two ends of the broken bone from the original position is characteristic of the fracture type. In other words, the doctor will describe on the x-ray how far the bone has moved out of position using the following terms:No displacement: Where the bone is broken but the axis of the bone is still intact as original Minimum displacement: There is a slight change in position, usually negligible Displacement: Where the fracture tip has been significantly displaced, this is expressed as a percentage of the estimated body width Bone Dislocation: Fracture within the joint and the ends of the bones are pushed out of the socket Angle flexion: The angle created by the bone head being displaced from the axis of the original normal bony body, described by degrees of Short Overlap: An effect caused when The surrounding muscles pull the ends of the bones together due to the pain reflex causing muscle spasticity, shortening the length of the bone. Diagnosis of complex fractures on radiographs of bone trauma The doctor will need a detailed description for the radiographic diagnosis of bone trauma caused by high-impact traumatic settings such as a car accident or major fall, such as:
Multi-segment fracture: Wall fracture More than two segments Complex fracture: Fracture in which multiple fragments of bone of various sizes are formed, separating from the main body of the bone Diagnose a pathological fracture on radiographs Pathological fracture occurs when the bone is weak caused by a disease that moves bone material or interferes with the normal metabolism (regeneration) of bone. These cases will cause spontaneous fractures without bone trauma or just a force of impact, even a slight fall can cause a fracture. Abnormalities when diagnosing pathological fractures are described as follows:
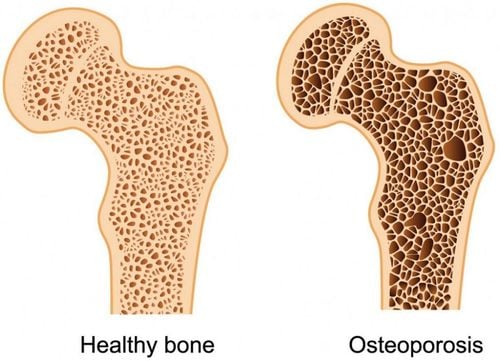
Decrease in bone density: A condition in which the body does not make new bone rapidly by resorption of old bone, regenerating new bone. As a result, bone density decreases, which in the long run can lead to osteoporosis.
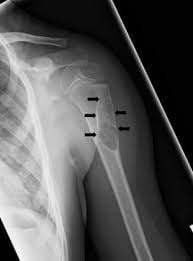
Bone healing: New bone growth around the fracture is considered a good sign that the bone fragments are recombining. Healing: Describe the process of perfecting the shape of the bone due to remodeling Slow healing: When a broken bone does not heal due to poor blood circulation, infection, unstable fracture site or other causes Prosthetic joint : The process of bone healing does not take place but instead is the process of creating cartilage.
6. Radiological diagnosis of joint injury
The structure of most joints is basically composed of a synovial layer and two ends of bone joined in the socket, lined with hyaline cartilage and enclosed in a synovial capsule.Soft tissues in the joint organization such as cartilage, ligaments, and synovial fluid are low density and therefore will be less clearly identified on radiographs, although radiological diagnosis of joint trauma is still the method. primary imaging convenience.
Information on joint trauma radiographs helps diagnose any structural abnormalities in joints, including dislocation, joint displacement, joint deformity, joint compression. In cases of suspected fracture to the joint, a radiograph of the joint trauma should also be ordered following the radiograph of the bone injury.
In addition, X-ray diagnosis of joint injury also helps to describe the condition of soft tissue around the joint after injury, such as inflammation, edema,...
In short, with hospitalized patients due to trauma, a musculoskeletal radiograph is the baseline test. Through that, X-rays will help doctors identify fractures as well as joint injuries, from simple to complex, in order to orient the right intervention at the beginning as well as follow up after the injury.
Musculoskeletal doctors Skilled joints at Vinmec will help you heal quickly. Currently, the ultrasound and MRI system at the hospital is very modern, helping to quickly and accurately assess the damage caused in the joints to help doctors have the right and quick treatment direction
To improve the examination and treatment process Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has applied X-ray technique of bones and joints in examination and diagnosis of many diseases. X-ray technique at Vinmec is carried out methodically and in accordance with standard procedures by a team of highly qualified medical professionals, modern machinery system, thus giving accurate results, making a significant contribution to diagnosis and staging of the disease.
For consultation and examination at Vinmec medical system nationwide, please register at the Website for the best service.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.