This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by doctors of Internal Oncology - Radiation Oncology Center, Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.Colon cancer has recently become younger, making the need for screening tests to detect this disease more and more necessary. Colon cancer screening tests look for polyps or early cancer, and regular polyp screening and removal reduces the risk of developing colorectal cancer (up to 90% during colonoscopy). Early detection of cancer increases the chances of successful treatment and reduces the risk of dying from cancer.
1. Risk factors
Most colorectal cancers develop from precancerous polyps. Polyps are growths that arise from within the lining of the colon and can be seen during colonoscopy (colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy) or computed tomography (CT/scan) There are two types of polyps: adenomatous polyps. (adenomatous and dysplastic (hyperplastic.) Adenomatous polyps can become cancerous over time, most of which takes at least 10 years.
Certain characteristics increase the risk of colorectal cancer. Factors may appear singly, but the risk can be greatly increased if several factors are present together
Family history: If a close relative has had colorectal cancer in the family. grade 1 (parent, sibling, or child) If you have had colorectal cancer yourself or have polyps, you are at increased risk of developing new colorectal cancer, especially before age 60. Although the average person has a 4.5% risk of colorectal cancer, up to 90% of these cancers occur in people over the age of 50. The risk increases with age throughout life. element lifestyle such as:
Diet high in fat and red or processed meat and low in fiber Sedentary lifestyle Smoking Tobacco use Obesity Certain conditions significantly increase the risk of colorectal cancer :
Familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) is an uncommon genetic condition. Nearly 100% of people with this condition will develop colorectal cancer during their lifetime, and most occur before age 50. People with this condition have hundreds of polyps that develop throughout the colon starting in adolescence. Hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer (HNPCC), also known as Lynch syndrome, is another genetic condition associated with an increased risk of colorectal cancer. This type is more common than FAP but accounts for less than 1 in 20 cases of colorectal cancer. About 70% of people with HNPCC will develop colorectal cancer by the age of 65. Cancer also tends to occur at a younger age. People with HNPCC are also at increased risk for other types of cancer, including cancers of the uterus, stomach, bladder, kidney, and ovaries.
Inflammatory bowel disease - People with Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis have an increased risk of colorectal cancer. The increased risk depends on the degree of colitis and the duration of the disease. People who have had colitis for 10 years or longer have the highest risk of colorectal cancer. But the risk of colorectal cancer was not increased in people with irritable bowel disease.
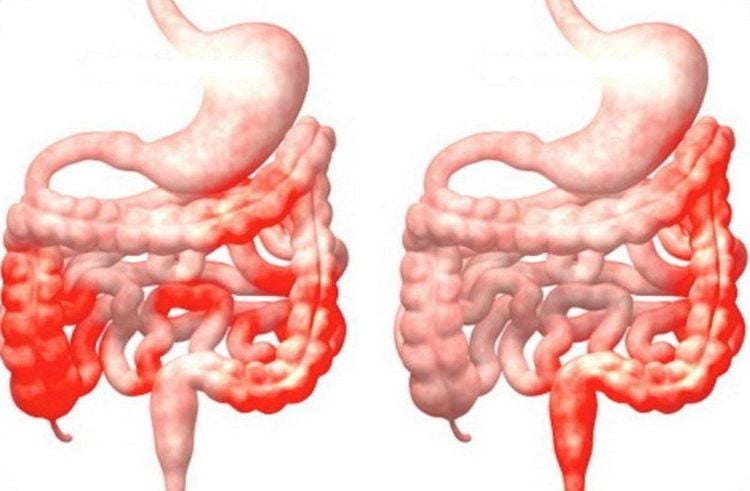
Những người mắc bệnh Crohn hoặc viêm loét đại tràng có nguy cơ mắc ung thư đại trực tràng
Remedies to reduce the risk of rectal cancer
Aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may reduce the risk of developing colorectal cancer.
2. Screening plan
Your colorectal cancer screening plan depends on your colorectal cancer risk.Average colorectal cancer risk - People with average colorectal cancer risk should begin screening at age 50.
Colonoscopy 10 years/computed tomography (CT) /scan ) every 5 years/sigmoidoscopy every 5 years, with or without stool test Annual stool test (with routine fecal blood test or immunohistochemistry) Stool examination once a year with DNA technology Screening plan for people at increased risk: can start at a younger age, screen more often, or use more sensitive screening tests (usually endoscopy) ). The optimal screening plan depends on the presence of risk factors.
People who have a first-degree relative (parent, brother, sister or brother) with colorectal cancer or adenomatous polyps at a young age (before age 60), or two first-degree relatives diagnosed at any age, colorectal cancer screening should be started earlier, preferably at age 40, or 10 years younger than the family member was diagnose . usually screened with a colonoscopy every five years. People who have a first-degree relative (parent, brother, sister, or child) with colorectal cancer or adenomatous polyps at age 60 or older, or two or more second-degree relatives (grandparents, aunts, uncle) with cancer, screening with colonoscopy should be started before age 40, but the same screening schedule should be applied to people at average risk. People who have a second-degree relative (grandparent, aunt, or uncle) or third-degree relative (grandparent or cousin) with colorectal cancer are considered to have an average risk of colorectal cancer. Inflammatory bowel disease – People with ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease have an increased risk of colorectal cancer. The best screening plan depends on how much colon is affected and how long you have had the disease.
Early detection of cancer increases the chances of successful treatment and reduces the risk of dying from cancer. Vinmec International General Hospital always deploys the Colon Cancer Screening and Early Detection Package for customers at risk of cancer, especially customers with colon polyps and inflammatory bowel disease (Inflammatory bowel disease). ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease), a family history of colorectal cancer; Suspected familial adenomatous polyposis, Lynch syndrome. With a system of modern machinery, it is possible to perform colonoscopy tests, closely monitored by specialist doctors. Especially, Vinmec is the leading hospital in implementing the method of colorectal cancer treatment by robotic laparoscopic surgery with many outstanding advantages.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Source: update 2019