This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Vo Thi Thuy Trang, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General HospitalIn Vietnam, gastritis is considered a fairly common disease. According to statistics of the Vietnam Association of Gastroenterology, 70% of cases of gastritis are caused by HP infection.
1. What is a stomach ulcer?
Peptic ulcer disease, commonly known as gastric ulcer, occurs when the lining of the stomach or duodenum is damaged, leading to an ulcer, usually an ulcer about 0.5 cm in size or more. . The mucosa is damaged when the lining of the stomach and duodenum is perforated, causing the underlying tissue to be exposed, combined with the penetration of toxins such as excess acid, drugs or bacteria to form ulcers. Usually, ulcers are more common in the stomach than in the duodenum.Gastritis is a fairly common disease in Vietnam. Symptoms are often insidious, not easy to detect, even in many people, there are almost no symptoms. Some typical symptoms of the disease are epigastric pain, bloating, indigestion, nausea, belching, heartburn, abdominal pain that is seasonal or seasonal in nature.
2. Helicobacter pylori (HP) bacteria – The main cause of stomach ulcers
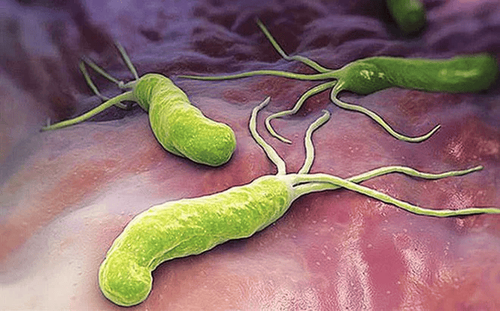
According to statistics of the Vietnam Association of Gastroenterology, on average 70% of cases diagnosed with stomach ulcers are caused by HP infection. If not detected and treated promptly, HP infection for a long time can lead to more dangerous complications such as stomach bleeding, gastric mucosal perforation, even the risk of stomach cancer. thick .
Helicobacter pylori causes disease through 2 main ways:
HP bacteria have the ability to secrete an enzyme that removes the protective mucus layer of the stomach lining, which is a prerequisite for stomach acid to penetrate into the mucosal layer. cause damage. Helicobacter pylori produces a toxin capable of degrading and necrosis of gastric cells, from which gastric acid penetrates strongly, causing ulcers and gastric erosion. Therefore, HP infection can be considered as the main cause of gastric ulcer. In addition, the abuse of antibiotics; use alcohol, tobacco regularly; unhealthy diet and living; Mental stress ... are also some of the causes that can lead to stomach ulcers.

3. HP bacteria transmitted by which way?
According to statistics, currently about 50% of the world's population is infected with HP bacteria, and this bacteria is completely capable of being transmitted from person to person.3.1 Oral-oral transmission This is considered the main mode of transmission of HP bacteria. Because HP bacteria exist in gastric juice, saliva, and dental plaque, they are transmitted from one person to another when sharing dishes, utensils, toothbrushes, kissing, and when a mother feeds her child. .
According to many medical experts, if someone in the family is infected with HP bacteria, the rate of the remaining people infected is very high.
3.2 Infection through fecal – oral HP bacteria will be eliminated by the body into the environment through the faeces. Therefore, after going to the toilet or before eating, the patient should pay attention to wash their hands with soap to avoid HP infection.
3.3 Infection through the stomach - mouth HP bacteria usually reside and develop in the stomach, so when people infected with HP appear gastroesophageal reflux or heartburn, it will be a common transport route for HP. with gastric juice to the mouth.
3.4 Infection through the gastro-intestinal tract In this case, healthy people are at risk of HP infection through medical instruments and equipment when performing gastroscopy. When performing gastroscopy, if the transducer is not cleaned and disinfected properly, HP bacteria can stick and enter the body of the person performing the next endoscopy.
4. Screening for HP . bacteria
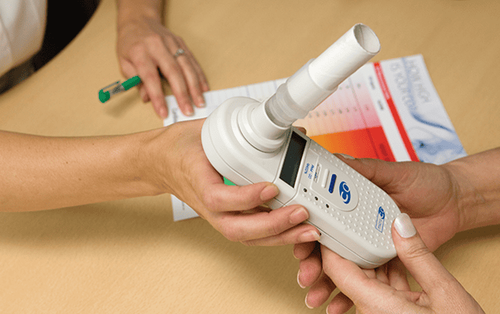
Currently, many methods to help screen for HP bacteria are being applied, in which the CO test method is used quite commonly, but if this method is applied to each individual, the results cannot be obtained. forward. In addition, in clinical medicine, HP testing is often combined with gastroscopy or histopathology, these are the two most common methods.Besides, a method that is also currently being preferred is the breath test, because it can specifically quantify the content of HP bacteria on each individual, through which the doctor can consider and make recommendations. suitable treatment methods. This is also the method with the highest specificity currently available.
5. Subjects and treatment methods for HP infection
The treatment to kill HP depends on many factors, it is necessary to consider the type and clinical manifestations of each patient. It is recommended to eliminate HP bacteria for cases of lesions detected through gastroscopy, people with a family history of stomach cancer, cases over 40 years old with high risk of dangerous diseases. .The method of killing HP bacteria currently applied is using drugs to reduce fatty acid secretion in the stomach in combination with antibiotics to destroy HP. This HP eradication regimen gives positive results up to 90%, but because HP bacteria are easily spread through eating, the re-infection rate is quite high in community activities.
Therefore, after completely eradicating HP bacteria, patients still need to pay attention to take measures to prevent HP infection, not to share personal items with others, to minimize the risk of re-infection.
Early detection of HP bacteria makes the treatment process more effective. At Vinmec International General Hospital, using 13C carbon isotope in the breath test to diagnose H. pylori bacteria with the most advanced machine with 02 airbags, it has a very high diagnostic value (> 95%) ) while ensuring patient safety.
If you have unusual symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: Mayoclinic.org