This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Specialist Doctor II Nguyen Quoc Viet - Interventional Cardiologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Currently, the rate of patients suffering from cardiovascular diseases such as coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction... is increasing. One of the main causes of a heart attack is the formation of blood clots in the lumen of the coronary arteries (the arteries that feed the heart). For this reason, patients with coronary artery disease often need the help of antiplatelet drugs.
1. Platelets, blood clots and cardiovascular disease
1.1. The role of platelets Platelets are a very small component of the blood circulatory system. Although small, platelets play an extremely important role, helping the body to prevent bleeding (ie, assisting in blood clotting).For example: If you accidentally have a wound that causes bleeding, platelets are immediately mobilized to concentrate at the site of injury, along with some other components that form a clot to temporarily stop bleeding.
The process of thrombus formation, however, they can also block blood vessels in the body and lead to dangerous conditions such as: coronary artery occlusion causing myocardial infarction, cerebral vascular occlusion causing stroke cerebral vessels, peripheral occlusion causing foot necrosis...
1.2. Causes of Thrombosis There is normally no blood clot in the circulation. Blood components such as red blood cells, platelets, and white blood cells usually do not stick to the walls of blood vessels, causing blood clots. Only when fatty deposits (due to atherosclerosis) damage the vascular endothelium, does a thrombus form.
Predisposing factors for blood clots and endothelial damage are hypertension, diabetes and smoking habits.
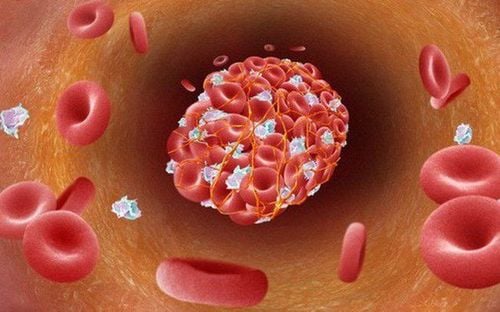
The formation of a thrombus progresses in a stepwise manner. At first, the platelets will stick together into a patch, this plaque will grow larger and larger enough to cause blockage of the blood vessels.
In general, platelets play a very important role in the formation of blood clots in the lumen, so antiplatelet drugs are especially necessary to combat this formation. Limiting and preventing the formation of blood clots is a very important part of the fight against cardiovascular diseases such as stroke and myocardial infarction.
2. Antiplatelet drug characteristics
Drugs that affect platelet function can be divided into 3 categories: drugs for prevention of cardiovascular disease, drugs for emergency treatment and drugs for long-term treatment. The route of administration of these drugs also has two types: oral and injectable.2.1. Aspirin Aspirin (Acetylsalicylic Acid) is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that plays an important role in the treatment of many cardiovascular diseases.
Characteristics of the drug
It is a very popular and inexpensive over-the-counter (OTC) drug. Antipyretic and headache treatment (500mg dose). For the treatment of cardiovascular disease, aspirin is suggested to use from 75mg - 325mg. Aspirin comes as an intramuscular injection but is usually given in hospitals or some emergency rooms. Reduce the risk of death from myocardial infarction and cerebrovascular accident if used as soon as symptoms are detected. Indication case
Prophylaxis for some patients at high risk of myocardial infarction, cerebrovascular accident, atherosclerosis. Used for patients undergoing procedures such as coronary artery bypass graft surgery, coronary intervention to reduce the rate of myocardial infarction and vascular accident. Unless there are contraindications, most prescriptions for patients with coronary artery disease must include aspirin (usually a dose of 100mg). Note: Caution should be exercised when combining aspirin with other antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants such as: Heparin, Coumarin derivatives.
2.2. Clopidogrel Clopidogrel with the brand name Plavix (75mg) is widely used to prevent platelet clotting and reduce the rate of some cardiovascular diseases.
Characteristics of the drug
The drug is quite expensive, about 25,000 VND/tablet or more. Blocks the activation of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa by fibrinogen on platelets, reducing the ability to bind fibrinogen to platelets. Capable of selectively inhibiting platelet ADP receptors. Reduces the risk of blood clots and cardiovascular events. Indications
Antiplatelet therapy with a single dose of 75mg/day. Used with aspirin for patients with unstable angina, various types of myocardial infarction, before and after coronary artery bypass surgery, coronary artery bypass surgery. Regular use of clopidogrel after myocardial infarction or cerebrovascular accident will provide similar effects as aspirin. Used after coronary stenting, especially drug-eluting stents. In addition, there are a number of other antiplatelet drugs used clinically to treat blood clots such as: Dipyridamol, Ticlopidine, glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors
3. Attention when treating with antiplatelet drugs
Because all antiplatelet agents act on common blood clots, the most common side effect is bleeding. From minor bleeding such as a nosebleed to more serious bleeding such as a brain bleed. But the majority of bleeding cases are moderate, not life-threatening and do not require a blood transfusion.The most common site of bleeding is gastric bleeding (especially if the patient has pre-existing gastric disease), less commonly bleeding in the urinary tract (hematuria). When there is bleeding, the patient should go to the hospital for careful monitoring and treatment. Some other very rare risks of antiplatelet drugs, such as allergy to aspirin or thrombocytopenia bleeding, are seen in people taking glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors.
It is necessary to use exactly as prescribed by the doctor to be effective in treatment as well as to avoid the side effects caused by the drug.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.