This is an automatically translated article.
Malaria is divided into two main types: common malaria and malignant malaria. People with severe malaria will develop life-threatening complications if not detected and treated promptly. Prominent signs are confusion, high fever continuously for many days, severe headache, profuse diarrhea or vomiting.
1. Why is malignant malaria dangerous?
What is malaria? Malaria is a contagious disease that can be passed from an infected person to a healthy person. Typical symptoms of malaria are high fever, chills, and sweating.
Malaria in Vietnam is divided into 2 clinical levels:
Common malaria (usually not dangerous with proper care and rest). Severe malaria (very dangerous to life if not detected and treated promptly). Malignant malaria is a serious form of malaria caused by infection with Plasmodium falciparum malaria parasites, causing hemodynamic disturbances, visceral microcirculation, especially in the brain. The disease can cause damage to many different viscera such as brain, liver, spleen, kidney, heart, lung... with the main mechanism being reduced blood supply, lack of oxygen in the organs.
Malignant malaria is a disease with a high mortality rate, this rate also varies depending on the type of malignant malaria, the patient's location and the timely or delayed emergency treatment. Therefore, when detecting a patient with symptoms of severe malaria, it is necessary to urgently bring the patient to the nearest medical facility for timely treatment, to avoid dangerous complications for the patient.
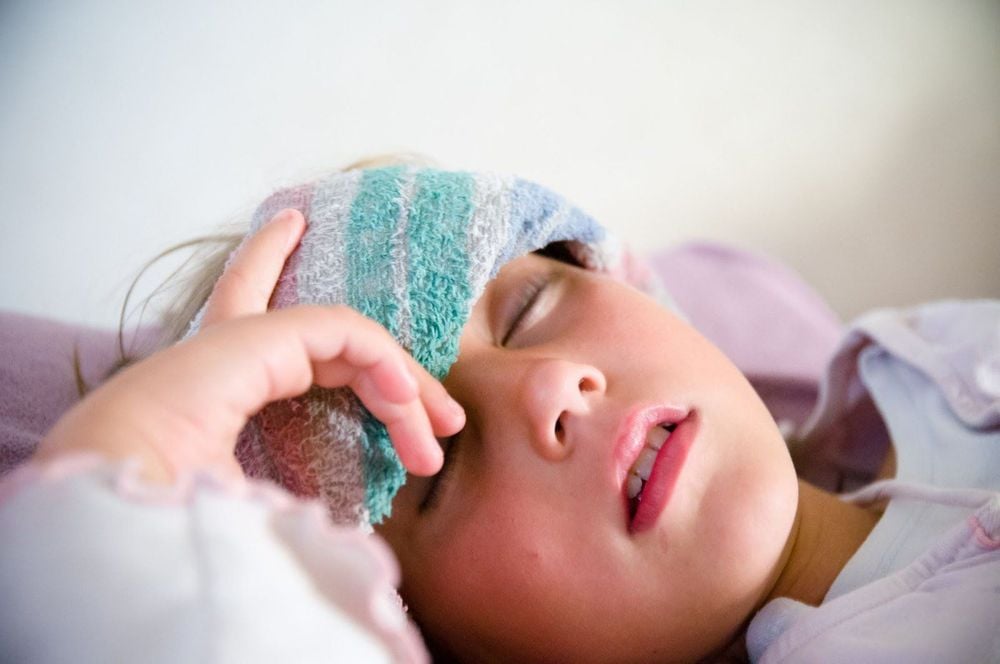
Sốt rét ác tính có thể gây ra nhiều biến chứng nguy hiểm, ảnh hưởng đến tính mạng
2. Signs to recognize malignant malaria
Recognizing signs of severe malaria is one of the prerequisites to avoid unwanted complications caused by the disease. Therefore, the common signs of severe malaria include:
Cerebral body (accounting for 80-95%):
Consciousness disturbance, lethargy, delirium, slurred speech, high fever continuously, a lot of insomnia, severe headache, vomiting or diarrhea. Coma suddenly or slowly, coma deepening (usually coma lasts from 1-3 days, most does not exceed 6 days, rarely lasts up to 10-15 days). Epileptic seizures. Sphincter disorders, dilated pupils. May cause respiratory failure or respiratory disturbances. Decreased blood pressure due to dehydration, or increased blood pressure due to cerebral edema. Vomiting and diarrhea. There may be renal failure, oliguria or anuria, high blood urea nitrogen, hemoglobinuria due to massive hemolysis. Hemoglobinuria:
Massive hemolysis, cardiovascular collapse, renal failure. Severe fever, dry vomiting or vomiting yellow fluid. Backache. Jaundice, mucous membranes due to hemolysis. Hematuria in urine, red-brown urine then turns coffee color or thick water color, urine volume gradually decreases, even leading to anuria. Anemia and acute hypoxia. Red blood cells and hemoglobin decreased sharply. Cold body:
Cold body, low blood pressure. Pale skin, sweating profusely. Headache. Pulmonary form:
Shortness of breath or rapid breathing, cyanosis, pink foam. The bottom of the lung has many moist rales, snoring rales.

Một trong những dấu hiệu nhận biết bệnh sốt rét ác tính là tiêu chảy hoặc động kinh
Hepatobiliary system:
Jaundice yellow eyes, nausea and vomiting. Yellow stools, yellow urine with a lot of bile salts. Comatose. Digestive:
Abdominal pain, vomiting. Acute diarrhea. Hypothermia. Malaria in pregnant women:
Pregnant women with malaria are more susceptible to severe malaria or miscarriage, stillbirth or premature delivery. Congenital malaria: A pregnant mother infected with malaria and damaged placental cells may give birth to a baby with malaria. The disease appears soon after birth, the child is fussy, feverish, jaundiced, hepatosplenomegaly. Malaria in children:
Children with malaria often have high fever, chills that are continuous or fluctuating. Vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal distension, hepatosplenomegaly. There are meningeal signs and convulsions. High mortality rate.
3. What to do when you have malaria?
So what to do when suffering from malaria to avoid dangerous complications for the patient? Accordingly, the patient should:
Absolutely not self-treat at home, to avoid spreading the disease to healthy people. Besides, if the disease condition is prolonged, not improved, dangerous complications will appear and can cause death for the patient. Treatment should be initiated as soon as possible after the onset of symptoms: children within 12 hours, adults within 24 hours. If in an epidemic area, malaria patients do not need to be isolated, but if in an epidemic area, they should be isolated early to avoid infecting the community. People with malaria absolutely must take medicine according to the treatment regimen of doctors and medical staff. The early, correct and adequate treatment will help the patient recover early and not waste time. Therefore, when there are signs of malaria, patients can visit hospitals under Vinmec Health System nationwide for timely advice and treatment.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a high-quality medical facility in Vietnam with a team of highly qualified medical professionals, well-trained, domestic and foreign, and experienced.
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.