This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by MSc Nguyen Thi Le - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Danang International HospitalChorionic Villus Sampling (CVS) is a technical operation applied in obstetrics: taking a sample of cells that is the chorion that surrounds the embryo, also known as the chorion, to analyze and find out. chromosomal abnormalities.
1. What are chorionic villus biopsies and prenatal diagnostic tests?
A prenatal diagnostic test is a test that helps your doctor know for sure if your baby has genetic abnormalities and infections. Usually these tests are based on amniocentesis, chorionic villus sampling, or fetal umbilical cord blood collection.2. How is a chorionic villus biopsy done?
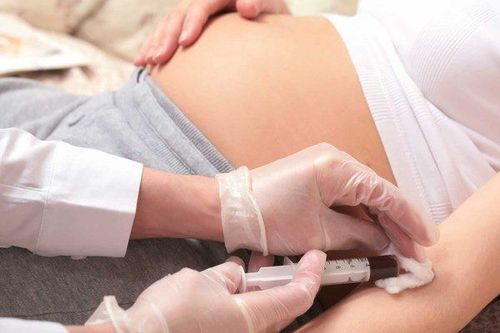
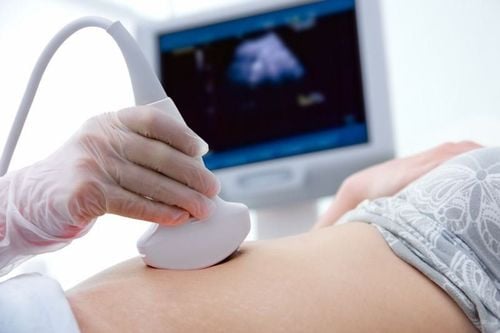
The chorionic villus sampling test is the removal of a small amount of placental tissue from the mother's uterus. The placental sample is obtained with a needle or catheter through the abdomen, in rare cases in the cervix. The procedure is performed under ultrasound guidance.In this procedure, the woman is anesthetized to relieve pain and relieve stress. After the procedure, you may experience light vaginal bleeding.
The risk of miscarriage with a chorionic villus procedure is about 1/500, which means 1 out of every 500 women who have this procedure will have a miscarriage. Therefore, before performing prenatal diagnostic tests, pregnant women will be consulted about the benefits as well as the disadvantages that the test brings.
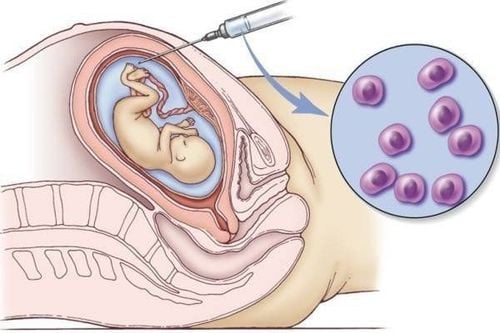
3. When to perform a chorionic villus biopsy?
A biopsy of the placenta is performed at 12-14 weeks of gestation, with a favorable placental position, before the amniotic sac fills the uterine cavity.Doctors usually do not recommend routine chorionic villus sampling at screening, but only when screening tests show that your baby is at high risk for genetic diseases (tests: NIPT, combined test: nuchal translucency and double test, triple test).
Some of the conditions that can be detected by a chorionic villus biopsy include:
Chromosomal disorders – such as Down syndrome (a disorder that causes mental retardation and some other physical features) or Edward (disorder that can lead to miscarriage, premature birth, or developmental loss). Genetic disorders – such as cystic fibrosis, which make the body's secretions thicker and stickier, interfering with the proper functioning of certain organs. Musculoskeletal system disorders – such as Duchenne myasthenia gravis, a genetic disorder that leads to progressive muscle weakness and deformities. A blood disorder – like thalassemia, a condition that affects the body's ability to make red blood cells, or anemia that affects how red blood cells carry oxygen around the body. Metabolism disorders – such as antitrypsin deficiency, the body cannot produce the protein alpha-1 antitrypsin, phenylketouria or the enzyme phenylalanine hydroxylase. Neuropathy – like fragile X syndrome, is a condition that affects appearance, intelligence and behavior. In addition to the above conditions, there are other less common conditions that are diagnosed by performing a chorionic villus biopsy.
4. Notes after performing a placental biopsy
After the chorionic villus sampling, pregnant women can go home immediately, rest for about 24 hours, should avoid heavy labor and avoid sex for about 3 to 4 days. In case a pregnant woman finds amniotic fluid leaking, vaginal redness or cramping increases every time, at this time, the pregnant woman should go to the hospital immediately because there is a possibility of threatened miscarriage. Monitor the mother's body temperature after the biopsy of the placenta, if there is a fever, it is likely that the pregnant woman has an infection, she needs to go to the hospital to check immediately. It usually takes 7-10 days after the procedure for the results of the chromosomal analysis and 2-4 weeks for the results of a genetic disorder.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.