This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Thanh Nam - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. The doctor has over 10 years of experience in the fields of Diagnostic Imaging.Brain CT is the gold standard in the diagnosis of traumatic brain injury. This is an easy technique to perform, which can help accurately diagnose intracranial bleeding (epidural hematoma, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage, cerebral hemorrhage), brain parenchymal contusion and cubital fracture. skull as well as maxillofacial.
1. What is a traumatic brain injury?
A traumatic brain injury occurs when a blow or trauma is severe to the head. If an object penetrates brain tissue, it can also cause traumatic brain injury. A mild traumatic brain injury can temporarily affect cells in the brain, and more seriously it can lead to contusion, bleeding, and other physical damage to the brain. Traumatic brain injury can cause disability, leave severe sequelae, even death, affect social relationships, seriously affect economic, physical and mental health. of patients and their families.For patients with traumatic brain injury, most injuries can be completely treated, but a few will have to live with long-term sequelae.
When having a traumatic brain injury, depending on the severity of the head injury, the patient may show some symptoms such as vomiting, drowsiness, headache, paralysis, confusion, coma. In some severe cases, the patient has additional symptoms such as:
Loss of consciousness, dilated pupils and vision changes such as blurred or double vision, unable to move eyes, more severe can lead to blindness blind; Cerebrospinal fluid drains from the ear or nose during a traumatic brain injury. In addition, the patient may hear echoes in the ears or hearing changes suddenly; Dizziness and balance disorder, consciousness becomes more difficult People with traumatic brain injury often have breathing problems, slow heart rate, slow breathing with symptoms of high blood pressure; In addition, the patient often responds inappropriately, with drooping eyelids or weakened facial muscles; Due to muscle weakness, it leads to difficulty swallowing, difficulty speaking, stuttering, not being able to understand what the patient is saying or not speaking fluently; Paralysis Patient has a feeling of numbness or ants crawling on the body; Loss of bowel movements as well as loss of bladder control.
2. CT scan is the gold standard in diagnosing traumatic brain injury
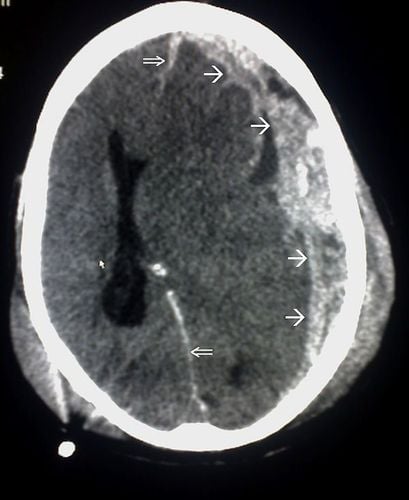
As with other injuries, patients with traumatic brain injury require rapid evaluation in the emergency room. The first function that needs to be evaluated is cardiopulmonary disease, then a comprehensive neurological examination and a rapid general examination.In traumatic brain injury, cranial CT is the gold standard for imaging evaluation of patients. This is an easy technique to perform, which can help accurately diagnose intracranial bleeding (epidural hematoma, subdural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage, cerebral hemorrhage), brain parenchymal contusion and cubital fracture. skull as well as maxillofacial.
Cranial MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is not usually recommended for use in acute traumatic brain injury because it takes longer than a CT scan of the brain. However, when the clinical picture is not suitable for CT imaging, cranial MRI can be used to detect subtle lesions such as diffuse axonal injury (DAI), a very severe form of brain injury. discreetly on CT.
3. Treatment of traumatic brain injury
Treatment for a traumatic brain injury will be based on the severity of the damage. In case the patient has a mild traumatic brain injury, just rest and use pain relievers to treat the headache, no further treatment is required.However, in the case of mild traumatic brain injury the patient also needs to be closely monitored at home. Close monitoring at home can help detect new unusual symptoms as well as persistent or worsening symptoms for the patient. The usual treatment of traumatic brain injury is as follows:
Urgent care Urgent care is usually indicated for some subjects with moderate to severe traumatic brain injury. Urgent care will primarily focus on making sure the person has enough oxygen and blood supply, maintaining blood pressure, and preventing any damage to the head or neck. Use medications to limit secondary damage: Diuretics: These diuretics reduce fluid retention in tissues and increase urine output. Besides, people with traumatic brain injury intravenous diuretic drugs will help patients reduce pressure inside the brain; Antiepileptic drugs: Usually, after a moderate - severe traumatic brain injury, the patient is often at risk of having a seizure in the first week. Therefore, the use of antiepileptic drugs during this time can avoid additional brain damage caused by seizures; Anesthesia: Doctors may use anesthetic to put the person in a temporary coma because the comatose brain requires less oxygen to function. Using anesthetics to temporarily put the patient into a coma will help in cases where the patient has symptoms of increased intracranial pressure, because the blood vessels are compressed, resulting in nutrients and oxygen not being supplied to the patient. brain cells as normal. Urgent surgery to minimize damage in case: Surgery to remove the hematoma; Cure for fractured skull bones; Bleeding in the brain; Reducing intracranial pressure by opening "windows" in the skull. Rehabilitation: Most people with traumatic brain injury will need the support of rehabilitation methods after trauma. Rehabilitation involves rehearsing basic skills such as walking or talking. The goal of rehabilitation methods for people with traumatic brain injury is to improve the patient's ability, thereby helping them to perform activities in daily life. The type of function and the length of time it takes to recover is often different for each person, depending on the severity of the brain injury and the location where the brain is damaged. Therapy will usually begin in a hospital and continue in inpatient rehabilitation units, inpatient facilities, or through outpatient services. Traumatic brain injury is a dangerous condition that requires immediate emergency care, therefore, it is necessary to take the patient to a reputable hospital for examination and treatment as soon as there are signs of traumatic brain injury. Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the leading prestigious hospitals in the country, trusted by a large number of patients for medical examination and treatment. Not only the physical system, modern equipment Vinmec is also the place to gather a team of leading medical experts. In particular, with a space designed according to 5-star hotel standards, Vinmec ensures to bring the patient the most comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.