This is an automatically translated article.
Autoimmune disease is an abnormal increase in the immune response from organs in the body that were previously completely normal. Therefore, the treatment of autoimmune diseases will be much more difficult than other diseases.
1. What is an autoimmune disease?
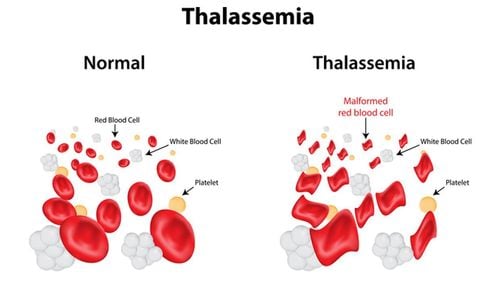
Autoimmune disease is the result of a mistaken state of the immune system, leading to the destruction of organs in the body. Normally, the immune system is able to tell the difference between foreign cells and cells in the body. Accordingly, autoimmune disease occurs when the immune system treats a part of the body – like joints or skin. They release proteins called autoantibodies that attack healthy cells. Therefore, autoimmune disease is considered a dangerous disease with no complete treatment, even serious complications if not examined and treated properly.
Currently, the cause of autoimmune diseases is still not clear, some common autoimmune diseases such as: familial systemic lupus erythematosus, type 1 diabetes that damages the pancreas, diseases related to Grave's thyroid, irritable bowel syndrome (Irritable Bowel Syndrome), multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, there are some autoimmune diseases that target only one organ in the body.
Bệnh vảy nến có thể là một trong nhiều nguyên nhân gây bệnh tự miễn
Therefore, regular physical examination is very important to detect the symptoms of autoimmune disease early. It is possible that the symptoms of an autoimmune disease appear for a while and then go away, but they may recur in episodes.
2. Can autoimmune diseases be cured?
Most autoimmune diseases currently do not have a cure for autoimmune diseases. Medication can help you control overactive immune responses and reduce inflammation and, in some cases, even slow the progression of an autoimmune disease. Currently, there are two main classes of drugs used to treat autoimmune diseases: anti-inflammatory drugs and immunosuppressants.
2.1. Anti-inflammatory drugs Anti-inflammatory drugs treat the symptoms of autoimmune diseases such as diclofenac, indomethacin, aspirin, ibuprofen and glucocorticoids. Diclofenac, a derivative of phenylacetic acid, is a drug with strong anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects. Because diclofenac belongs to a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, it has undesirable effects such as damaging the gastrointestinal tract, reducing the role of maintaining renal perfusion. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, so they can cause interstitial nephritis, glomerulonephritis, papillary necrosis and nephrotic syndrome, especially in people with kidney disease or chronic heart failure. However, in people with autoimmune diseases, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can increase acute renal failure and acute heart failure. Indomethacin is a derivative of indolacetic acid. Pharmacological properties of this drug have analgesic, antipyretic, anti-inflammatory and inhibiting platelet aggregation. However, drugs often cause many undesirable effects, especially prolonged bleeding time (risk of bleeding from gastrointestinal tract ulcers) and risk of kidney dysfunction (causing fluid retention). .

Thuốc Aspirin điều trị bệnh tự miễn
Aspirin is a pain reliever, antipyretic, indicated in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis. The drug has side effects that affect the gastrointestinal tract (stomach bleeding), nervous system (fatigue) and hemostasis (prolonged bleeding). Ibuprofen is a propionic acid derivative. Ibuprofen is a pain reliever, antipyretic, and anti-inflammatory drug. It is indicated for mild to moderate pain and inflammation in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Using ibuprofen can reduce the dose of opiate drugs to treat pain after major surgery or for cases of pain caused by cancer, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Some common undesirable effects of the drug are fatigue, abdominal bloating, nausea, dizziness, restlessness, headache, rash. Glucocorticoids are drugs with good effects in anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic and immunosuppressive. This is also a drug indicated in the treatment of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus... The side effects caused by the drug are also not less dangerous such as: irritation. nervous system causes insomnia , excitability; increased appetite, indigestion; hirsutism; muscle weakness, osteoporosis; can cause diabetes; increase joint pain; cataracts, glaucoma, edema, hypertension; stomach ulcers ...
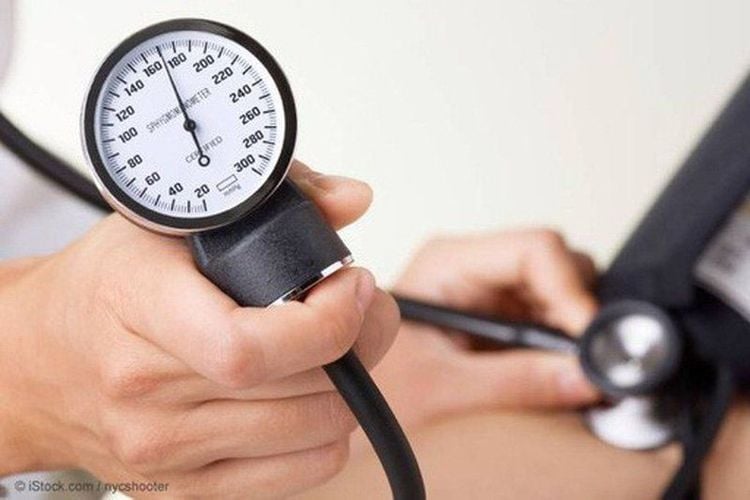

Tăng huyết áp do sử dụng Glucocorticoid
2.2. Immunosuppressive drugs Immunosuppressive drugs are effective in treating autoimmune diseases such as cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine A, mycophenolate mofetil, etanercept... These are drugs that are effective in some autoimmune diseases such as lupus. systemic erythema, polyarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, autoimmune hepatitis. However, these drugs are all toxic and relatively expensive, so they are only used in cases that do not respond to anti-inflammatory drugs. In cases of autoimmune disease with damage leading to dysfunction of internal organs, supportive treatment to reduce symptoms of the disease is essential.
2.3. Treatment with bone marrow transplant or stem cell transplant This is an autoimmune disease treatment with the aim of regenerating the autoimmune system that has been successfully applied in the treatment of some diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus. system, scleroderma, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, polyarthritis.
Người bệnh viêm khớp có thể điều trị bằng phương pháp ghép tủy xương
3. How to prevent autoimmune disease
To effectively prevent autoimmune diseases and protect the immune system, you need to maintain a reasonable diet, get enough rest, in moderation, limit smoking and follow the following recommendations :
Control your weight : You should not be overweight or obese because being fat can also increase your risk of some autoimmune diseases , like rheumatoid arthritis or psoriatic arthritis . You need to maintain regular health check-ups 1-2 times a year in order to detect early and promptly treat dangerous diseases, including autoimmune diseases. At the same time, you also need to increase physical activity, choose a suitable sport to practice regularly every day. When it is discovered that you have an autoimmune disease, you should go to the doctor immediately for advice on appropriate autoimmune disease treatment methods, do not arbitrarily use drugs of unknown origin, which can make the disease worse. more important.

Khám sức khỏe định kỳ giúp mọi người sớm phát hiện bệnh tự miễn
Currently, although there have been many new drugs and techniques to treat autoimmune diseases, these methods only work to treat the symptoms of the disease. Therefore, you need to raise the awareness of protecting the body's immune system with simple daily methods.
To register for examination and treatment of autoimmune diseases at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System, or register online HERE.
MORE:
What is an autoimmune disease? Tests to diagnose autoimmune diseases Joint problems are common in autoimmune disease