This is an automatically translated article.
Influenza is a respiratory infection caused by influenza virus. The spread of flu is strong in winter when temperatures are low, starting in October, peaking around December to February of the following year. So why is the flu so contagious during the winter?
1. Overview of the flu
Influenza is a respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses when they cause inflammation in the nose, throat and lungs. The disease can range from mild to severe and can sometimes lead to death. The best way to prevent the flu is to get a flu shot every year.
The flu is different from a cold, it comes on suddenly with mild to severe symptoms. Flu patients often face the following symptoms:
Fever or chills Cough Sore throat Runny nose Body aches Body aches Headache Fatigue Some patients have vomiting and diarrhea, despite the symptoms. This is more common in children than in adults. It is important to remember that all flu patients have a fever.
Một số triệu chứng cảm cúm
2. The spread of flu
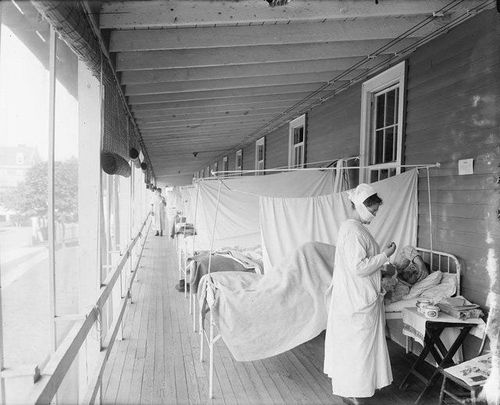
Influenza patients can spread to others from a distance of about 2 meters. Many experts believe that the spread of the flu occurs primarily when the flu virus spreads to the surrounding environment from small droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, and talks. Drops of these secretions can fall on the mucous membranes of the mouth or nose of people standing close. In a less common way, a person can get the flu by touching a surface or object containing the flu virus and then touching their nose, mouth, or eyes.
Patients with influenza are most contagious about the first 3 to 4 days after the onset of illness. Most healthy adults can infect others for only about 1 day before symptoms appear, and up to 7 days after symptoms disappear. Children and people with weakened immune systems can prolong the infection longer than 7 days.
On average, about 2 days after the virus enters the body, the patient will begin to show clinical symptoms. This means that flu patients have the ability to spread the disease to others before being sick. Some people are infected with the flu virus but have no symptoms. During that time, these people can still spread the virus to others around.

Virus cúm lây lan ra môi trường thông qua các hạt chất bắn nhỏ
3. Why is flu contagious in winter?
Many studies suggest that influenza viruses spread through the air more easily at low humidity and temperature conditions. So flu viruses are most common during the fall and winter. The exact duration of the flu can vary, but flu virus activity starts to increase in October and peaks from December to February. Some tips to help limit the spread of the flu are
Stay room temperature above 20 degrees Celsius Keep the humidity of the room at least 50%. Dr. Anice Lowe and colleagues at New York's Mount Sinai medical school study swine influenza viruses. The scientists changed the temperature and humidity in the pig houses and found that the flu virus spread more at low temperatures of about 5 degrees Celsius and low humidity between 20% and 35%.
Many new studies suggest ways to reduce the risk of flu infection by changing the humidity inside the home. Setting the humidity to 43% or more quickly inactivates about 86% of airborne virus droplets.
Learn more about how the flu virus spreads in the following article: How does the flu virus spread and spread?

Nên duy trì nhiệt độ phòng trên 20 độ C
4. Prevention of flu
Influenza is a disease that can be effectively prevented by various active and passive measures, including:
Get vaccinated against flu:
US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends getting an annual flu shot as the first and foremost thing to protect against flu and other serious complications. While there are many different viruses that cause flu, the flu vaccine can only protect against 3 or 4 of the most common viruses. The 3-component vaccine contains the H3N2, H1N1 and B viruses. The 4-component vaccine contains another additional B virus. Vaccinations – flu vaccines help reduce the incidence of influenza, flu-related hospitalizations. Influenza vaccine significantly reduces the risk of death from influenza in children Everyone 6 months of age and older should get a flu vaccine each year before the onset of disease activity in the community. CDC recommends the time of vaccination - at the end of October every year. People who are at high risk for various complications from the flu include young children, pregnant women, people with chronic medical conditions such as asthma, diabetes or cardiopulmonary disease, and people over 65 years of age. Subjects need to comply with the vaccination - flu vaccine.

Đăng kí tiêm chủng vắc-xin phòng virus cúm tại Vinmec
Maintain daily routines to prevent the spread of flu:
Avoid close contact with sick people. When you are sick, consciously limit contact with others as much as possible to avoid spreading. If you are sick with flu-like symptoms, the CDC recommends that the sick person stay home for at least 24 hours after the fever has gone without the use of fever-reducing medications, except to go outside to visit other facilities. Health service Dept. Cover your nose and mouth with a tissue when coughing or sneezing. After use, throw away the tissue and wash your hands. Wash your hands with soap and water or an alcohol-based quick hand sanitizer. Avoid touching your eyes, nose and mouth with your hands as this is a common entry point for the virus. Sanitize surfaces and utensils that may harbor the flu virus. Follow antiviral medication if prescribed by your doctor:
If you have the flu, antivirals can be used to treat them Antiviral drugs are not antibiotics, they are prescription drugs. single. Antiviral drugs ease illness, shorten the duration of illness, and prevent flu complications. The CDC recommends that antivirals be treated for people who are very sick and who are at high risk for serious complications from the disease. Studies show that antivirals for influenza are most effective if they are started within the first 48 hours of illness, but taking them later can still be beneficial, especially for people who are sick. high-risk patients. Reference source: cdc.gov; webmd.com