This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Dang Thi Ngoc Chuong - Department of Pediatrics - Neonatology, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Vomiting is a common condition in young children, especially when they are still breastfed. The reason is that during this period, the child's digestive system is still immature and weak, the valves in the stomach do not work synchronously. Vomiting in children is usually benign, resolves on its own when the child is older, but sometimes Vomiting is a symptom of digestive problems.
1. Benign / physiological vomiting
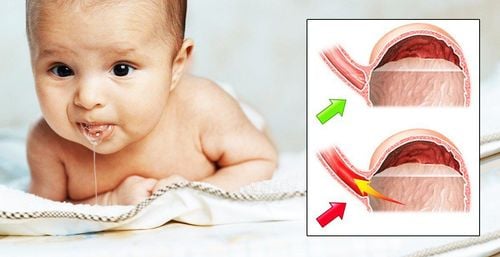
Babies and young children are prone to spitting up some milk during and after feeding. Regurgitation is a phenomenon in which milk comes out of the mouth easily, sometimes accompanied by belching. Vomiting is stronger than spitting up, the amount of milk that comes out is also more.Children often vomit at birth months is considered normal, also known as physiological or benign vomiting. The reason is because the baby's stomach is still horizontal, the gastric sphincter is weak, causing the child to vomit after eating. Vomiting in young children will decrease as the child gets older and completely disappear by the time the child is 1 year old.
To overcome the vomiting and reduce the amount of milk spit out, the mother can hold the baby upright after each feed to burp the baby, do not feed the baby too much each time, and at the same time do not let the baby be too hungry to be hungry. suck. After that, you should rest assured to put the baby on his or her back when sleeping, because this position does not increase the rate of asphyxia in the baby or vomit, but also helps reduce the risk of sudden infant death.

2. Vomiting related to diet
There are many reasons why babies often vomit after eating, the most common of which is the way the mother feeds the baby. Specifically:Forcing the child to eat too much or suck too much; Bottle sucking, sucking pacifier; Improper mixing of milk; Lie down immediately after eating/feeding; Cow's milk/food intolerance; Start eating novel food supplements; Eating too much of a certain food.

Trắc nghiệm: các chỉ số cần chú ý về sự phát triển thể chất của trẻ
Chiều cao, cân nặng của bé ở từng giai đoạn nên là bao nhiêu là bình thường, bao nhiêu là bất thường? Cùng ThS.BS Ma Văn Thấm điểm lại xem bạn đã nắm được các chỉ số phát triển thể chất của bé chưa nhé!The following content is prepared under supervision of Thạc sĩ, Bác sĩ y khoa, Ma Văn Thấm , Nhi , Phòng khám Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec Dương Đông(Phú Quốc)
3. Vomiting due to medical reasons
3.1. Gastro-esophageal reflux disease Vomiting in infants and children due to the most common pathological cause is gastro-oesophageal reflux. This occurs when the esophageal sphincter does not close properly. The ring of valve between the esophagus and the stomach of babies is not strong enough to stop food from the stomach back up into the esophagus, sometimes into the mouth.Because gastric juice is acid, while the esophagus is alkaline, reflux will adversely affect the child's health, which can lead to:
Esophagitis; Burning of the esophagus; Make the child very afraid to feed or eat; Aspiration pneumonia caused by much reflux of fluid into the mouth, causing children to aspiration into the lungs; Children with cyanosis due to spitting milk; Apnea is caused by gastric juice irritating nerves along the esophagus, inhibiting breathing. Therefore, gastro-oesophageal reflux is very dangerous for young children, especially newborn babies. The disease will go away with good treatment, or the symptoms will gradually decrease and then disappear when the baby is introduced to solid foods.

This congenital pathology usually begins a few weeks after the baby is born until 4 months of age, with the following manifestations:
The child often vomits incessantly in the first month after birth; Every time you eat or drink, you will vomit; Vomiting, vomiting forcefully out of the child's mouth. If a child shows signs of pyloric stenosis, parents should contact their doctor as soon as possible because the condition needs to be managed surgically.
3.3. Other diseases In the first months after birth, vomiting in young children can also be a manifestation of:
Gastrointestinal diseases: Intestinal infections, viral infections in the stomach, food poisoning eating, or other problems in the stomach - intestines; Surgical pathology: Intussusception, intestinal obstruction, etc.; Systemic diseases: Respiratory tract infections, pneumonia, meningitis, reactions to food or food intolerances... If the child gets older and the vomiting persists, then parents need to bring their children. I visit a specialist to find out the cause and have appropriate and timely treatment.
Note, do not arbitrarily buy any anti-vomiting medicine without taking the child to the doctor and prescribed by the doctor. Especially for babies under 6 months old, it will be very dangerous.

4. Warning signs of pathological regurgitation
Some warning signs of pathology accompanying vomiting in young children include:Fever, loose stools, cough, runny nose, rash,...; Cramping abdominal pain, abdominal distension; Drowsiness, irritability, convulsions; Continuous regurgitation for more than 24 hours; Occurrence of blood during regurgitation in an increasing amount (if there is a red streak in the vomit, it may also be due to a wound in the mouth or a nosebleed); There is bile (blue) when vomiting ... When experiencing the above symptoms with prolonged vomiting, parents need to take the baby to the hospital immediately. You can keep some vomit with blood or green bile for your doctor to check.
In summary, vomiting in young children in the early stages of life is a common phenomenon and does not affect the health and development of the children. Parents should not be too stressed when they see their children vomiting, instead need to adjust their feeding habits and diet more appropriately. However, when an adult child vomits suddenly or for a long time, accompanied by medical symptoms, it is necessary to take the child to the doctor for timely treatment.
According to the recommendations of the World Health Organization (WHO), babies will be introduced to solid foods when they are 6 months old and need to be fed properly to give them a healthy digestive system.
>> See more: Notes when feeding 6-month-old babies - the article was professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Phan Thi Cam Van - Neonatologist - Pediatrics - Neonatology - National General Hospital Vinmec Danang International.
In Vietnam today, 7 out of 10 children under 5 years old have zinc deficiency and 8 pregnant women have zinc deficiency. The prevalence of zinc deficiency in pregnant women is 80.3%, women of childbearing age 63.6% and children under 5 years old is 69.4%. The most common manifestations of zinc deficiency in children are growth retardation, mild and moderate malnutrition, delayed growth in height, and some observable symptoms such as anorexia or decreased appetite, decreased suckling, and no meat. fish, slow digestion, mild constipation, persistent nausea and vomiting in children. In addition to reasonable zinc supplementation, parents also need to provide their children with other important vitamins and minerals such as lysine, chromium, B vitamins,... resistance to less minor illnesses and less digestive problems.
Please regularly visit the website vimec.com and update useful information to take care of your baby and family.