This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Nguyen Hong Phuc - Emergency Department - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital.
Acute renal failure is a dangerous disease, with many causes of acute renal failure, these causes are divided into: Group of causes of prerenal acute renal failure, group of causes of renal failure and group of causes of acute renal failure. post-renal failure.
1. What is acute kidney failure?
Acute kidney failure is a dangerous disease with a high risk of death. The disease can occur from many causes, which cause a rapid cessation or decline in glomerular filtration rate, thereby causing temporary, acute loss of function in both kidneys. The clinical manifestations of acute renal failure are:Acute oliguria or anuria occurs Serum creatinine rate > 42.5 μmol within 24-48 hours of baseline serum creatinine if the patient's baseline creatinine < 221 μmol/l. If the patient's baseline creatinine is > 221 μmol/l, acute renal failure is diagnosed when the rate of increase in serum creatinine is > 20% over 24-48 hours. After anuria, the glomerular filtration rate decreases to <60 ml/min. Blood potassium is often elevated, possibly with metabolic acidosis. The course of acute renal failure occurs in 4 stages, respectively: Attack stage of the pathogen, stage oliguria, anuria, urinary return and rehabilitation phase.
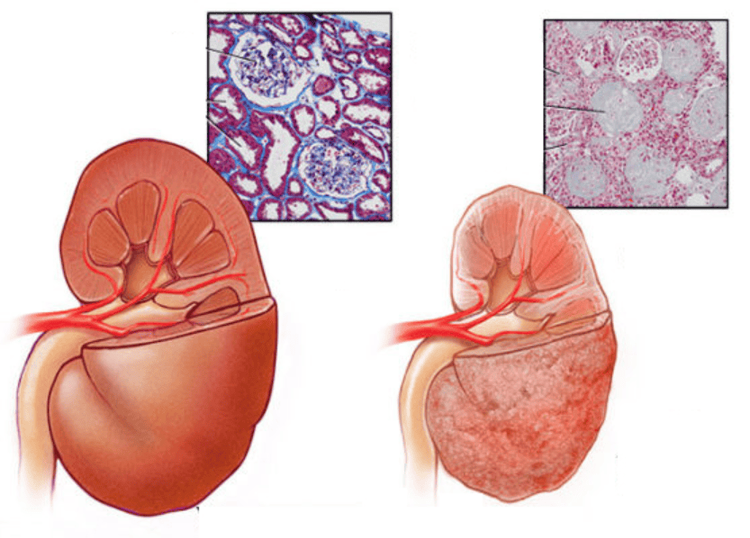
2. Causes of acute kidney failure
Based on the pathogenesis, the causes of acute kidney failure can be divided into 3 main groups:2.1 Causes of prerenal acute renal failure Causes of prerenal acute renal failure include all causes decreased blood flow to the kidney such as dehydration, blood loss causing hypovolemic shock, cardiogenic shock, septic shock, anaphylaxis,... Other causes of circulatory volume reduction such as decompensated cirrhosis, malnutrition, decreased oncotic pressure in nephrotic syndrome.
2.2 Group of causes of renal failure in the kidney Renal failure in the kidney due to physical damage to the kidney, including:
Glomerulonephritis: Glomerular vasculitis in diseases: malignant hypertension, vasculitis , Wegener's vasculitis, hemolytic uremic syndrome, disseminated intravascular coagulation, pregnancy toxicity, systemic vascular disease, scleroderma,... Anti-glomerular basement membrane antibody disease such as syndrome Goodpasture Glomerular damage due to drugs with toxic side effects on the kidneys such as Amphotericin B, Cyclosporin, Cisplatin,... Tubular disease: The most common cause of acute renal failure. There are many causes of tubular diseases such as: Necrosis of the kidney due to anemia. The cause of anemia is usually severe, prolonged pre-renal failure. Acute kidney failure secondary to severe infections that are not treated in time, ischemic damage to the kidneys due to decreased blood flow to the kidneys, the kidneys lose the ability to regulate themselves. Renal tubules are blocked by cellular breakdown products such as myoglobulinuria, hemoglobulin, myeloma, urate crystals, oxalates Drug-induced nephrotoxicity: Many drugs have side effects that damage the renal tubules such as aminoside antibiotics, some cephalosporin antibiotics, amphotericin B antifungal drugs, iodinated contrast agents, cisplatin chemicals,... Interstitial kidney disease: Interstitial nephritis can be caused by Stresptococcus, Pneumococcus, bacteria. .. viruses such as EBV, CMV,... fungi, Mycoplasma. Some drugs can cause interstitial nephritis, such as: antibiotics (quinolones, cephalosporins, vancomycin, rifampicin, penicillin,...), furosemide diuretics, thiazides, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory pain relievers (diclofenac, meloxicam). , ibuprofen,...), ACE inhibitors for high blood pressure, gout medicine Allopurinol,...

2.3 Group of causes of postrenal renal failure Postrenal renal failure occurs when the urinary tract of the kidney is blocked. Urinary tract stones, necrotic kidney papillae, blood clots, tumors, posterior wall peritoneal fibrosis, ... cause high urinary tract obstruction. While neurogenic bladder syndrome, bladder neck obstruction, urethral obstruction cause lower urinary tract obstruction.
3. Treatment of acute kidney failure
Principles of treatment The general principle in the treatment of acute renal failure is to identify the cause of renal failure in any group (pre-renal, renal or renal failure) and then seek to eliminate the cause as quickly as possible. Along with that is correcting circulatory disorders, restoring blood volume, maintaining stable systolic blood pressure at 100-120mmHg. Correction of homeostasis disturbances, restoration of urine flow, and emergency management of potentially life-threatening symptoms such as hyperkalemia, convulsive cerebral edema, acute pulmonary edema, and severe metabolic acidosis. When necessary, dialysis can be indicated.Specific treatment according to the stage of the disease 3.1 Stage of the disease agents attack This stage takes place in the first 24 hours, the patient has symptoms of fatigue, shortness of breath, chest pain, nausea, decreased urine or no urine. In addition, the patient also has symptoms of other causes of kidney failure such as infection, poisoning, dehydration.
This stage, if properly and promptly treated, can prevent the disease from progressing to the next stage. Treatment at this stage focuses on trying to eliminate the cause of the disease, rehydrating when there is dehydration, gastric lavage if poisoning occurs, removing urinary obstructions, etc. Closely monitor the condition. oliguria, anuria of the patient.
3.2 Stages of oliguria, anuria Full-blown disease with severe symptoms and complications. Patients with oliguria, anuria, edema. In some patients, oliguria appeared very quickly, with symptoms of excess fluid such as congestive heart failure, pulmonary edema. Urea, blood creatinine increased rapidly, electrolyte disturbances, blood potassium increased. Metabolic acidosis, pH, HCO3 decrease, anions have gaps. Patient breathes deeply, vasodilates, lowers blood pressure.
4. Prevention of acute kidney failure
In order to prevent acute kidney failure and dangerous complications of the disease, people need periodic health check-ups to detect risk factors early, thereby preventing and treating them early.Use drugs according to the instructions of medical staff to avoid toxic effects on the kidneys of some drugs. Good treatment of some diseases that are at risk of affecting the kidneys such as high blood pressure, diabetes, chronic heart failure, prostate cancer,...
In patients with many risk factors such as: Large urinary tract If you have pre-existing kidney disease, heart failure, etc., before surgery, doctors need to perform prophylaxis for patients with acute kidney failure. During surgery, it is necessary to compensate with enough fluid to ensure blood pressure.
BSCK I Nguyen Hong Phuc has nearly 20 years of experience in Emergency Resuscitation. Before being an Emergency Medicine Doctor at Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital, Dr. Phuc worked at hospitals: Bac Ninh Lung Hospital, Cu Chi Regional General Hospital - Ho Chi Minh City Bright.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.