This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Van Thanh - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Ha Long International HospitalGiving birth at the age of 35 or older is associated with a higher risk of fertility problems. Carrier testing is considered an optimal measure to help couples who want to have children reduce anxiety about this issue. Testing can help determine if your child has genetic diseases.
1. What is a carrier test?
Carrier testing is a type of genetic test used to determine if you carry a copy of the mutated gene that causes genetic disorders. This type of test is mostly used by couples or individuals with a family history of genetic diseases to determine the risk of a child developing genetic diseases.For some genetic disorders, a carrier is someone who has only one gene for the disorder. Transmitters are usually asymptomatic or have only mild symptoms. They don't know that they have a disorder gene.
2. Chances of your child having a genetic disorder
If a couple both carry a recessive gene for the disorder, there is a 25% chance that their child will receive the gene from one parent and carry the disease. In 50% of cases, the child will carry the disease but have no symptoms and the remaining 25% will give birth to a perfectly healthy baby.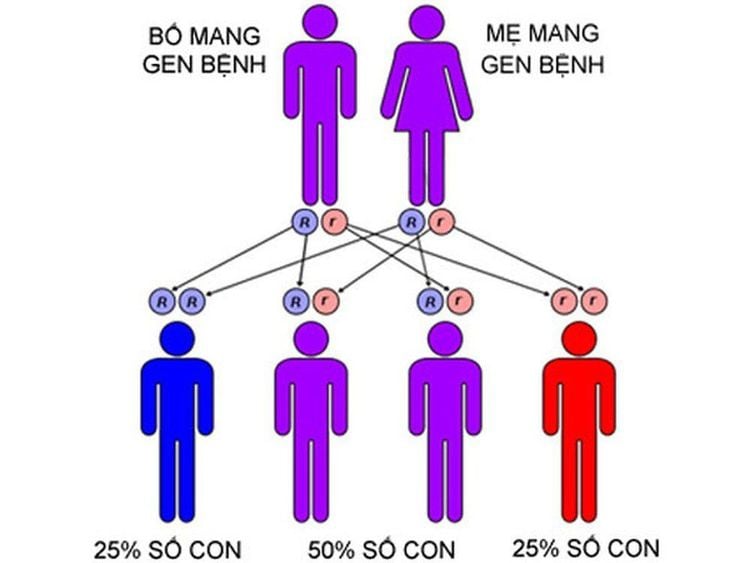
3. How is carrier testing done?
Carrier testing involves testing a sample of blood, saliva, or tissue from the inside of the cheek. Test results can be negative or positive. In a couple, a doctor will choose one person to do the first carrier test to determine if that person is a carrier of the disorder. If the test results show that the first person is not a carrier of the disorder, no additional testing is needed. Conversely, if they are carriers of the disorder, the doctor will test the other. When the test results show that the other person is a carrier with a specific disorder, testing will be stopped.4. When can carrier testing be done?
Pregnancy testing can be done before or during pregnancy. In particular, this is an important test before pregnancy because through the test, you can consult your doctor's options and have more time to consider and make the right decision.5. What carrier tests are there?
Carrier testing is commonly used for a number of conditions, including cystic fibrosis, Fragile X syndrome, sickle cell disease, and Tay-Sachs disease. These disorders occur more often in certain races or ethnic groups. For example, sickle cell disease most commonly occurs in African-Americans. Tay-Sachs disease is most common in people of Eastern or Central European Jewish ancestry and French Canadians. However, diseases caused by genetic disorders are not unique to a particular country or region, but any one of us is likely to suffer. Therefore, those who are planning to become pregnant need to do prenatal genetic testing to make sure your baby doesn't "copy" the disease from your parents.6. Who should be tested for carriers?
All women who are thinking about becoming pregnant or have become pregnant are advised to be tested for the genes that cause cystic fibrosis, hemoglobinopathy, and spinal muscular atrophy (SMA).
7. What is an extended carrier test?
In expanded carrier testing, multiple disorders are screened with a single sample. This type of screening is done without regard to race or ethnicity. Health care professionals will create lists of disorders they will check for. This list is essentially a screening panel for more than 100 different disorders. Screening panels often focus on serious disorders that affect a person's quality of life from an early age.8. What options are there if both parents are carriers of the genetic disorder?
You should have a pre-pregnancy screening test to diagnose whether your baby has a disorder or is a carrier of any disease. You can also get pregnant through in vitro fertilization (IVF) with donor eggs or sperm. With this option, the embryos will be examined before being transferred to the uterus. If you have genetic disorder screening after pregnancy, your options will be more limited. In either case, rest assured that the doctor will explain to you what the risks are when your baby has a genetic disorder9. Is the carrier test absolutely accurate?
There is no such thing as a perfect test. In rare cases, the test results may be wrong. A negative test result when you have the disorder gene is called a false negative result. A positive test result when you don't have the disorder gene is called a false positive.If you have unusual symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
References: Acog.org














