This is an automatically translated article.
The Pap test helps to screen for precancerous and cancerous lesions on the cervix. Screening for early detection of cervical cancer by Pap smear is extremely important, providing a higher chance of treatment for patients.1. What is a Pap test?
The Pap test was invented and named after the eminent Greek physician, Georgios Nikolaou Papanikolaou (1883-1962). The Pap test is also known as the Pap smear or Pap smear. This is the most common type of test used to detect and look for early changes in cells that can lead to cervical cancer.During a Pap test, the doctor collects a small sample of cells from the surface of the cervix, then puts it on a slide (Pap smear) or mixes the sample in a fixative for examination under the microscope. micrograph. Examining the cells will help the doctor find abnormalities and abnormal changes in the cells. How often to have a Pap test depends on your age, previous test results, and other factors. You should talk to your doctor about how soon you will have the test again.
Some cells collected from the cervix during the Pap test may also be tested for human papillomavirus, also known as HPV. HPV infection is a risk factor for cervical cancer. HPV is usually passed from one person to another through sexual contact. HPV includes many different types, in which HPV types 16 and 18 have a risk of causing cervical cancer. Your doctor will order an HPV test at the same time as the Pap test or after the results of the Pap test show abnormal changes to the cervix. HPV testing is only for women age 30 and older.
MORE: Do HPV 16 and 18 easily cause cervical cancer?
2. When to have a Pap test
If you have the following risk factors, you should have regular Pap tests:There is an increased risk of cervical cancer or the Pap smear shows precancerous cells;
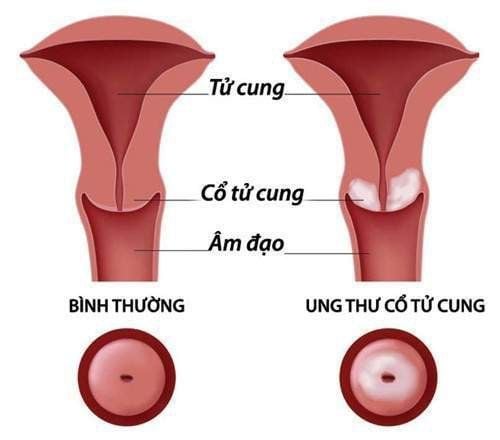
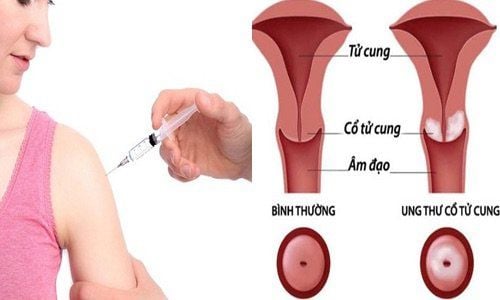
Ung thư cổ tử cung
Exposure to diethylstilbestrol (DES- a synthetic estrogen, used in people with hormone-sensitive tumors, such as breast cancer) before birth; A weakened immune system due to chemotherapy, an organ transplant, or prolonged use of corticosteroids (a powerful anti-inflammatory drug); Being infected with HIV.
3. How to prepare for a Pap test?
To ensure that your Pap test results are as accurate as possible, follow these guidelines:
Do not have sex for 2-3 days before the test; To avoid washing away abnormal cells, do not use things like birth control foams, tampons, vaginal suppositories, and do not douche for 2 to 3 days before the test; The best time to schedule your Pap test is at least 5 days after your period ends. Although it is still possible to perform the test during the "red light" days, doctors recommend avoiding periods to achieve the most accurate results; You should urinate before the Pap test because a full bladder can make you uncomfortable during the test.
4. Pap test procedure
The Pap test is usually very quick and simple, usually taking only a few minutes. You will be supported by doctors and nurses and guided to perform the test. The test can be uncomfortable, but it's usually not painful. You may feel less discomfort if you empty your bladder before the exam. Also, take a deep breath and relax your muscles during the procedure.
Before performing a Pap test, your doctor may ask you some basic questions related to the test, including:
Are you pregnant? Do you use birth control? What medications have you taken recently? Do you smoke? When was your last period and how long did it last? Do you have any symptoms, such as itching, redness or sores? Have you undergone surgery or other procedures on your reproductive organs? Have you ever had an abnormal result from a previous Pap test? The patient will lie in the gynecological examination position: supine, knees bent, legs spread and body relaxed. During the test, your doctor will gently insert a lubricated plastic or metal instrument into your vagina. This instrument, called a speculum, helps the doctor see the cervix clearly. After visually examining your cervix, your doctor will use a cotton swab or cervical brush to gently scrape cells from 2 samples of the outer and inner cervix.
These cells will be placed on a slide and taken to the laboratory for analysis. Results will be available within 1 week.
5. After Pap Test

Hiện tượng chảy máu âm đạo có thể xảy ra sau khi làm xét nghiệm Pap
You can resume your normal activities right after your Pap test. Vaginal bleeding after the test may occur. In case you have excessive bleeding, notify your doctor for advice and solutions.
If the Pap test shows abnormal cells and the HPV test is positive, your doctor may recommend one or more additional tests. The Pap test is a great screening tool, but it's not perfect. Sometimes the results are normal even in the presence of abnormal cervical cells. This is called a "false negative" test result.
Regular screening is very important. You should ask your doctor how often to have a Pap test. Research shows that almost all cervical changes can be found with regular screening and treatment before they become cancerous.
Screening for early detection of cervical cancer by Pap smear is extremely important, providing a higher chance of treatment for patients, detecting abnormalities in the structure and activity of cells. cervical cells. From there, shows the risk of cancer in the future. Screening for these abnormal cells is the first step in stopping the possible development of cervical cancer.
In order to further improve the quality of diagnosis and treatment, Vinmec International General Hospital has applied the ThinPrep Pap Test for early detection of cervical cancer, this new method is now commonly used in Vietnam. America, Europe. ThinPrep Pap Test has made a breakthrough compared to the traditional Pap smear method, through membrane controlled cell transfer technology, which increases the sensitivity and specificity in detecting precancerous cells. , especially adenocarcinoma cells, a type of cancer cell that is difficult to detect.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to the source: Cancer.net
How often should Pap smear screening for cervical cancer? What to do when cervical cancer screening results are abnormal