This is an automatically translated article.
Atrial fibrillation is an increased or irregular heartbeat, which can increase the risk of stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related complications. Common symptoms of atrial fibrillation include heart palpitations and shortness of breath.
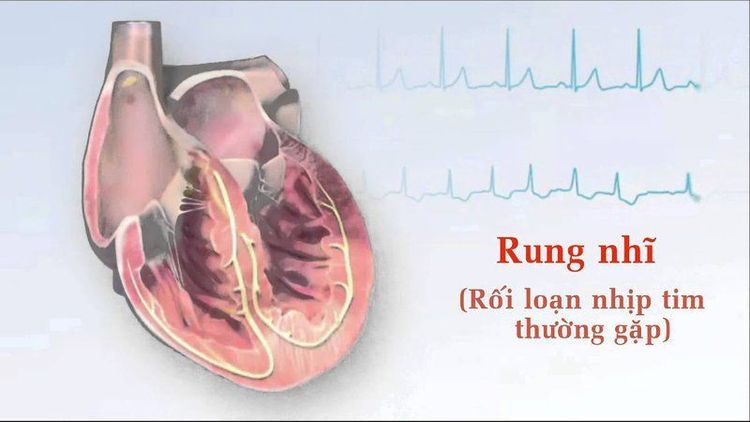
1. Signs of atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation episodes can come and go, or they can be long-lasting and require treatment. Although atrial fibrillation is not usually life-threatening, it is a serious health problem that sometimes requires urgent treatment.
The concern of atrial fibrillation is the possibility of developing blood clots in the upper chambers of the heart. Blood clots that form in the heart can circulate to other organs and lead to blockage of blood flow, causing ischemia. Treatment for atrial fibrillation may involve medications and other interventions to try to change the heart's electrical system.
Some cases of atrial fibrillation have no symptoms until it is discovered during a physical examination. People with symptoms of atrial fibrillation may experience signs and symptoms such as:
Tachycardia, irregular heartbeat Feeling sick Decreased mobility Fatigue Delirium Dizziness Shortness of breath Chest pain
Triệu chứng của bệnh rung nhĩ rất khó phát hiện
2. Classification and treatment of atrial fibrillation
2.1 Sudden atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation episodes can have symptoms and frequency that come and go fairly quickly, usually lasting only a few minutes to a few hours. Sometimes symptoms occur for a week. Symptoms may resolve on their own or may require treatment.
2.2 Persistent atrial fibrillation
The manifestation of this type of atrial fibrillation is that the heart rate after the fibrillation will not return to normal. For this condition, treatment such as electric shock or medication will be needed to restore heart rhythm.
2.3 Persistent atrial fibrillation
This type of atrial fibrillation is continuous and lasts more than 12 months.
2.4 Permanent atrial fibrillation
This type of atrial fibrillation manifests as an irreversible irregular heartbeat. Treatment requires medication to control heart rate and prevent blood clots.
3. Recommendations for people with symptoms of atrial fibrillation
If there are any symptoms of atrial fibrillation, seek help from doctors and medical staff. The patient will have an electrocardiogram to identify symptoms related to atrial fibrillation or other arrhythmia. If in case of chest pain, the patient needs urgent medical help as this is a sign of a heart attack.
4. Causes of atrial fibrillation
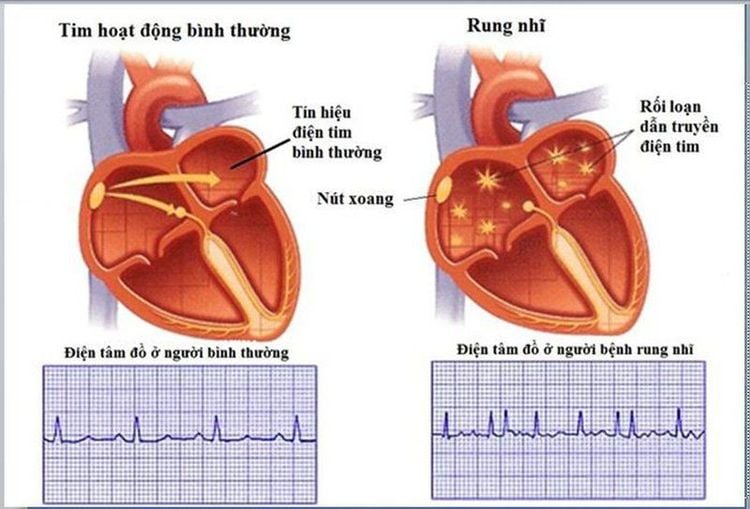
Atrial fibrillation is an arrhythmia that occurs when the two upper chambers of the heart encounter mixed electrical signals. The heart rate in atrial fibrillation can range from 100 to 175 beats per minute. Whereas, the normal range for heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute.The heart is made up of four chambers - two upper chambers (atria) and two lower chambers (ventricles). In the upper right chamber of the heart (right atrium) is a group of cells called the sinus node. This is a natural pacemaker. Normally, the signal travels through the two upper chambers of the heart and then through a junction between the upper and lower chambers called the atrioventricular node. The movement of the signal causes your heart to contract and send blood to your heart and body.
When atrial fibrillation occurs, the signals in the upper chambers of the heart are confused. The atrioventricular node that electrically connects the atria and ventricles is destroyed by impulses trying to pass through the ventricles. In addition, other causes can cause atrial fibrillation such as:
High blood pressure Heart attack Coronary artery disease Abnormal heart valves Congenital heart defects Overactive thyroid or other metabolic imbalances Abuse of drugs stimulants, such as drugs, caffeine, tobacco, or alcohol Lung disease Previous heart surgery Viral infection Stress, pneumonia Sleep apnea However, some people have atrial fibrillation but don't have any defects heart disease or damage, this is also known as isolated atrial fibrillation. In isolated atrial fibrillation, the cause is often unclear, and serious complications are rare.
Những người béo phì có nguy cơ mắc chứng rung tâm nhĩ cao hơn.
5. Risk factors for atrial fibrillation
Several factors can increase the risk of developing atrial fibrillation such as:
The older you are, the higher your risk of developing atrial fibrillation. Anyone with heart disease such as valve problems, congenital heart disease, congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease or a history of heart attack or heart surgery, etc. is at high risk for fibrillation. atrium. Patients with high blood pressure, especially if it is not well controlled, with lifestyle or medication changes can increase the risk of atrial fibrillation. People with certain chronic conditions such as thyroid problems, sleep apnea, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, or lung disease are at increased risk of atrial fibrillation. For some people, drinking can trigger an episode of atrial fibrillation. Drinking alcohol can increase your risk of atrial fibrillation. Obese people have a higher risk of developing atrial fibrillation.
6. What complications can atrial fibrillation lead to?
6.1 Stroke
During atrial fibrillation, the heartbeat becomes chaotic causing blood to rush into the upper chambers of the heart (atria) and form blood clots. When a blood clot forms, it can travel to the brain and block blood flow, causing a stroke. The risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation also depends on age and on whether the patient has high blood pressure, diabetes, a history of heart failure or previous stroke, and other factors. Certain medications, such as blood thinners, can greatly reduce the risk of stroke or other organ damage caused by blood clots.
6.2 Heart failure
Atrial fibrillation if left unchecked can weaken the heart and lead to heart failure - a condition in which the heart cannot circulate enough blood as the body needs.
7. Prevention of atrial fibrillation
To prevent atrial fibrillation, it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle to reduce the risk of heart disease. A healthy lifestyle includes:
Having a heart-healthy diet. Increase physical activity. Avoid smoking. Maintain a healthy weight. Limit or avoid stimulants such as caffeine and alcohol. Reduce stress, as intense stress and anger can cause heart rhythm problems. Use over-the-counter medications with caution, as some cold and cough medicines contain stimulants that can cause heart palpitations. Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consulting services. and comprehensive, professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
If you have unusual symptoms, you should be examined and consulted with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article referenced source: Mayoclinic.org