This is an automatically translated article.
Screening test is the initial basis to determine the risk of disease of healthy people, especially women. Therefore, proper screening in women will help prevent disease and can be timely intervention and effective treatment if detected.
1. The role of screening tests for women
Screening tests are a way of identifying healthy people who may be at increased risk for a particular disease. It's the early screening that can help prevent diseases like cancer, diabetes and osteoporosis in the first place, and when it's caught early, it's easier to treat. In addition, screening tests can detect disease even before symptoms of the disease appear.
Screening tests or routine health checkups are recommended for everyone throughout life as an important part of health care and prevention.
2. Screening tests in women
2.1. Breast Cancer
The earlier breast cancer is detected, the better the chance of a cure. Small breast cancers are less likely to spread to the lymph nodes and vital organs such as the lungs and brain. If you're in your 20s or 30s, some experts recommend getting a breast screening done as part of your routine checkups. In case, there may be any additional risk factors then you need to be tested more often.
Breast cancer screening tests with mammograms A mammogram is with low-dose X-rays that can often find a lump before you feel it. Although the results are normal, they do not completely eliminate the risk of cancer. Some experts recommend that women in their 40s get a mammogram every year. Then, during your 50s to 70s, you can move on to getting tested at least once a year. Of course, in cases where there is a higher risk, your doctor will order more frequent checkups.
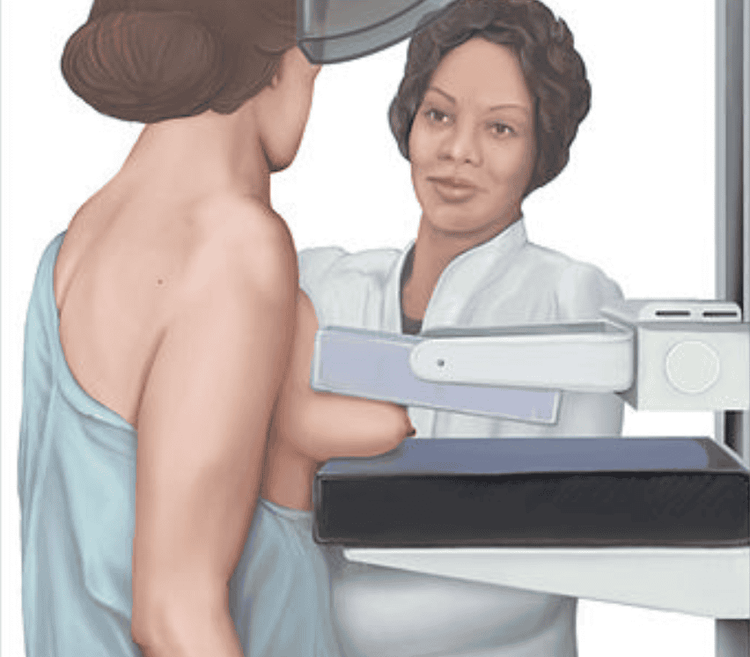
Chụp X quang tuyến vú giúp chẩn đoán ung thư
2.2. Cervical cancer
The cervix is a narrow passageway between the uterus (where a fetus develops) and the vagina (birth canal). Cervical cancer is an easily preventable disease. Your doctor may use a Pap test (smear smear) or an HPV test to screen for cervical cancer. The Pap test can find abnormal cells on the cervix and remove them before they turn cancerous.
The main cause of cervical cancer is the Human Papillomavirus (HPV).
During a Pap test, your doctor removes some cells from your cervix and sends them to a lab for analysis. Your doctor will talk to you about when to be tested for combined with HPV and how often to be tested. If sexual activity poses a risk to you, you should get a vaginal test for gonorrhea.
2.3. Osteoporosis and Fractures
Osteoporosis is a state when a person has weak and fragile bones. After menopause, women begin to lose more bone mass. However, men are also not immune from this situation. The first symptom is usually a pain from falls, bumps, and sudden changes in position. Prevention of osteoporosis requires early treatment. Osteoporosis screening test: Using special X-rays called dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) can measure bone strength and find disease. osteoporosis before the bones are pitted. It can also help predict future risk of bone weakness. This screening in women is recommended for all women 65 years of age and older. If you have risk factors for osteoporosis, you need to start earlier on osteoporosis screening tests

Phụ nữ trên 65 tuổi nên kiểm tra sàng lọc loãng xương
2.4. Skin cancer screening
There are some types of skin cancer that need to be treated early for better results. The most dangerous are melanoma, which affects the cells that give skin color. Sometimes, everyone is at risk for this type of skin cancer, and the risk is increased with overexposure to the sun.
Skin cancer screening: Watch for any signs of skin changes including moles and freckles. Changes in shape, color and size should be noticed. Some experts recommend that you also have your skin checked by a dermatologist to find out the specific cause.
2.5. High blood pressure
As you get older, your risk of high blood pressure increases, especially if you are obese or have some bad health habits. High blood pressure can cause life-threatening heart attacks or strokes without any warning. So, go see your doctor for advice and control of the disease. Lowering blood pressure can prevent long-term dangers like heart disease and kidney failure.

Huyết áp cao gây nguy hiểm đến tính mạng người bệnh
2.6. Cholesterol
High cholesterol can cause plaque to clog arteries. This plaque can build up for years without symptoms and eventually cause heart attacks or strokes. High blood pressure, diabetes, and smoking can also cause these plaques. This condition is called hardening of the arteries or atherosclerosis. Lifestyle changes and not using tobacco can reduce your risk of disease
Check cholesterol: To get your cholesterol checked, you may need to fast for 9-12 hours. You will then have a blood test that measures your total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, and triglycerides (blood fats). Your doctor will advise when to start and how often to check.
2.7. Type 2 diabetes
Diabetes can cause heart or kidney disease, stroke, blindness from damage to retinal blood vessels, and other serious problems. You can control your diabetes with diet, exercise, weight loss, and medication, especially when it's caught early. Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of the disease. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children or young adults.
Diabetes screening: You need to fast for 8 hours or longer before having a blood test for diabetes. A blood sugar level of 100-125 can be seen in prediabetes, while a blood sugar level of 126 or higher means diabetes. Other tests to diagnose diabetes are the A1c test and the oral glucose tolerance test. Your doctor will advise you on when to start and how often to check your blood sugar readings. If you feel at risk or have a family history of diabetes, talk to your doctor for more detailed advice.

Khám sức khỏe định kỳ, giúp chị em phụ nữ phát hiện sớm bệnh lý
2.8. Colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer is the most common cause of death after lung cancer. Most colorectal cancers are from polyps (abnormal masses) that grow on the inner lining of the large intestine. Polyps may or may not be cancerous. If so, the cancer may have spread to other parts of the body. Removing polyps early, before they become cancerous, is possible and prevents disease.
Colorectal Cancer Screening: Colonoscopy is a common screening test for colorectal cancer. The doctor will use a flexible tube with a camera attached to the end of the tube so that polyps can be found and removed. This screening process is usually recommended for people starting at age 50.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or Register online HERE
References: webmd.com, raffleshealth.com, health.harvard.edu
SEE MORE
Screening packages for some dangerous cancers Learn about the screening package for 4 gynecological cancers even without symptoms at Vinmec Early cancer screening at Vinmec - Peace of mind to live healthy