This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Master - Doctor Huynh An Thien - Department of Medical Examination and Internal Medicine, Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.Peripheral polyneuritis is a common disease in people who are often active or have to work hard. If not detected early and treated properly, the disease can leave many lasting sequelae, affecting the patient's health and life.
1. What is peripheral polyneuritis?
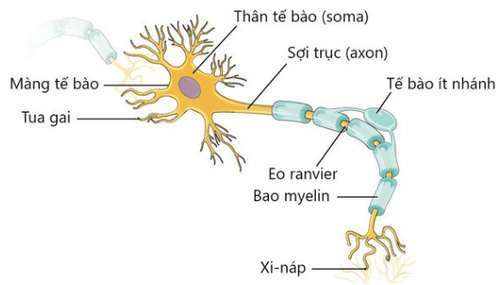
The nervous system in the body is divided into two types: the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system (the rest of the nerves). Peripheral nerves are nerves that are not located in the human brain and spinal cord. The function of the peripheral nerves is to connect the central nervous system with the limbs and organs of the body.Because they are not located in the brain and spinal cord, the peripheral nerves are not protected by the spine and skull. Therefore, they are easily affected by factors inside and outside the body, causing inflammation. Diseases affecting the nerves include:
Nerves that sense heat, pain or touch; Motor nerves control the movement of muscles; Autonomic nerves control automatic functions such as heart rate, digestion, blood pressure, and bladder function. Common causes of peripheral polyneuritis include:
Nerve injury: Car accidents, falls, sports injuries, ... leading to rupture, damage, inflammation of the nerves peripheral nerves; Infections of the muscles: When there is damage and infection in the muscles, viruses or bacteria will have the opportunity to attack, causing inflammation of the peripheral nerves. Lyme disease, shingles, Epstein-Barr, hepatitis C and HIV/AIDS are common causes;

2. Peripheral polyneuropathy symptoms
When the peripheral nerves are damaged, the process of exchanging information between the brain and muscles or other organs will malfunction. Some signs to help identify the disease include:Numbness in the limbs, feeling like a needle or electric shock; Itching in the damaged nerve area, then the itch quickly spreads to the arms and calves; Frequent pain in the wrist, shoulder and leg joints, often with a burning sensation in the areas where the peripheral nerves pass;
Acute inflammation: Normal to severe pain that can last for days or weeks. The disease can be relieved if using specific drugs such as pain relievers, anti-epileptic drugs or antidepressants,...; Chronic inflammation: In patients with acute peripheral polyneuritis, if not detected or untreated (or not treated completely) will progress to chronic with serious complications such as impotence, hypotension. pressure, ... In addition, the patient also has to endure a lot of pain and face the risk of muscle atrophy, weakness, gradually leading to paralysis of the limbs. 4. Measures to prevent and control peripheral polyneuropathy Take care of your feet, check your feet daily, look for signs of acne, calluses, cuts,... (especially for patients) diabetes). People who are sick or at risk of disease should also not wear tight shoes and socks because they can cause pain, itching, sores that do not heal; Quit smoking: The toxic substances in cigarette smoke can affect the blood circulation of the extremities, increase the risk of disease, may cause the patient to amputate the leg due to complications; Exercise regularly: Patients should consult a doctor about the appropriate exercise intensity and exercise to reduce neuropathic pain and control peripheral polyneuropathy;

Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.