This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Do Tuong Huan - Oncologist - Oncology Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Metastatic cancer is cancer that has spread to another part of the body from the original site. Cancer cells often metastasize to nearby sites, spread through blood vessels, lymph nodes, depending on the type of cancer. Distant metastasis sites are mainly liver, bone, brain and lymph nodes.
1. Overview of metastatic cancer
The main reason cancer gets worse is because cancer cells move to other organs in the body. Cancer cells can spread locally by moving into nearby normal tissue. Cancer can also spread to regional lymph nodes, to nearby lymph nodes. And it can also spread to other parts of the body away from the tumor. These phenomena are called distant metastases. For many types of cancer, it is also known as stage IV cancer. The process by which cancer cells spread to other parts of the body is called metastasis.Metastatic cancer cells observed under the microscope and tested in other ways show features that are similar to the cancer at the original site and unlike the cells where the cancer was found. This is an accurate method of diagnosing cancer that has spread from another part of the body.
Metastatic cancer has the same name as the cancer at the original site . For example, breast cancer that has spread to the lungs is called metastatic breast cancer, not lung cancer. It is treated like stage IV breast cancer, not lung cancer.
In some cases, patients are diagnosed with metastatic cancer but the origin is unknown. This type of cancer is called cancer of unknown origin (CUP).
New metastatic cancer that occurs in a person with a history of cancer is called a second primary cancer. Second primary cancer is very rare. When a person with cancer has cancer again, it does not mean that the original primary cancer has returned.
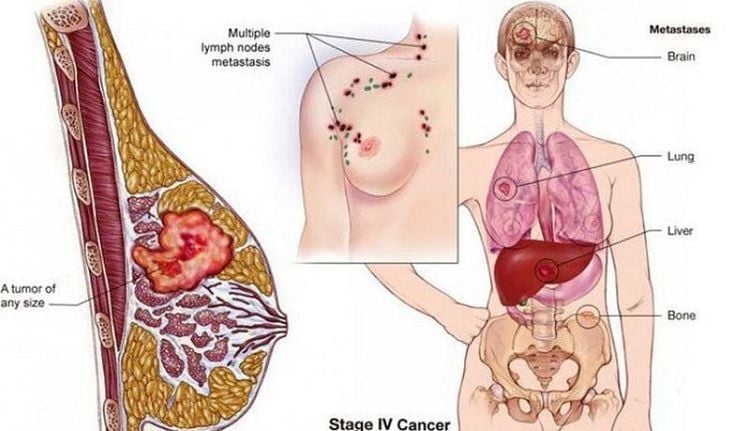
2. How does cancer metastasize?
Cancer cells metastasize through the body in a series of steps. These steps include:Grow into, or invade, nearby normal tissue Move into nearby lymph nodes or blood vessels Pass through the lymphatic system and blood to other parts of the body Stop at small blood vessels at a distant site, invade blood vessel walls and migrate into surrounding tissues Grow in cancerous tissue until a small tumor forms Make new blood vessels grow, creating a blood supply that allows the tumor to continue to grow Most, metastatic cancer cells will die at some point in the process. However, when conditions are right, cancer cells are at every step, some of them can form new tumors in other parts of the body. Metastatic cancer cells can also remain dormant in a distant location for years before they begin to grow again.
Trắc nghiệm: Thử hiểu biết của bạn về bệnh ung thư
Ung thư là nguyên nhân gây tử vong hàng thứ 2 trên thế giới. Thử sức cùng bài trắc nghiệm sau đây sẽ giúp bạn có thêm kiến thức về yếu tố nguy cơ cũng như cách phòng ngừa bệnh ung thư.
Bài dịch từ: webmd.com
3. How often does cancer metastasize?
Cancer metastasizes to almost any part of the body, although different types of cancer are more likely to spread to certain areas than others. The most common sites where cancer cells spread are the bones, liver, lungs, and brain. The following list shows the most common metastatic sites for some common cancers, excluding the lymph nodes:| Loại ung thư | Vị trí di căn thường gặp |
| Ung thư bàng quang | Xương, gan và phổi |
| Ung thư vú | Xương, não, gan và phổi |
| Ung thư đại tràng | Gan, phổi và phúc mạc |
| Ung thư thận | Tuyến thượng thận, xương, não, gan, phổi |
| Ung thư phổi | Tuyến thượng thận, xương, não, gan, phổi còn lại |
| Ung thư da | Xương, não, gan, phổi, da, cơ |
| Ung thư buồng trứng | Gan, phổi, phúc mạc |
| Ung thư tụy | Gan, phổi, phúc mạc |
| Ung thư tuyến tiền liệt | Tuyến thượng thận, xương, gan, phổi |
| Ung thư trực tràng | Gan, phổi, phúc mạc |
| Ung thư dạ dày | Gan, phổi, phúc mạc |
| Ung thư tuyến giáp | Xương, gan, phổi |
| Ung thư tử cung | Xương, gan, phổi, phúc mạc, âm đạo |
4. How does metastatic cancer develop?
Cancer often develops into metastatic cancer when cancer cells break away from the main tumor and enter the blood or lymph system. These systems are responsible for transporting substances throughout the body. This means that cancer cells can move away from the original tumor and form new tumors when they settle and grow in another part of the body.Metastatic cancer can also spread to nearby organs from the main tumor. Typically tumors in the abdominal or thoracic cavity, these tumors can rupture and spread to nearby organs in the abdominal or thoracic cavity.
All types of cancer can be spread. Whether or not cancer metastasis occurs depends on several factors, including:
Type of cancer: Some cancers are more likely to spread than others. Tumor growth rate Other factors about the growth pattern of cancer cells that doctors find during treatment.
5. Characteristics of metastatic cancer cells
Cancer cells that have spread to other areas have all the properties of the original cancer cells. That is why the name of the cancer in the new metastasis is still named after the original cancer. For example, breast cancer that has spread to the liver is called metastatic breast cancer, not liver cancer. Treatment for metastatic breast cancer is the same as for breast cancer.6. Is metastatic cancer curable?
In some cases, metastatic cancer can be cured, but often, treatments do not cure the cancer but only slow down its growth and symptoms. Many people can still live long after the cancer has spread. The effectiveness of the treatments depends on many factors:
The type of cancer How far and where the cancer has spread Number of sites of metastasis The cancer is growing quickly or slowly The treatments The patient's response to treatment The treatment methods vary depending on the patient's response to treatment. Palliative care is used in conjunction with a treatment plan to minimize symptoms of pain, nausea, and other side effects.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Specialist Doctor II Do Tuong Huan has 20 years of experience in the examination, diagnosis and surgical treatment and chemotherapy of cancer pathologies. Dr. Huan used to work for a long time at Ho Chi Minh City Oncology Hospital from 1999 to 2017 and now works at Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital from March 2017.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
The article references the source: Cancer.net, cancer.govMORE:
What is metastatic cancer? What does metastatic cancer mean? Diagnosis and treatment of metastatic cancer